Mekong Delta pays a high price from sand mining – Mekong Eye
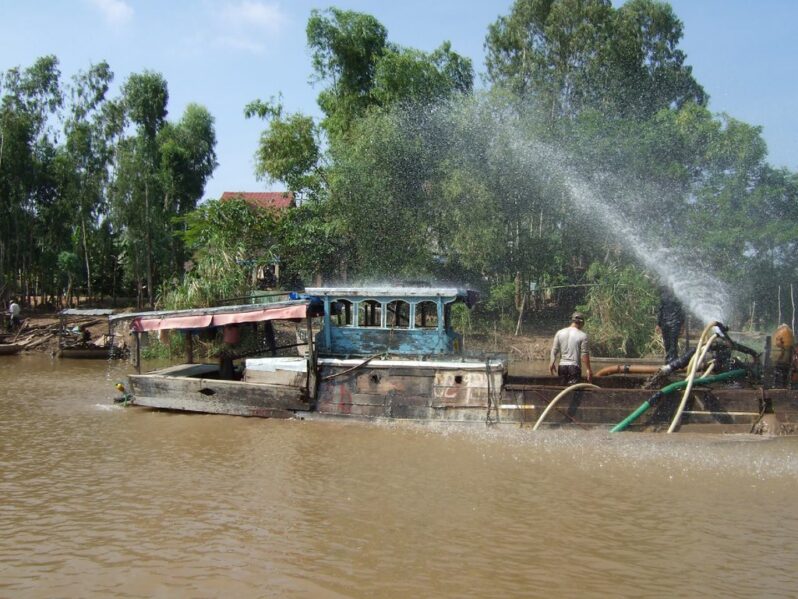

The need for sand to build roads and infrastructure in Vietnam charges ahead with few restraints as land and houses are lost.
The only traces of Long Phu Thuan, an islet in the Mekong River in Vietnam’s Dong Thap province, can now only be found in old maps.
Much of the islet belonged to Le Van Phi, a 70-year-old farmer. Back in 1976, he explored the islet and converted 0.4 hectares of it into farmland. He grew corn, soybeans and chili peppers in the dry season, and rice in the flooding season…
Shifting Sands: The Messy Business of Sand Mining Explained – Reuters Graphics
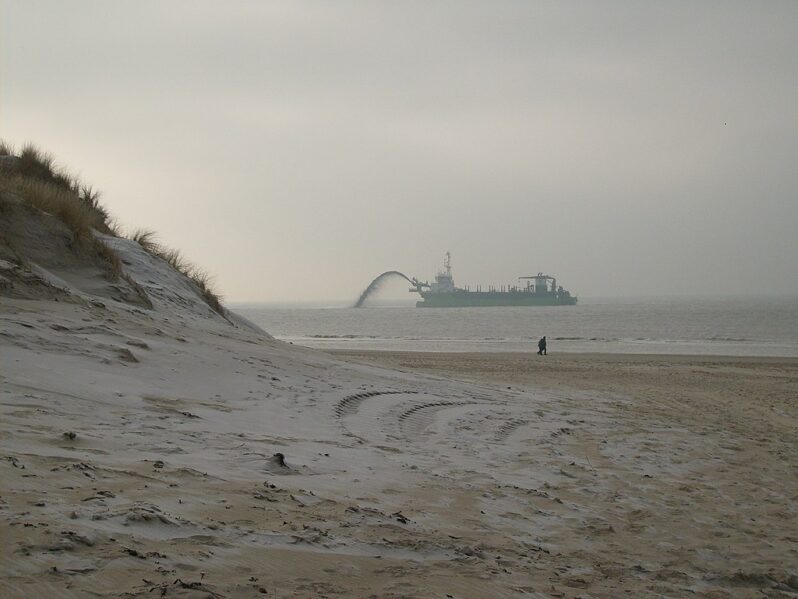

From Shanghai to Seattle, the world’s cities are built on sand – massive amounts of sand. It’s in the cement and concrete that make the bulk of most buildings. The glass in those buildings’ windows is made with sand, too. So is the tarmac laid onto the roads around them. Sand is the planet’s most mined material, with some 50 billion tons extracted from lakes, riverbeds, coastlines and deltas each year, according to the United Nations Environment Programme. Per person, that’s about 6,570 kilogrammes (14,500 pounds) per year – more than an elephant’s weight in sand…
Four questions for Eric Lambin on the sand shortage – Stanford News
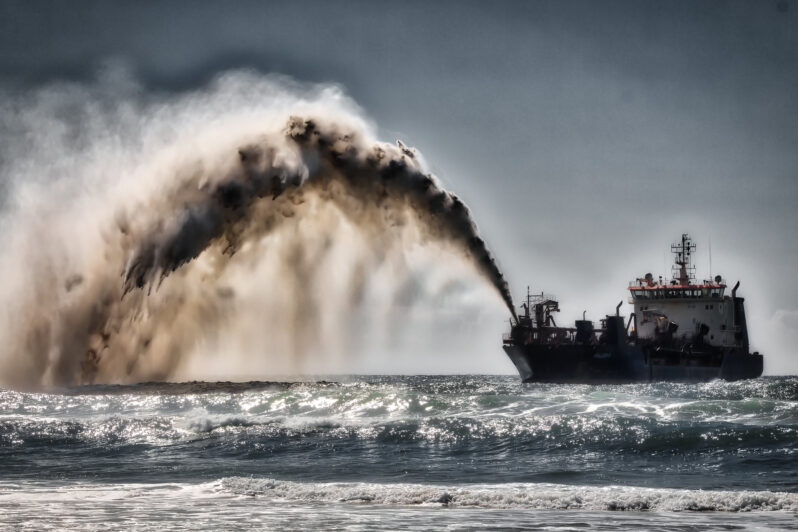

