Weaving the Harbor Back to Life – Hakai Magazine
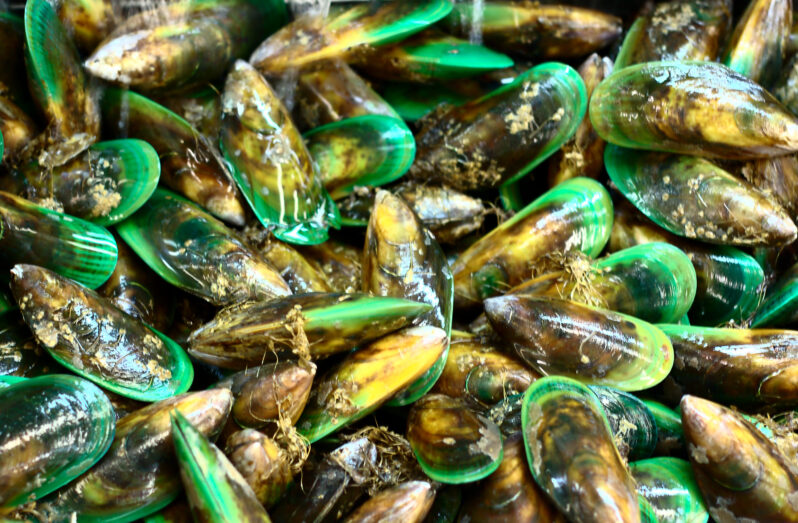

How Māori knowledge is helping to revive the mussel population in New Zealand’s Ōhiwa Harbour…
Research Confirms Link Between Snow Crab Decline and Marine Heatwave – NOAA Fisheries
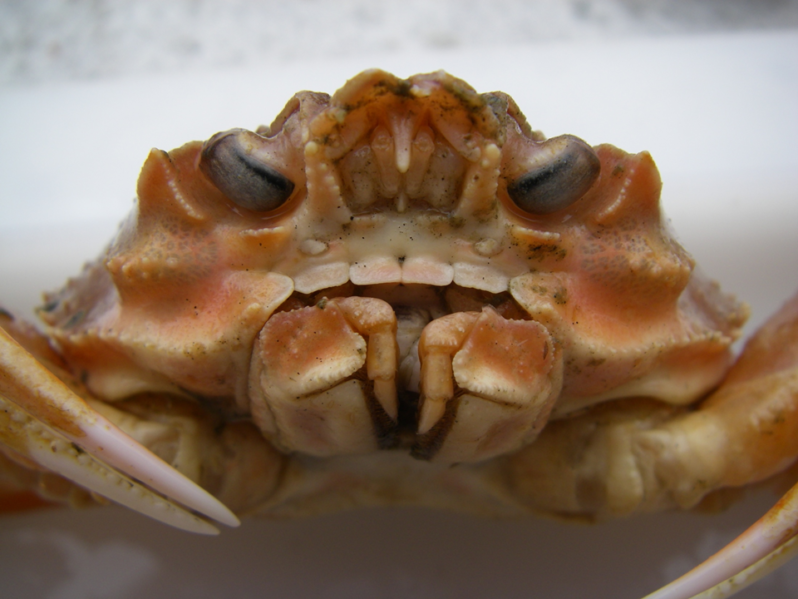

“During the marine heatwave, snow crabs faced a triple threat,” said lead author and Alaska Fisheries Science Center stock assessment scientist Cody Szuwalski. “Their metabolism increased, so they needed more food; their habitat was reduced so there was less area to forage; and crabs caught in our survey weighed less than usual. These conditions likely set them up for the dramatic decline we saw in 2021…”
Seaweed is mucking up beaches. This robot could stop it — and fight climate change – NPR
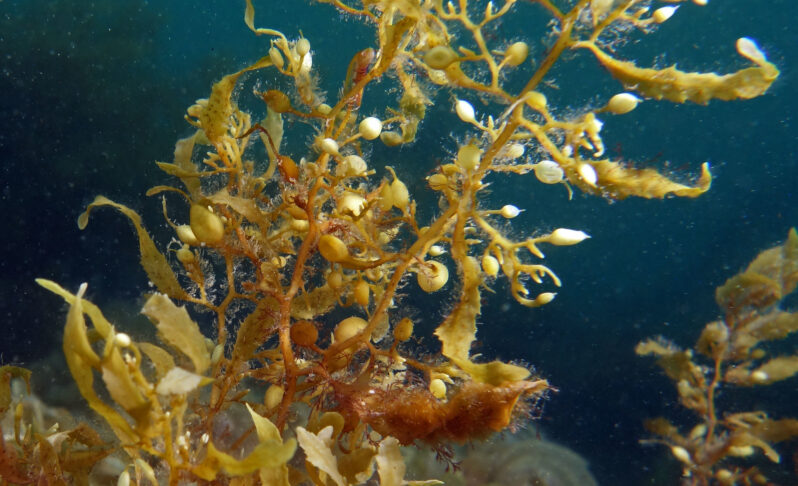

