The Atlantification of the Arctic Ocean Is Underway – Hakai Magazine
In the Fram Strait off Greenland’s west coast, Véronique Merten encountered the foot soldiers of an invasion.
Merten was studying the region’s biodiversity using environmental DNA, a method that allows scientists to figure out which species are living nearby by sampling the tiny pieces of genetic material they shed, like scales, skin, and poop. And here, in a stretch of the Arctic Ocean 400 kilometers north of where they’d ever been seen before: capelin.
And they were everywhere…
As Ocean Oxygen Levels Dip, Fish Face an Uncertain Future – Yale Environment 360
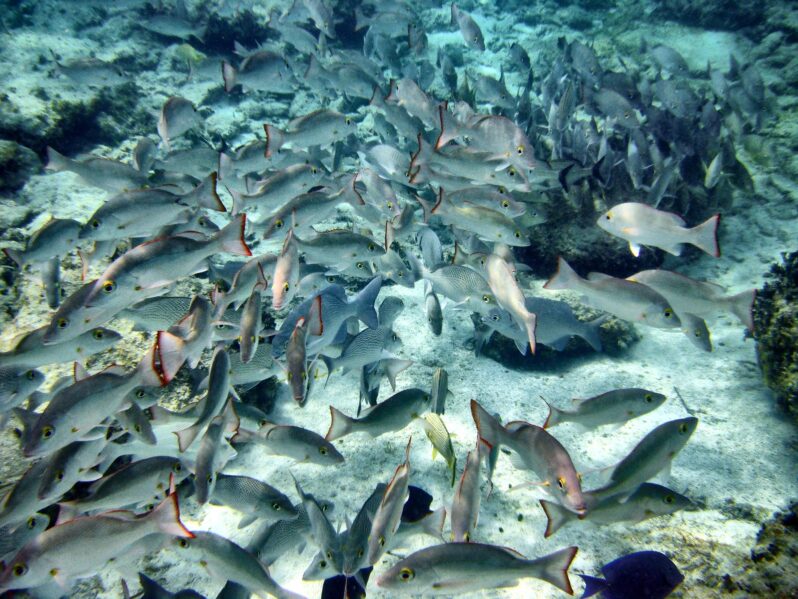

Global warming not only increases ocean temperatures, it triggers a cascade of effects that are stripping the seas of oxygen. Fish are already moving to new waters in search of oxygen, and scientists are warning of the long-term threat to fish species and marine ecosystems.
ff the coast of southeastern China, one particular fish species is booming: the oddly named Bombay duck, a long, slim fish with a distinctive, gaping jaw and a texture like jelly. When research ships trawl the seafloor off that coast, they now catch upwards of 440 pounds of the gelatinous fish per hour — a more than tenfold increase over a decade ago. “It’s monstrous,” says University of British Columbia fisheries researcher Daniel Pauly of the explosion in numbers…
Bleaching, It’s Not Just for Corals – Hakai Magazine
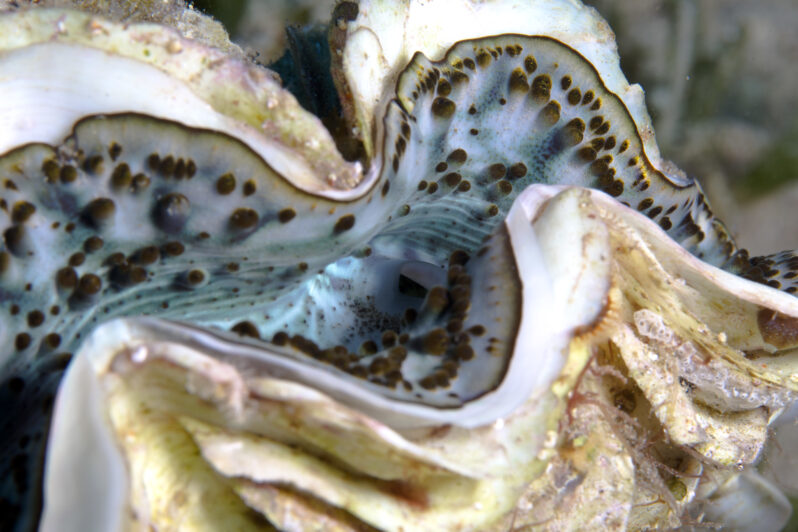