The Stanford geographer and environmental scientist discusses the sand shortage crisis and what it means for the future of the environment.
The ongoing surge in demand for sand has made it a scarce commodity. This natural resource is commonly used in computer microchips, construction, and is an active ingredient in cosmetics. But the current supply of this material has not been able to keep up with the speed of global urbanization. Now, sand is approaching a cost of $10 a ton, while it was just under $4 a ton 31 years ago…
What China Has Been Building in the South China Sea – the New York Times
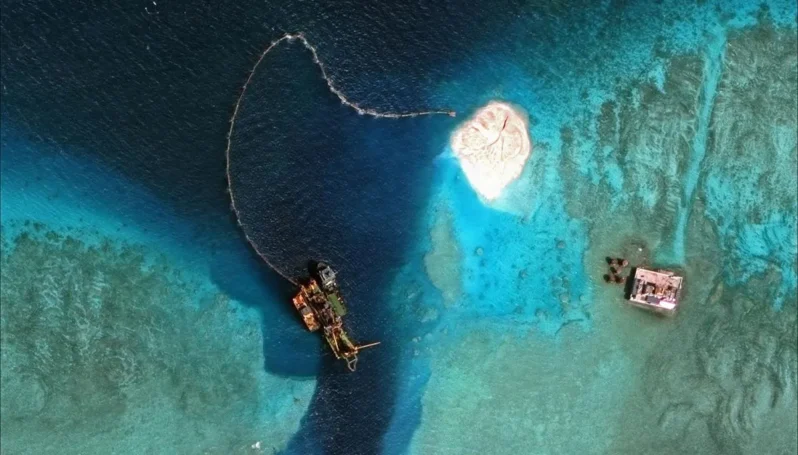

China has been rapidly piling sand onto reefs in the South China Sea, creating seven new islets in the region. It is straining geopolitical tensions that were already taut.
China’s activity in the Spratlys (Islands) is a major point of contention between China and the United States and was a primary topic of discussion between President Obama and President Xi Jinping of China during the Chinese president’s visit to the White House in September. On Monday, the United States sent a Navy destroyer near the islands, entering the disputed waters…
Sand – Planet Snapshots
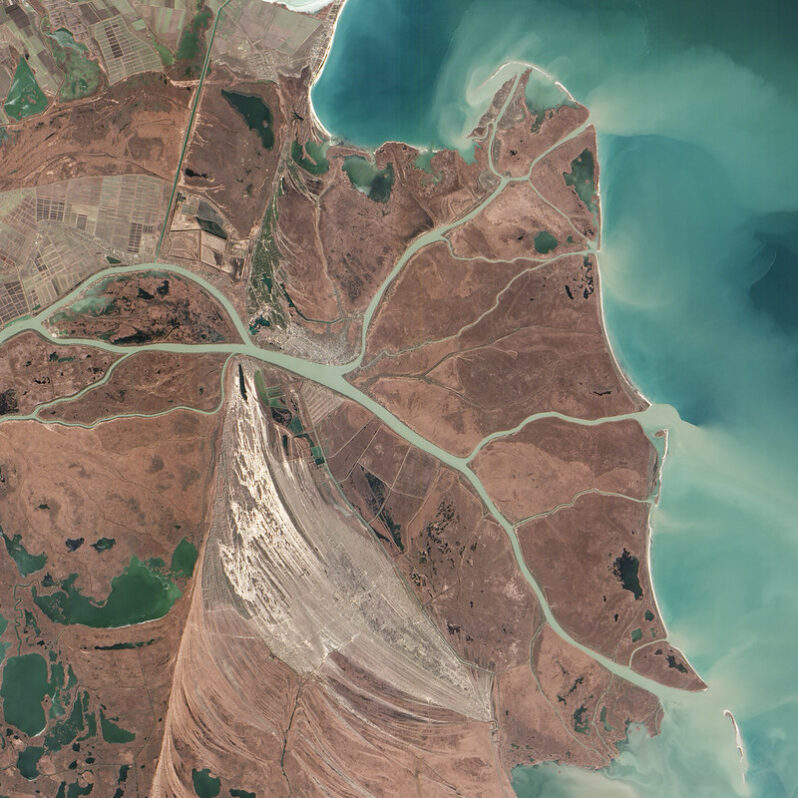