In shallow waters, sargassum can smother coral reefs and alter the water’s pH balance, killing off local seagrasses and mangroves. It can choke boat motors, constricting local fishing yields if not cutting off whole marinas. Sargassum once clogged a desalination plant so badly that residents of the U.S. Virgin Islands were told the drinking water may not be safe…
It’s Not Just Coral. Extreme Heat is Weakening Entire Marine Ecosystems in Florida – Grist Magazine

Anemones, sponges, and jellyfish are bleaching throughout the Everglades amid record temperatures. It’s a troubling sign for Florida Bay and beyond.
We studied more than 1,500 coastal ecosystems – they will drown if we let the world warm above 2℃ – the Conversation
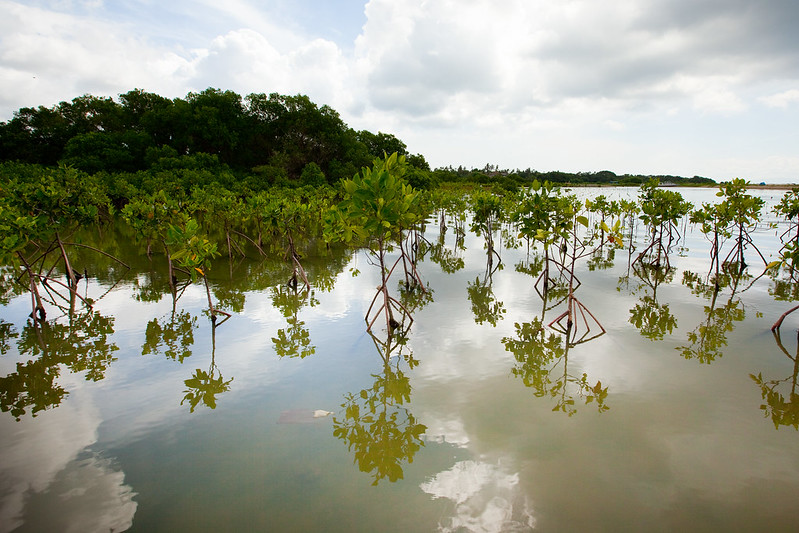

Much of the world’s natural coastline is protected by living habitats, most notably mangroves in warmer waters and tidal marshes closer to the poles. These ecosystems support fisheries and wildlife, absorb the impact of crashing waves and clean up pollutants. But these vital services are threatened by global warming and rising sea levels…
One way to save coral reefs? Deep freeze them for the future – NPR
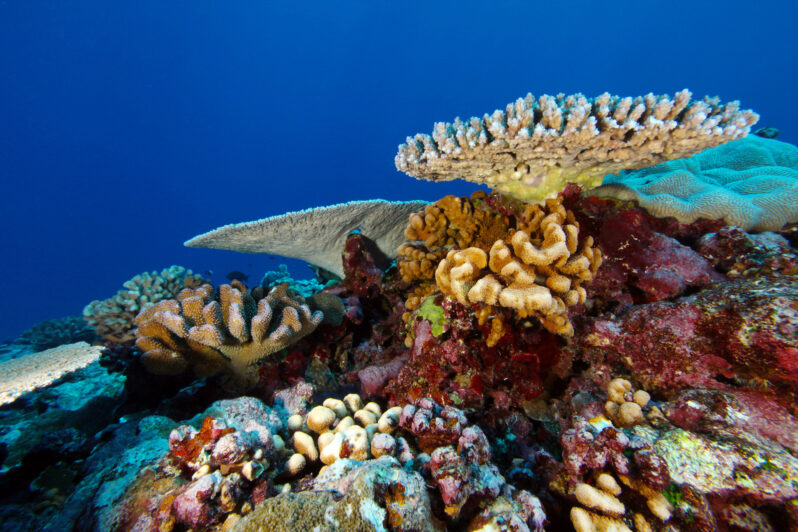

