Excerpt:
Updated, more accurate data gives a new look at the effects of sea level rise.
Around the world, communities are bracing for sea level rise: the Netherlands is stabilizing its dikes, Senegal is relocating neighborhoods, Indonesia is moving its entire capital city. These projects are hefty, expensive, and slow.
But they may need to pick up the pace. As new research shows, in many places, sea level rise will cause coastal flooding and other disruptions much sooner than anyone realized. It’s not that the water is rising faster; it’s that the land was lower to begin with.
Calculating when a rising sea will flood any one place involves a lot of math: you need to know the height of the water, the range of the tide, the elevation and slope of the land, the pace of sea level rise, and how much the land itself is rising or falling, among myriad other factors. As with all of science, the accuracy of these predictions is only as good as the data flowing into them.
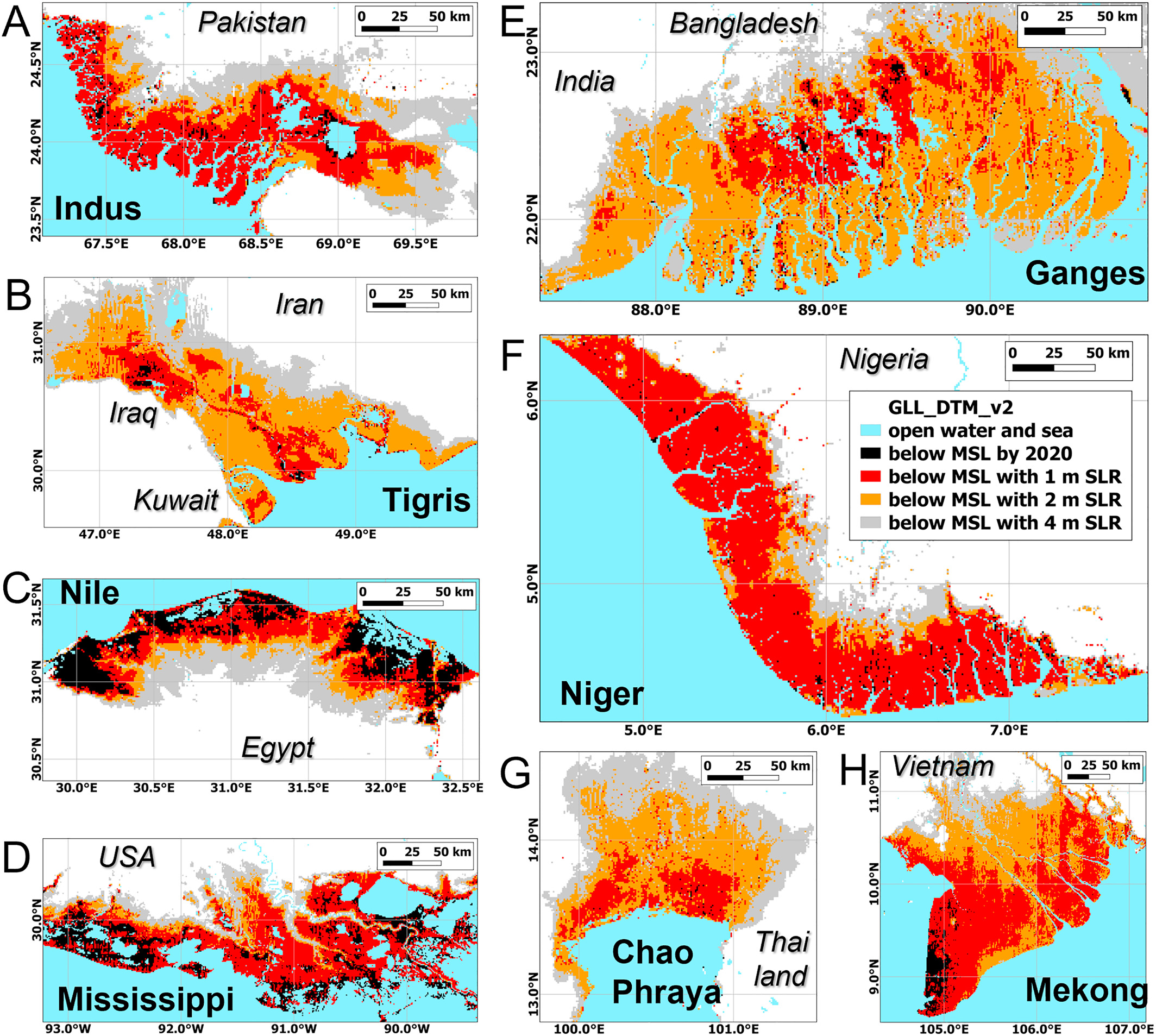
The problem, according to the new study by Ronald Vernimmen and Aljosja Hooijer, two data analysts working on flood risk in Southeast Asia, is that time after time, the measurements of coastal elevation that scientists feed into their models have been wildly inaccurate. In tropical forests, says Vernimmen, these misinterpretations can be off by 20 meters or more. “Obviously, you can’t use that,” he says.
The problem stems from limitations in the technology typically used to measure elevation: radar. Radar blankets an area in radio waves, then measures how long it takes the waves to bounce back. But radar isn’t precise enough to separate treetops from terra firma, and a patch of pines or cluster of condos can easily exaggerate the elevation. Many studies of sea level rise still use radar elevation data collected by the space shuttle in 2000.
Lidar is a lot like radar, but it uses lasers instead of radio waves. A lidar detector like the one on the ICESat-2 satellite, which NASA launched in 2018, can send up to one million pulses each second, firing lasers that can pinpoint the gaps between buildings and trees to more accurately gauge the elevation of the land underneath. Analysts still need algorithms to filter that barrage of information into a functional map, but the results are far more precise.
Vernimmen and Hooijer spent the past few years filtering the new satellite data for Earth’s immense coastline, comparing elevation estimates gathered from radar with the newer lidar-based measurements. It wasn’t pretty…