The Visions of Octavia Butler | Interactive – the New York Times

(Octavia) Butler was not a climate scientist, a political pundit, or a Silicon Valley technologist…Somehow she knew this time would come. The smoke-choked air from fire gone wild, the cresting rivers and rising seas, the sweltering heat and receding lakes, the melting away of civil society and political stability, the light-year leaps in artificial intelligence—(she) foresaw them all…
Dive Into Artist’s Beautiful, Sobering Visualization Of NASA Water Data – Forbes Magazine

“Art can serve as an exceptional vehicle for fostering a deeper understanding of pressing issues,” (Yiyun) Kang, a visiting lecturer at London’s Royal College of Art, said in an interview. “I also believe the role of art is particularly crucial in addressing highly complex issues like the climate crisis, which demand collective efforts from everyone…”
A Climate Change Poem Turned Hip-Hop Song – Whakaata Māori
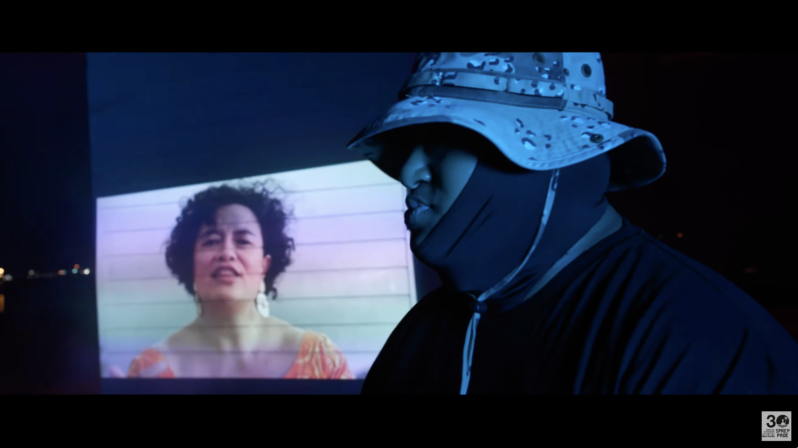

Based on poetry by Audrey Brown-Pereira, a hip-hop version of ‘They Taking Pictures of Us in the Water’ premiered at the Moana Blue Pacific Pavilion for COP28…“I heard her poem and I was like ‘I’m in, this is ticking so many boxes for me in terms of exploring our culture, exploring a kaupapa that’s very important to us all, exploring creative artistry in terms of not only but the music production and the visual production. From the outset, it was all go…” – Anonymouz
Natural causes: artists address climate crisis in inventive ways – The Art Newspaper

What can art do about a crisis? This is a question that a growing number of museums across the world have been faced with as they mount exhibitions addressing the climate emergency. In the past six months alone, institutions ranging from London’s Hayward Gallery (Dear Earth, now closed) to the Museum of Modern Art in New York (Emerging Ecologies: Architecture and the Rise of Environmentalism, until 20 January 2024) have opened eco-themed exhibitions. This month, a spate of new shows across London take up the baton, offering fresh perspectives on the subject’s relationship to wider society and taking the conversation out into the “real world”…
Can the tourism industry survive the climate crisis? – the Guardian
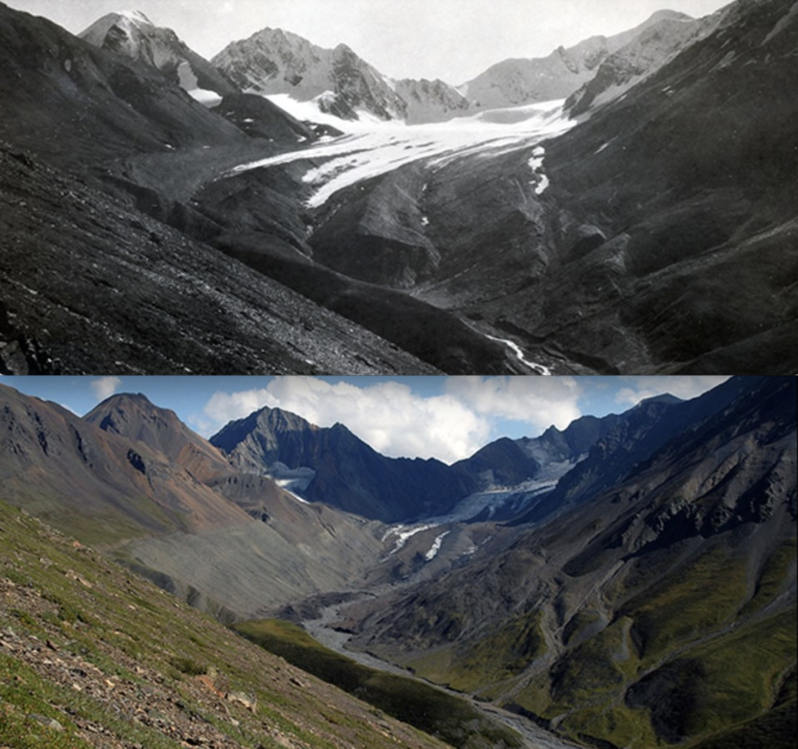

