Plastic bottles harm human health at every stage of their life cycle – the Grist

A new report says beverage companies like Coca-Cola must be “held accountable for the supply chain impacts of their plastics.”
In 1973, a DuPont engineer named Nathaniel Wyeth patented the PET plastic bottle — an innovative and durable alternative to glass. Since then, production has skyrocketed to more than half a trillion bottles per year, driven by beverage companies like Coca-Cola, PepsiCo, and Nestlé…
Yet Another Problem With Recycling: It Spews Microplastics – Wired Magazine

An alarming new study has found that even when plastic makes it to a recycling center, it can still end up splintering into smaller bits that contaminate the air and water. This pilot study focused on a single new facility where plastics are sorted, shredded, and melted down into pellets. Along the way, the plastic is washed several times, sloughing off microplastic particles—fragments smaller than 5 millimeters—into the plant’s wastewater…
From Gas Wells to Rubber Ducks to Incineration, the Plastics Lifecycle Causes ‘Horrific Harm’- Inside Climate News

With plastic production expected to triple by 2060, a scientific commission this week recommended banning or severely restricting the manufacture and use of unnecessary plastics.
Plastic causes illness and death across its lifecycle, from production to use and disposal, a team of nearly 50 scientists concludes in a report made public Tuesday…
How do you tackle microplastics? Start with your washing machine – the Grist

Simple filters could help remove microfiber pollution from your laundry. But experts say a broader portfolio of solutions is needed to address the problem.
As environmental challenges go, microfiber pollution has come from practically out of nowhere. It was only a decade or so ago that scientists first suspected our clothing, increasingly made of synthetic materials like polyester and nylon, might be major contributors to the global plastic problem…
American cities want to recycle their plastic trash in Mexico. Critics call it ‘waste colonialism.’ – the Grist

Just ahead of this year’s Super Bowl in February, the City of Phoenix, Arizona, published a peculiar press release touting its strategy for waste diversion. Thanks to its relationship with Direct Pack Incorporated, a multinational company that makes and recycles plastic, the city said it would be able to send much of its plastic waste to Mexico for recycling…
Microplastics Are Filling the Skies. Will They Affect the Climate? – Yale Environment 360
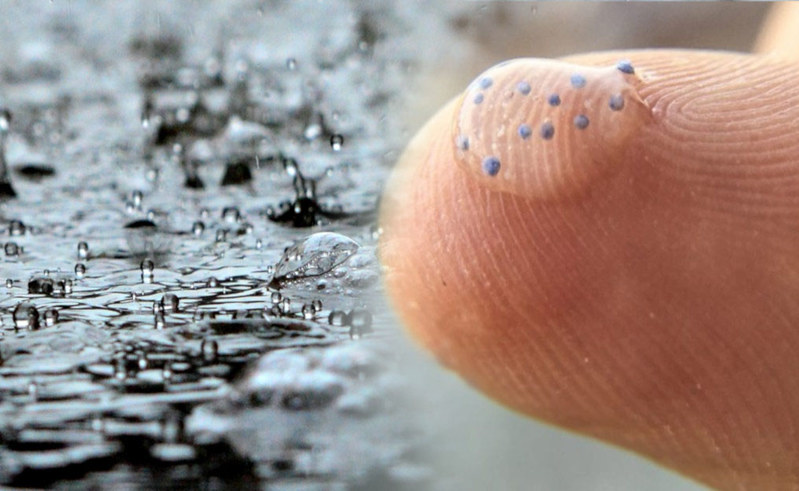
Recent studies reveal that tiny pieces of plastic are constantly lofted into the atmosphere. These particles can travel thousands of miles and affect the formation of clouds, which means they have the potential to impact temperature, rainfall, and even climate change.
Plastic has become an obvious pollutant over recent decades, choking turtles and seabirds, clogging up our landfills and waterways. But in just the past few years, a less-obvious problem has emerged…
There are 21,000 pieces of plastic in the ocean for each person on Earth – the Washington Post
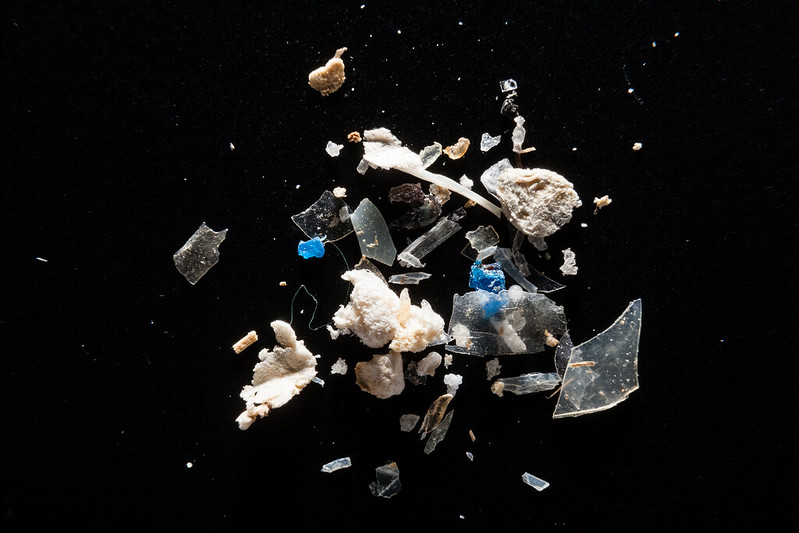

And plastic pollution has been doubling every six years.
Humans have filled the world’s oceans with more than 170 trillion pieces of plastic, dramatically more than previously estimated, according to a major study released Wednesday.
The trillions of plastic particles — a “plastic smog,” in the words of the researchers — weigh roughly 2.4 million metric tons and are doubling about every six years…
Here’s why a California beach town just banned balloons – the Grist

Celebrations in a beachside California city will soon have to take place without an iconic, single-use party favor: balloons.
The city council of Laguna Beach, about 50 miles southeast of Los Angeles, banned the sale and use of all types of balloons on Tuesday, citing their contribution to ocean litter as well as risks from potential fires when they hit power lines…
Bio-Based Plastics Aim to Capture Carbon. But at What Cost? – Wired Magazine

Growing crops to make plastic may theoretically reduce reliance on fossil fuels, but at an enormous environmental cost…bio-based plastics are problematic for a variety of reasons. It would take an astounding amount of land and water to grow enough plants to replace traditional plastics — plus energy is needed to produce and ship it all…But let’s say there was a large-scale shift to bioplastics — what would that mean for future emissions? That’s what a new paper in the journal Nature set out to estimate…