Ocean temperatures have been extremely hot this summer, wreaking havoc on some of the world’s highly vulnerable coral reefs. With marine heat waves only expected to get worse as the climate changes, scientists are increasingly focusing on an emergency plan: collecting coral specimens and safeguarding them onshore….
NOAA and partners race to rescue remaining Florida corals from historic ocean heat wave – NOAA Climate.gov
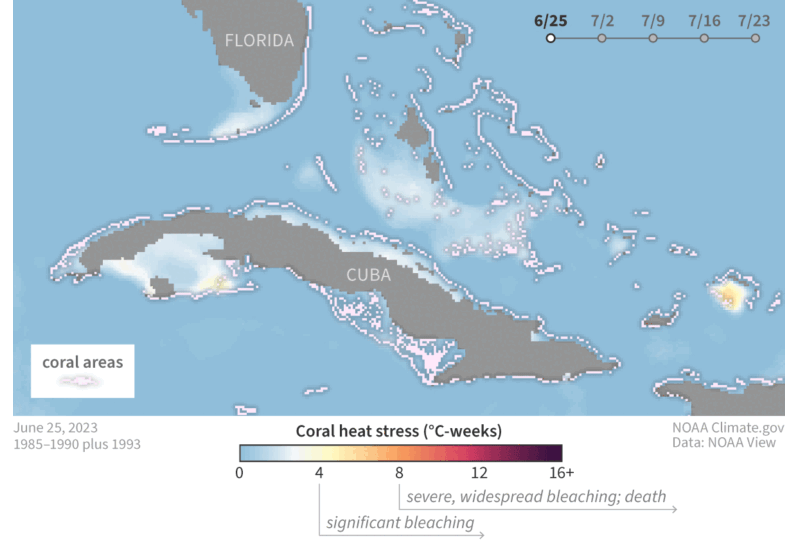
In mid-July 2023, heat-stressed corals in the southern Florida Keys began bleaching—expelling their food-producing algal partners—amid the hottest water temperatures ever documented in the region during the satellite record (dating back to 1985). As weeks of heat stress have continued to accumulate, bleaching and death have become more widespread, raising fears of a mass mortality event on the region’s already fragile reefs…
The real story behind the Atlantic’s record-breaking seaweed blobs – BBC
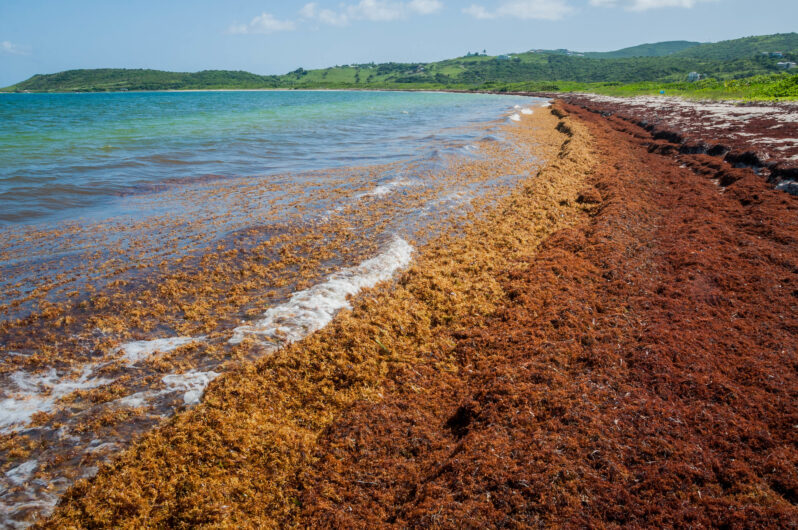

Along the coastlines of the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico, a monster is lurking. It creeps in with the tide and you’ll likely smell it before you see it. Giant clumps of sargassum seaweed have been washing ashore, choking the surf and blanketing beaches in a brown, stinking mass.
The clumps are breaking off an enormous raft of free-floating seaweed known as the Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt, which stretches 5,000 miles (8,047km) between the Gulf of Mexico and the west coast of Africa and can be seen from space…
To restore coastal marine areas, we need to work across multiple habitats simultaneously – PNAS

Restoration of coastal marine habitats—often conducted under the umbrella of “nature-based solutions”—is one of the key actions underpinning global intergovernmental agreements, including the Paris Agreement and the 2021–2030 United Nations (UN) Decade of Restoration. To achieve global biodiversity and restoration targets…we need methods that accelerate and scale up restoration activities in size and impact. Part of the solution is cross-habitat facilitation—positive interactions that occur when processes generated in one habitat benefit another…
