Opinion | Interactive: The Plan to Save New York From the Next Sandy Will Ruin the Waterfront. It Doesn’t Have To – the New York Times
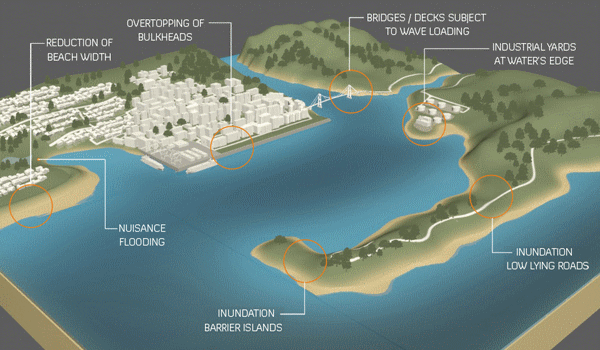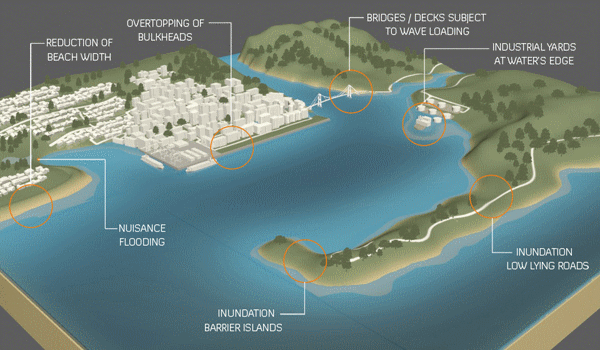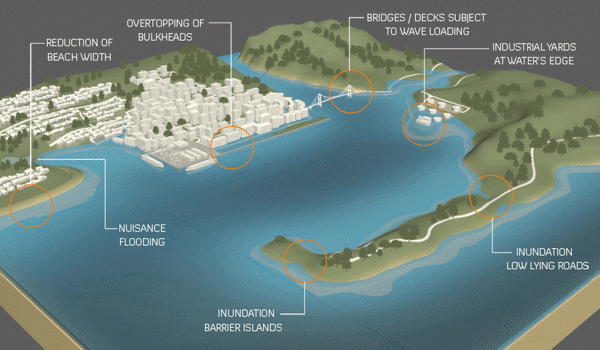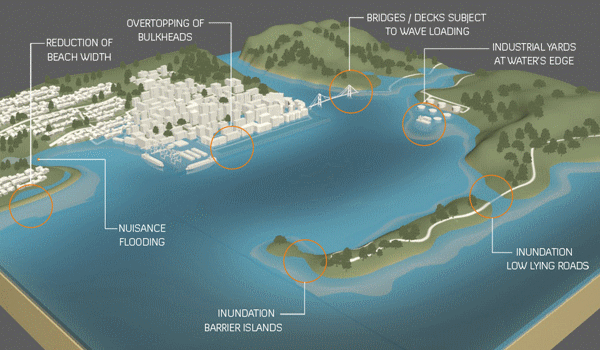
Last September, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers unveiled its proposal to protect the greater New York and New Jersey metro area from the next catastrophic flood. It is an epic plan that includes dozens of miles of floodwalls, levees and berms along the shoreline and 12 storm surge barriers — arrays of movable gates — across entrances to waterways throughout the region.
The plan is estimated to cost a staggering $52.6 billion. It’s by far the most expensive project ever proposed by the Corps.
The trouble is that despite its great ambitions, the Corps’s plan demonstrates the shortcomings of relying on massive shoreline structures for flood protection…
Study says buyout of threatened Outer Banks homes would be cheaper than beach nourishment – Star News Online
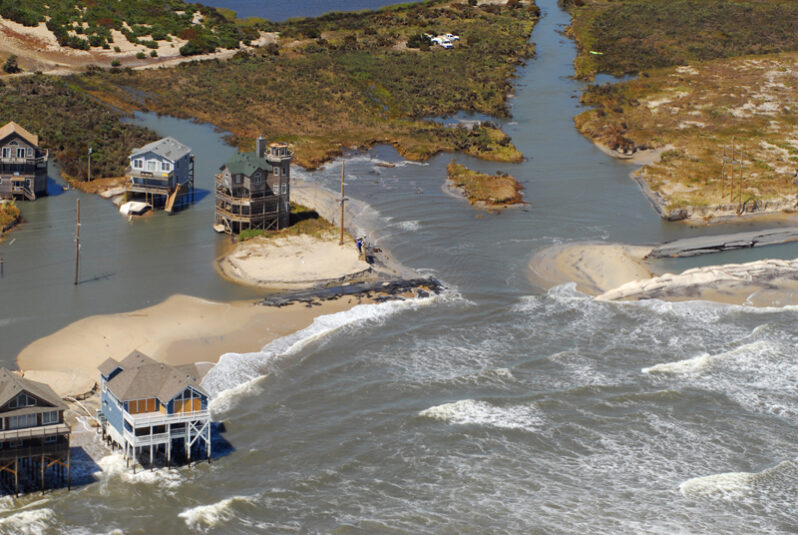

