Is YOUR town at risk? – Daily Mail

Terrifying interactive map reveals the areas that could be plunged UNDERWATER by 2050 amid sea level rise fuelled by climate change.
With the allure of deck chairs, ice cream and amusement arcades, the Great British seaside holds a special, nostalgic place in the hearts of UK holidaymakers.
But fast forward just 25 years and scores of the country’s beaches, piers and bays could be underwater because of increasing global sea levels caused by global warming…
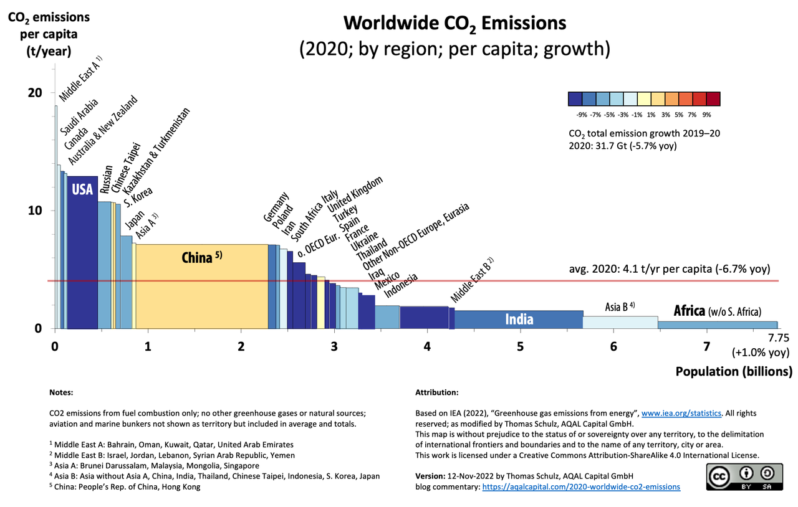
Why the Climate Fight Will Fail without India – Scientific American

India is in the midst of the biggest climate experiment the world has ever known.
It’s a test that aims to transform a nation marked by deep economic inequality and heavily polluting coal power to one where families drive electric scooters and cool their homes with the sun’s energy. And it could determine whether global temperatures exceed limits beyond which climate impacts become increasingly disastrous…
The Climate Impact of Your Neighborhood, Mapped – Interactive Feature – the New York Times
New data shared with The New York Times reveals stark disparities in how different U.S. households contribute to climate change. Looking at America’s cities, a pattern emerges.
Households in denser neighborhoods close to city centers tend to be responsible for fewer planet-warming greenhouse gases, on average, than households in the rest of the country. Residents in these areas typically drive less because jobs and stores are nearby and they can more easily walk, bike or take public transit…
Coastal erosion and landfill exposure: Future impacts of climate change – Legal Futures

The UK’s historic coastline is a ticking pollution time bomb that is being rapidly accelerated by the impacts of climate change and landfill exposure…
As an island nation the UK has the largest coastline in Europe of 17,381km and is surrounded by four water bodies (Atlantic ocean, North Sea, Irish Sea and English Channel). For this reason, 28% of the UK’s coastline is vulnerable to coastal erosion as climate change has accelerated rising sea levels and increasingly hazardous weather…
From Climate Exhortation to Climate Execution – the New Yorker
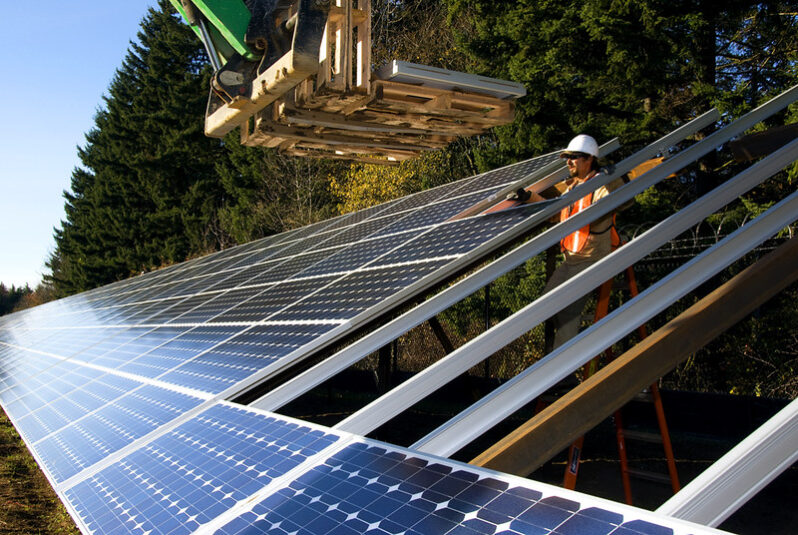