From the Solomon Islands to Denali national park, how five communities reliant on tourism are coping as climate change upends their industry…One of the terrible ironies of the climate crisis is that some of the most beautiful – and popular – places in the world are also the most vulnerable. Which means as temperatures rise, extreme weather events increase, water sources dry up and natural habitats die, these places are facing another devastating loss: tourists…
Earth on verge of five catastrophic climate tipping points, scientists warn – the Guardian
Humanity faces ‘devastating domino effects’ including mass displacement and financial ruin as planet warms…“Tipping points in the Earth system pose threats of a magnitude never faced by humanity,” said Tim Lenton, from the University of Exeter’s Global Systems Institute. “They can trigger devastating domino effects, including the loss of whole ecosystems and capacity to grow staple crops, with societal impacts including mass displacement, political instability and financial collapse…”
The Fantastical Mind of Benjamin Von Wong – Jejune Magazine
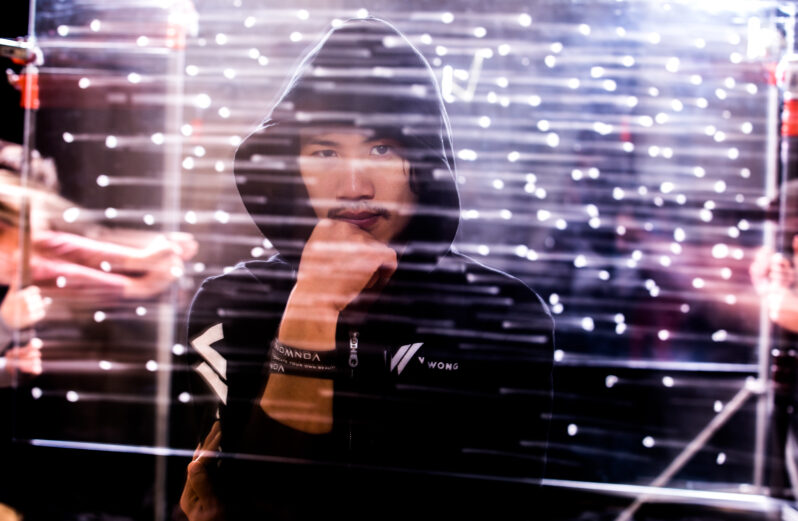

Bringing an idea to life takes innovation, passion and a whole lot of patience. What’s more powerful is if the creation brings people to another world for just a moment and sparks a new notion in the viewers…Benjamin Von Wong is doing it as we speak. The Canadian-born artist is a big advocate for Ocean Plastics and has been creating art pieces to bring awareness to the most critical issue faced today — Pollution…
A disappearing island: ‘The water is destroying us, one house at a time’ – NPR
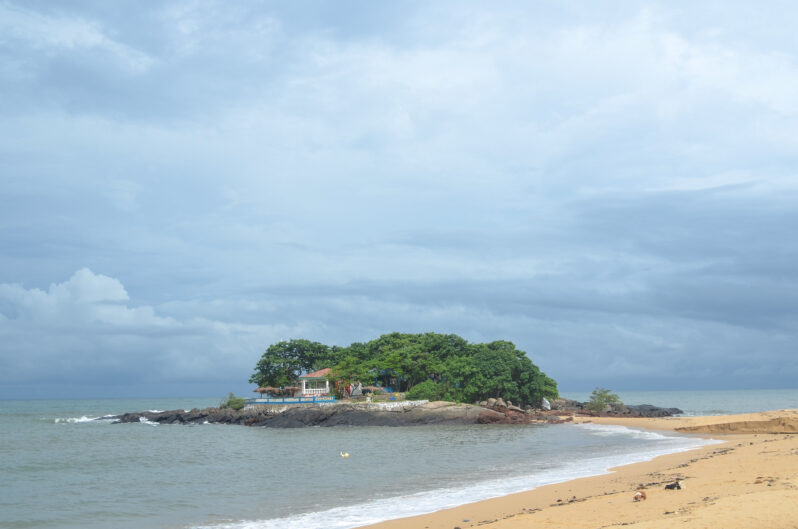

With nearly a third of its population living in coastal areas, and its heavy reliance on subsistence agriculture and fishing, Sierra Leone has been identified as one of the world’s most vulnerable countries to the impacts of climate change, despite having contributed just a tiny fraction of global CO2 emissions. With a GDP per capita of barely $2,000, it is also one of the least prepared to deal with those impacts….
Earth Just Had the Hottest 12-Month Span in Recorded History – Scientific American
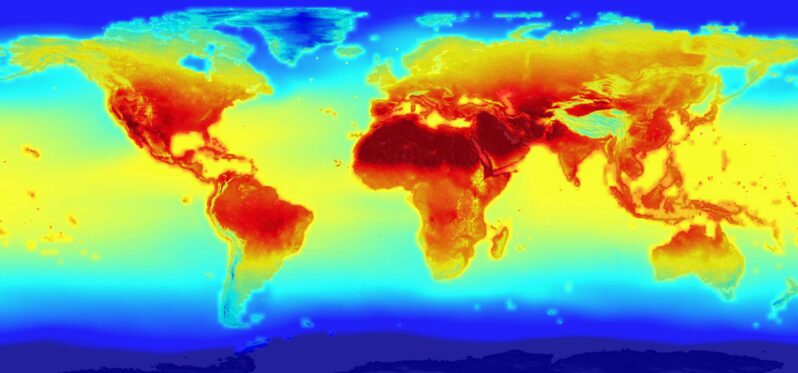
As this past October came to a close, it marked the hottest 12-month period ever recorded, a new analysis finds. This stark milestone is the latest in a string of superlatives to emerge this year that show how much carbon pollution has warmed the planet—and how that trend is accelerating. It also comes just weeks before international negotiators are set to meet and hash out issues around achieving the Paris climate accord’s fundamental goal: limiting global warming to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above preindustrial temperatures…