Along coastal North Carolina, engineering answers to threats from Mother Nature is a time-honored tradition to dealing with eroding beaches and threats from wandering inlets. But pumping sand isn’t cheap….Faced with a future of rising seas and stronger storms intensified by climate change, state and local officials are scrambling to keep up.(And) one option occupies a relatively rare seat at the table for discussion by local officials and residents: moving oceanfront structures out of harms way…
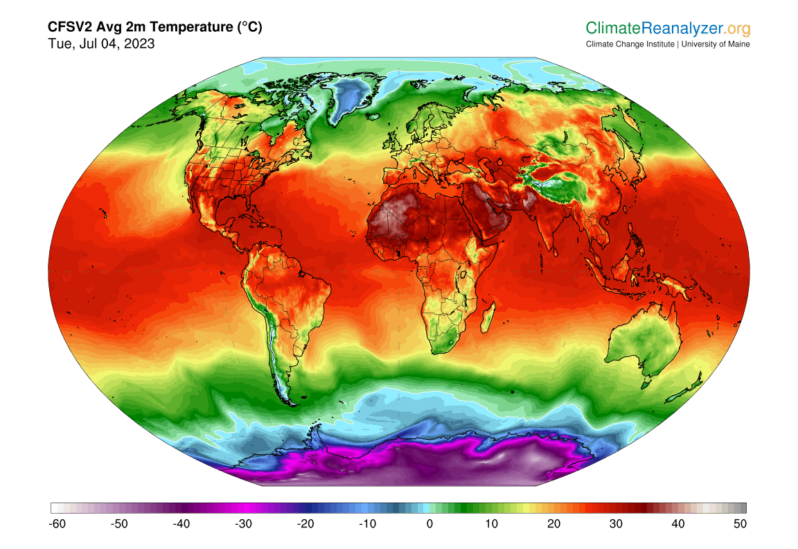
July 4, 2023: The Hottest Day in over 125,000 Years

“We have never seen anything like this before”
– Carlo Buontempo, director of Europe’s Copernicus Climate Change Service quoted in the Washington Post, 07-06-2023…
The world’s hottest day on record was Tuesday, scientists calculate – PBS News Hour

The entire planet sweltered to the unofficial hottest day in human recordkeeping July 3 and then blasted past that with an even hotter day on July 4, according to University of Maine scientists at the Climate Reanalyzer project…
The planet saw its hottest day on record this week – CNN

On Monday, the average global temperature reached 17.01 degrees Celsius (62.62 Fahrenheit), the highest in the US National Centers for Environmental Prediction’s data, which goes back to 1979. On Tuesday, it climbed even further, reaching 17.18 degrees Celsius and global temperature remained at this record-high on Wednesday…
What 120 Degrees Looks Like in One of Mexico’s Hottest Cities – the New York Times

People in Hermosillo are used to the heat: Enduring scorching temperatures is a local point of pride (for) the “city of sun.” But on a recent Sunday in June, temperatures reached a record high when thermometers registered 49.5 degrees Celsius, or 121 Fahrenheit…
Why a sudden surge of broken heat records is scaring scientists – the Washington Post
New precedents have been set in recent weeks and months, surprising some scientists with their swift evolution: historically warm oceans, with North Atlantic temperatures already nearing their typical annual peak; unparalleled low sea ice levels around Antarctica, where global warming impacts had, until now, been slower to appear; and the planet experiencing its warmest June ever charted, according to new data. And then, on Monday, came Earth’s hottest day in at least 125,000 years. Tuesday was hotter…
Venice Isn’t Alone: 7 Sinking Cities Around the World – How Stuff Works

Many big cities sit near the ocean. They became cities in the first place because their ports facilitated trade and travel by sea.
Coastal cities all over the world are sinking — a geological process called subsidence — and it’s happening at a rate that makes scientists nervous. If these bits of land didn’t have important cities on them, it’s likely nobody would notice, or, in some cases, that they wouldn’t be sinking at all…
Before the flood: how much longer will the Thames Barrier protect London? – the Guardian
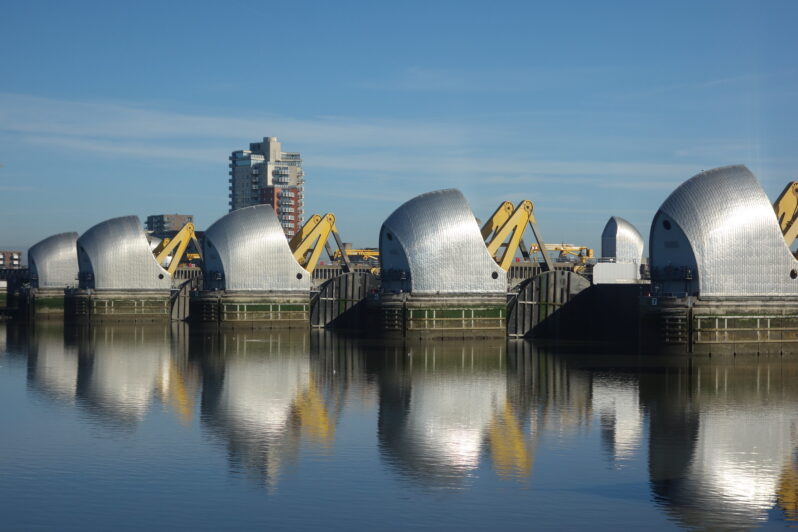

The last time the Thames broke its banks and flooded central London was on 7 January 1928, when a storm sent record water levels up the tidal river, from Greenwich and Woolwich in the east as far as Hammersmith in the west. Built on flood plains, the capital was defended only by embankments. The flood waters burst over them into Whitehall and Westminster, and rushed through crowded slums. Fourteen died and thousands were left homeless…