Sand. It’s coarse, rough, irritating, and it gets everywhere — perhaps more than you think. Sand is the second most used natural resource after water and the most extracted solid material, accounting for 85% of global mineral extraction. Like a messy trip to the beach, it has infiltrated our pockets and all our surroundings. It’s the key ingredient in cement, asphalt, glass, and silicon chips. Our cities are glorified sand castles, and our most advanced tech is built from this unimposing substance…
As Greenland’s Ice Melts, Glacial Sand Deposits May Offer a Welcome Economic Opportunity – Columbia Climate School
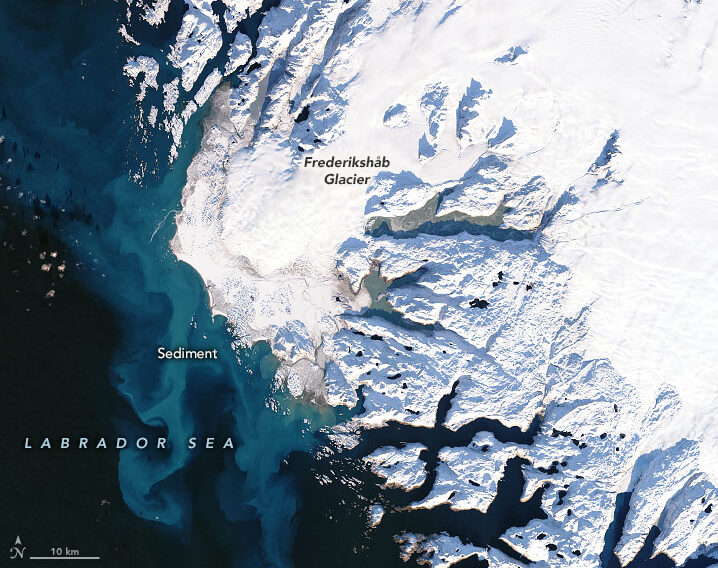
Greenland’s ice sheet is losing 280 billion tons of mass per year, and some models suggest that its glaciers may be melting up to 100 times faster than expected. But flowing off those glaciers comes a potential economic boom: sand. Each season, millions of tons of sediment flow from melting glaciers into the ocean, adding landmass to the largest island in the world. According to a research paper published in Nature last fall, three out of four Greenlanders support extracting and exporting sand — so long as they’re the ones in charge of managing the resource…
Lost Lands: Mining the Mekong – the South China Morning Post Films
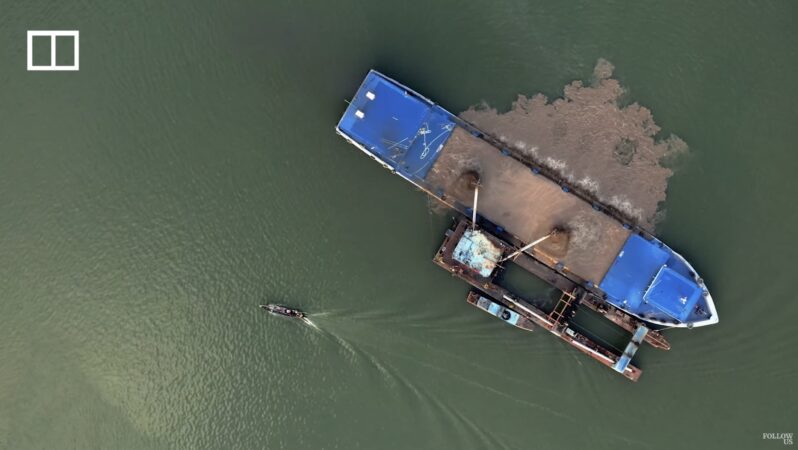

Cambodia’s appetite for sand has exploded as construction continues to fuel economic growth in the capital Phnom Penh. But as the thirst for sand grows, so does the uncertainty over the future of the river. Two families who rely on the river for a living share their stories of how sand dredging is causing pain and concerns for the future.
Beaches on Scotland’s ‘Hawaii of the North’ at risk after sand stolen – The Telegraph

With its stunning white crystal sands, it is known as “Hawaii of the North”. But beachcombers are said to be removing the famous sands of Tiree in the Hebrides on an industrial scale. Landowner Argyll Estates suspects sand is being “stolen” by “greedy” islanders under cover of darkness. Reports also suggest that it is “the more affluent residents” who are involved “so the reasons for this may not always be hardship but perhaps greed…”
The global impact of sand mining on beaches and dunes – Ocean & Coastal Management

Beaches and coastal dunes have always supplied sand for a wide range of uses, and initially the extracted volumes were limited to buckets, wheelbarrows, or small pickup truck loads. However, starting in the late twentieth century, and thanks to urban development, especially for coastal tourism, coastal and river sand has been extracted at an accelerated pace, and on a much grander scale…