Giant clams suffer similar struggles with warming water, though the consequences don’t seem quite as dire.
Bleaching occurs when a stressed marine creature, most commonly a coral, expels its symbiotic algae and turns a ghostly white, often in response to a warming sea. But bleaching affects more than just corals. Giant clams—massive mollusks that can grow more than 1.2 meters in diameter and weigh as much as 225 kilograms—can bleach, too. And in recent research, scientists have learned more about how bleaching disrupts these sessile giants, affecting everything from their nutrition to their reproduction…
The Foul Chartreuse Sea – Yale Climate Connections
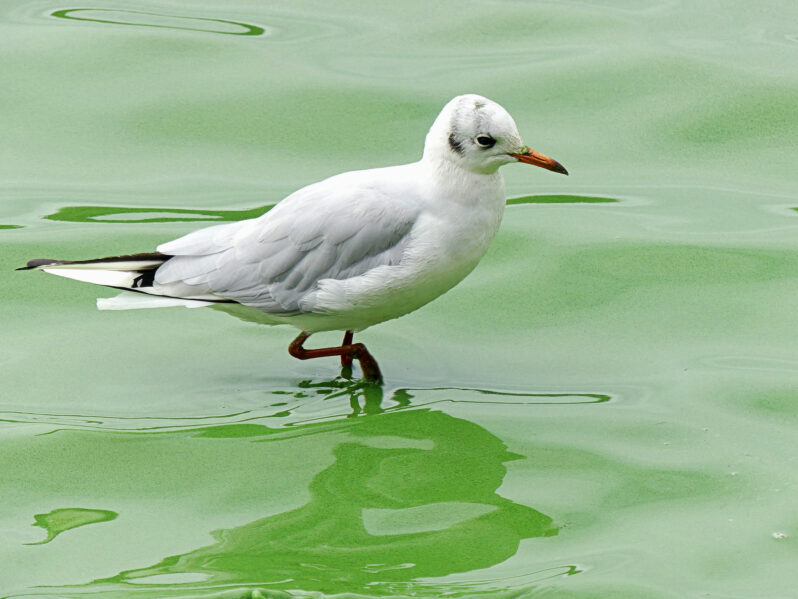

Researchers in Kotzebue, Alaska, are investigating why their town is increasingly playing host to harmful cyanobacteria.
Dead fish were everywhere, speckling the beach near town and extending onto the surrounding coastline. The sheer magnitude of the October 2021 die-off, when hundreds, possibly thousands, of herring washed up, is what sticks in the minds of the residents of Kotzebue, Alaska. Fish were “literally all over the beaches,” says Bob Schaeffer, a fisherman and elder from the Qikiqtaġruŋmiut tribe…
Giant blobs of seaweed are hitting Florida. That’s when the real problem begins – NPR
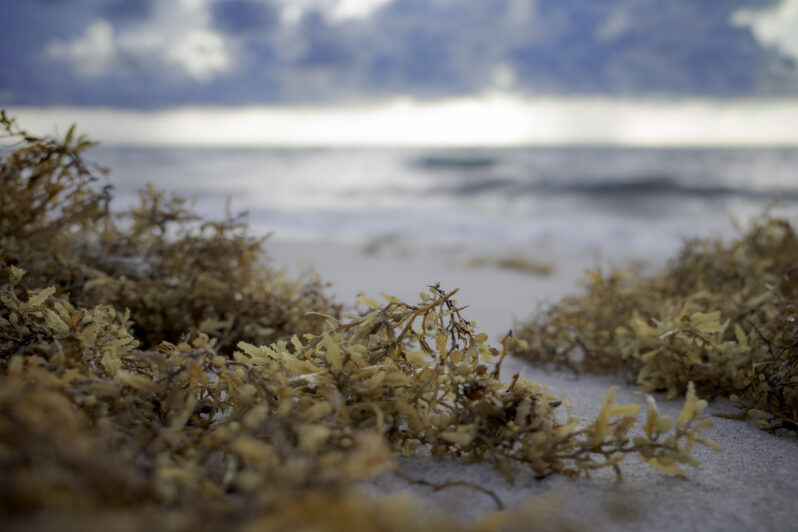

It used to be that the conversation around subtropical marine life centered on declines: the death of coral beds, the diminishing variety of seagrasses, the disappearance of fish. But for now, it’s an overabundance that’s hard to miss. From Montego to Miami, an influx of algae called sargassum is leaving stinky brown carpets over what was once prime tourist sand. It’s the most sargassum researchers have tracked this early in the year. Deciding what to do with it is proving more challenging the more we learn about it — and inspiring some entrepreneurs to rethink removing sargassum altogether…