The Inflation Reduction Act finally offers a chance for widespread change…
So far, the climate debate has gone on mostly in people’s heads and hearts. It took thirty years to get elected leaders to take it seriously: first, to just get them to say that the planet was warming, and then to allow that humans were causing it. But this year Congress finally passed serious legislation—the Inflation Reduction Act—that allocates hundreds of billions of dollars to the task of transforming the nation so that it burns far less fossil fuel. So now the battle moves from hearts and heads to houses…
How sea level rise contributes to billions in extra damage during hurricanes – Yale Climate Connections
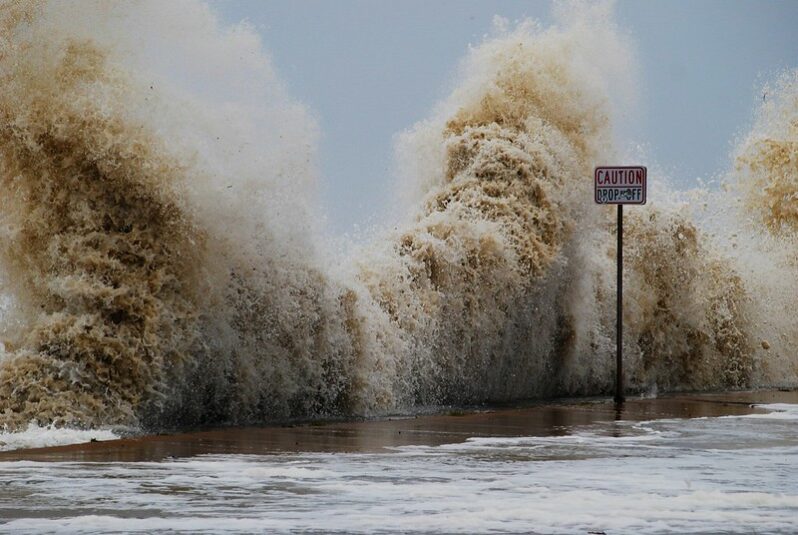

Had Ian hit a century ago, when sea levels were about a foot lower, the storm probably would have caused billions less in storm surge damage, judging by the results from two studies looking at storm surge damage from 2012’s Hurricane Sandy in New York. Taken together, the study results suggest that rising seas left a huge portion of U.S. coastal infrastructure – much of it built during the 20th century – vulnerable to storm surges.
Small increases in storm surge can cause huge impacts…
Extreme weather becoming a factor in where Americans choose to live – Fox Weather

