Shifting Sands: The Messy Business of Sand Mining Explained – Reuters Graphics
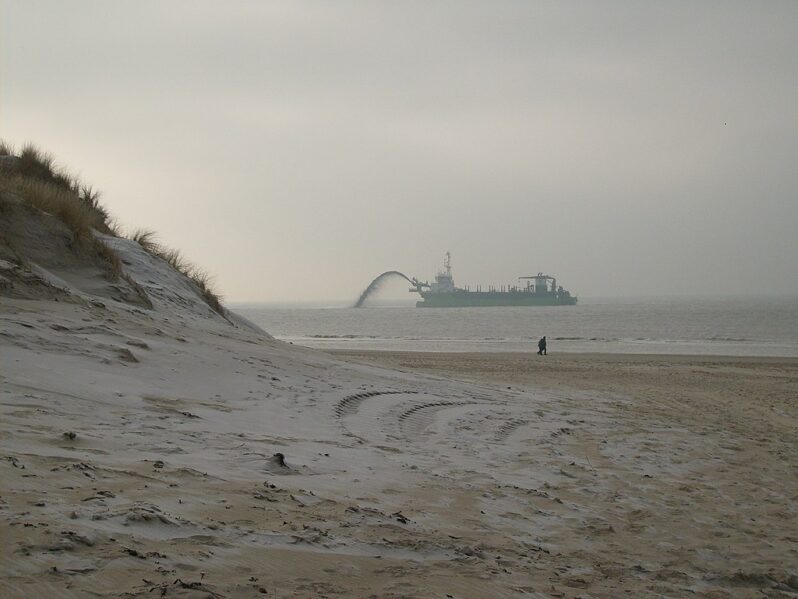

From Shanghai to Seattle, the world’s cities are built on sand – massive amounts of sand. It’s in the cement and concrete that make the bulk of most buildings. The glass in those buildings’ windows is made with sand, too. So is the tarmac laid onto the roads around them. Sand is the planet’s most mined material, with some 50 billion tons extracted from lakes, riverbeds, coastlines and deltas each year, according to the United Nations Environment Programme. Per person, that’s about 6,570 kilogrammes (14,500 pounds) per year – more than an elephant’s weight in sand…
In pictures: France demolishes beach apartments and relocates residents due to rising sea levels – Euronews | Reuters

When it was built at the end of the 1960s on one of France’s most glorious Atlantic coastlines, the beach was over 200 metres away.
Today, the hulk of the 80-flat Le Signal apartment block perches precariously on a dune just metres from the water and local authorities are tearing it down before it tumbles…
Why are Tunisia’s beaches disappearing and what does it mean for the country? – Reuters
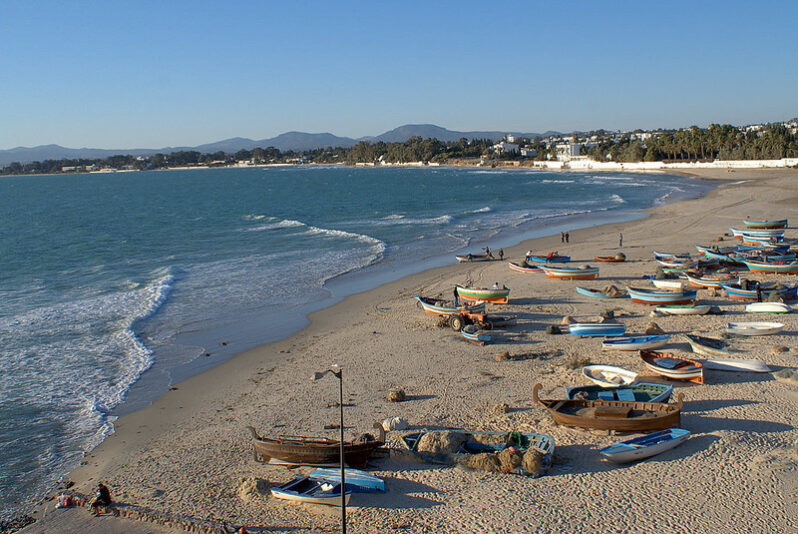