A report shows that over 60% of Americans that are planning to move in the next year are reluctant to move to areas with natural disaster-prone areas or areas that experience extreme weather and sea level rise.
“All of these costs associated with climate change are actually becoming a real drag on not only our economy but particular areas that are, let’s say, high-risk areas,” Jesse Keenan, professor of sustainable real estate at Tulane University told FOX Weather.
An Alaskan Town Is Losing Ground—and a Way of Life – the New York Times
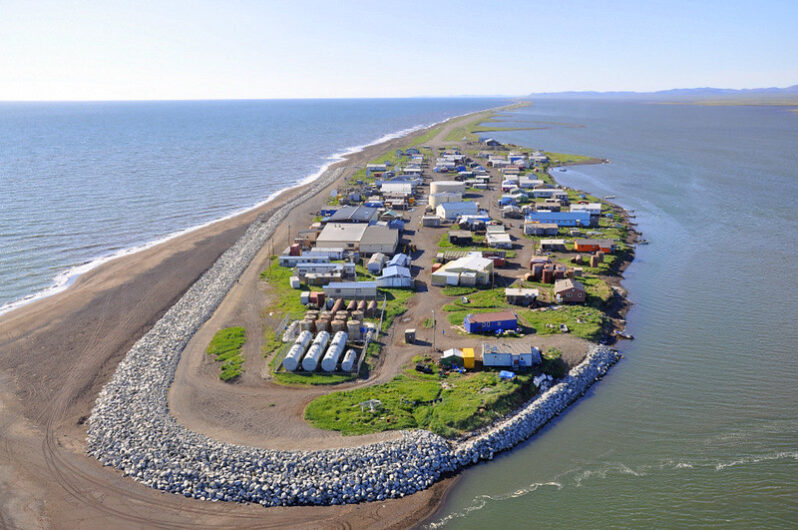

For years, Kivalina has been cited—like the Maldives, in the Indian Ocean, or the island nation of Tuvalu, in the Pacific—as an example of the existential threat posed to low-lying islands by climate change…
On a visit to the state in 2015, President Barack Obama flew over Kivalina and posted a photograph of the island on social media from the air. “There aren’t many other places in America that have to deal with questions of relocation right now,” Obama wrote, “but there will be.” He described what was happening in the village as “America’s wake-up call.”
Seven years later, Kivalina’s move is still mostly in the future, even though the island continues to lose ground…
Can Development Laws Elevate Us Out of Sea Level Rise?
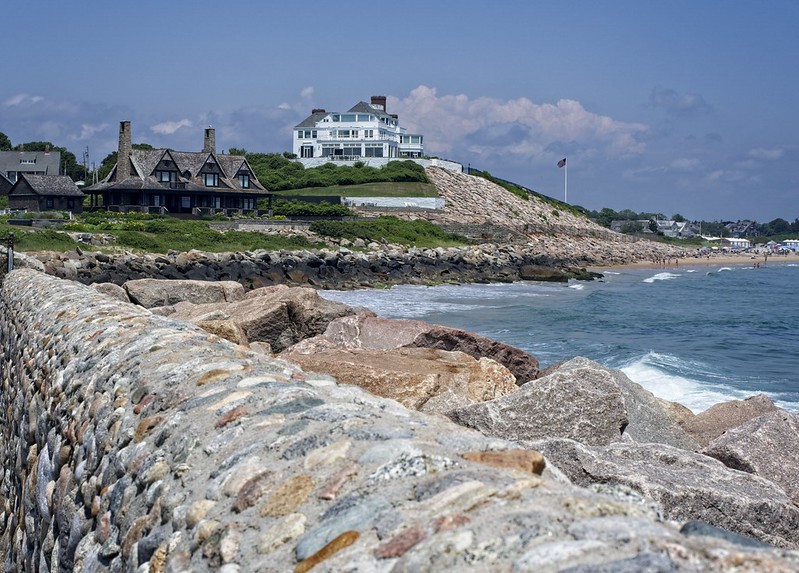

Watch Hill is an old neighborhood, where houses with names like Windridge, Waveland and Sea Swept began to take their positions on the ridge more than 160 years ago…
But Watch Hill’s most implacable foe has always been Mother Nature. In 1938, the Great Hurricane wiped fifty houses off Napatree Point, a finger of land curling into the sound. Today, the village is under the increasingly frequent assault of water coaxed by tidal force or blown in by Nor’easters over streets and parking lots, cutting off access to Napatree and giving the old house names a sardonic twist…