Rising sea levels are causing Tunisia’s beaches to gradually disappear. This is making life hard for the country’s tourism and fishing industries.
The Maghreb – made up of Morocco, Tunisia, Algeria and Libya – is more affected by coastal erosion than any region outside South Asia, the World Bank found in a 2021 study. Among these countries, Tunisia has had the highest erosion rates in the last three decades, averaging almost 70cm a year, it found…
California braces for two more atmospheric rivers – Rueters
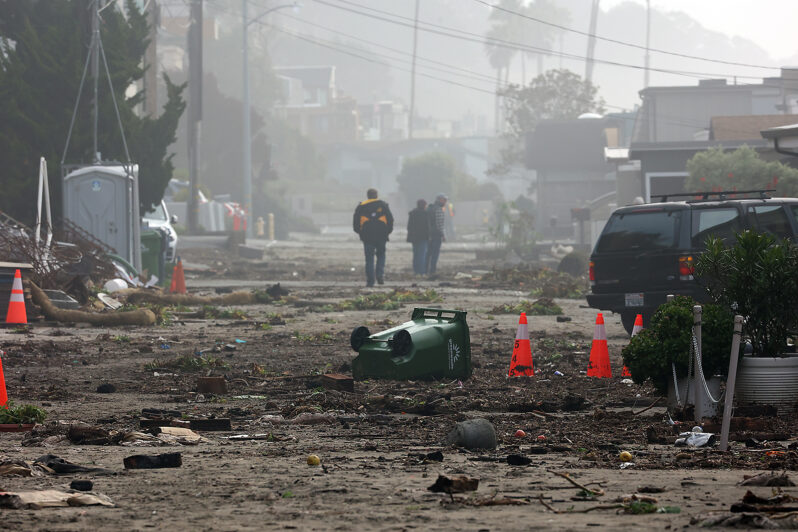

California’s parade of atmospheric rivers may be nearing an end but not before at least two more of the rainstorms are due to drench the waterlogged state starting on Saturday…
Starving the Mekong – Reuters
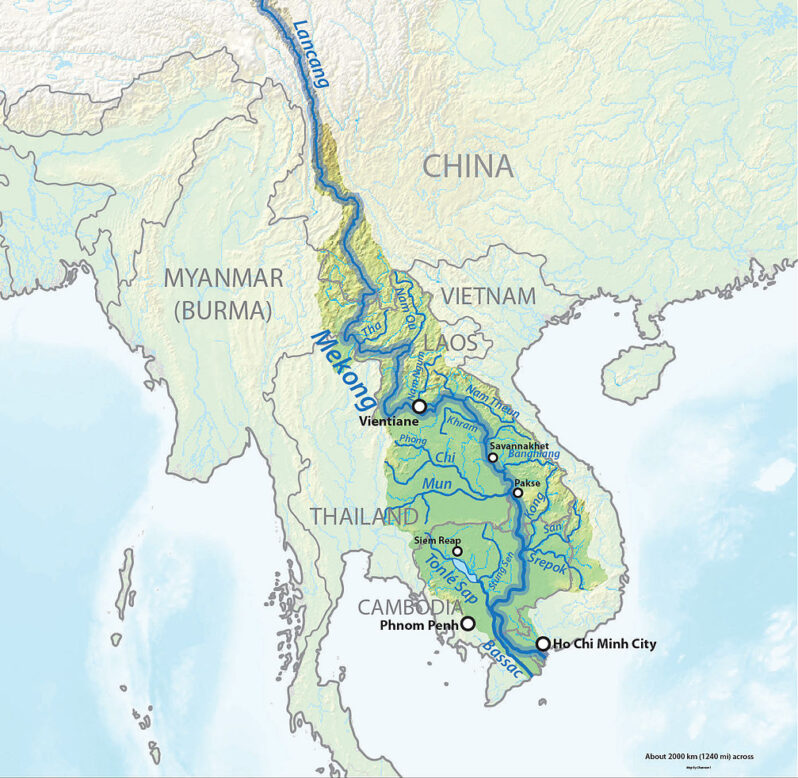
Lives are remade as dams built by China upstream deprive the Mekong River Delta of precious sediment
Standing on the bank of the Mekong River, Tran Van Cung can see his rice farm wash away before his very eyes. The paddy’s edge is crumbling into the delta.
Just 15 years ago, Southeast Asia’s longest river carried some 143 million tonnes of sediment – as heavy as about 430 Empire State Buildings – through to the Mekong River Delta every year, dumping nutrients along riverbanks essential to keeping tens of thousands of farms like Cung’s intact and productive…
