Rancho Palos Verdes landslide is creating a new beach. ‘It’s unreal’ – the Los Angeles Times
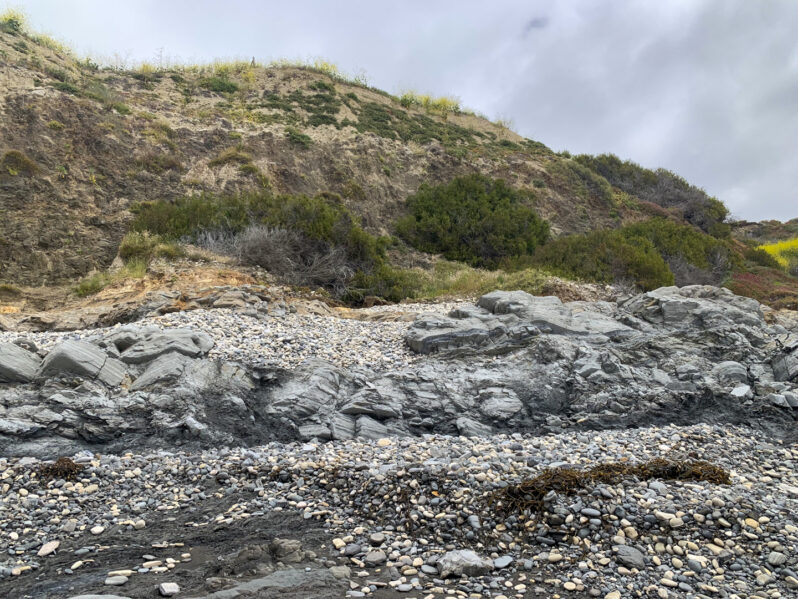

There’s an entirely new coastline in Rancho Palos Verdes…
California will help return tribal lands as part of the historic Klamath River restoration – the Los Angeles Times
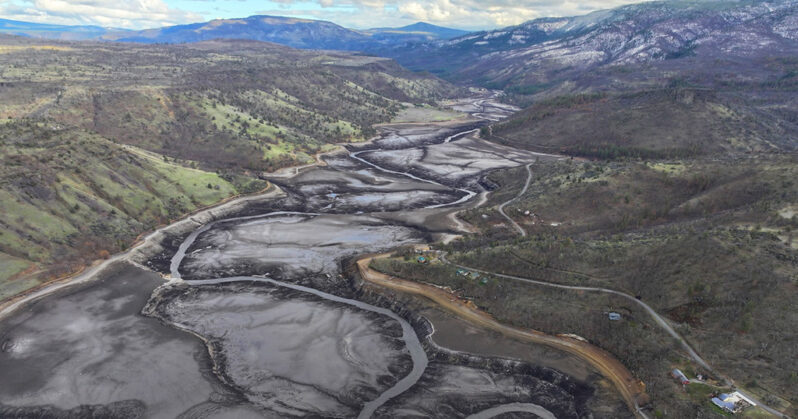

More than a century has passed since members of the Shasta Indian Nation saw the last piece of their ancestral home — a landscape along the Klamath River where villages once stood — flooded by a massive hydroelectric project.
Now more than 2,800 acres of land that encompassed the settlement, known as Kikacéki, will be returned to the tribe. The reclamation is part of the largest river restoration effort in U.S. history, the removal of four dams and reservoirs that had cut off the tribe from the spiritual center of their world…
Michael Hiltzik : Exxon Mobil is suing its shareholders to silence them about global warming – the Los Angeles Times

You wouldn’t think that Exxon Mobil has to worry much about being harried by a couple of shareholder groups owning a few thousand dollars worth of shares between them — not with its $529-billion market value and its stature as the world’s biggest oil company. But then you might not have factored in the company’s stature as the world’s biggest corporate bully…
Scientists warn that a crucial ocean current could collapse, altering global weather – the Los Angeles Times
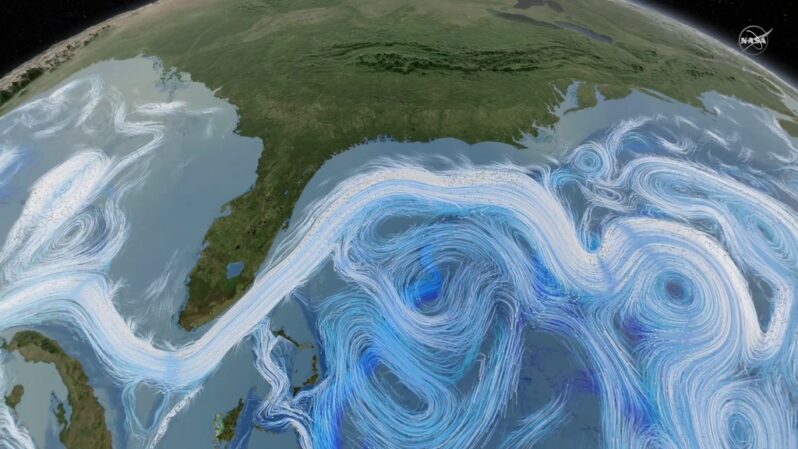
Scientists warn that a crucial ocean current could collapse, altering global weather…The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or AMOC, is a system of ocean currents that circulate water in the Atlantic Ocean like a conveyor belt, helping to redistribute heat and regulate global and regional climates. New research, however, warns that the AMOC is weakening under a warming climate, and could potentially suffer a dangerous and abrupt collapse with worldwide consequences…
It’s not just toxic chemicals. Radioactive waste was also dumped off Los Angeles coast – the Los Angeles Times

For decades, a graveyard of corroding barrels has littered the seafloor just off the coast of Los Angeles. It was out of sight, out of mind — a not-so-secret secret that haunted the marine environment until a team of researchers came across them with an advanced underwater camera…Startling amounts of DDT near the barrels pointed to a little-known history of toxic pollution…but federal regulators recently determined that the manufacturer had not bothered with barrels. (Its acid waste was poured straight into the ocean instead.)…
California’s war on plastic bag use seems to have backfired. Lawmakers are trying again – the Los Angeles Times
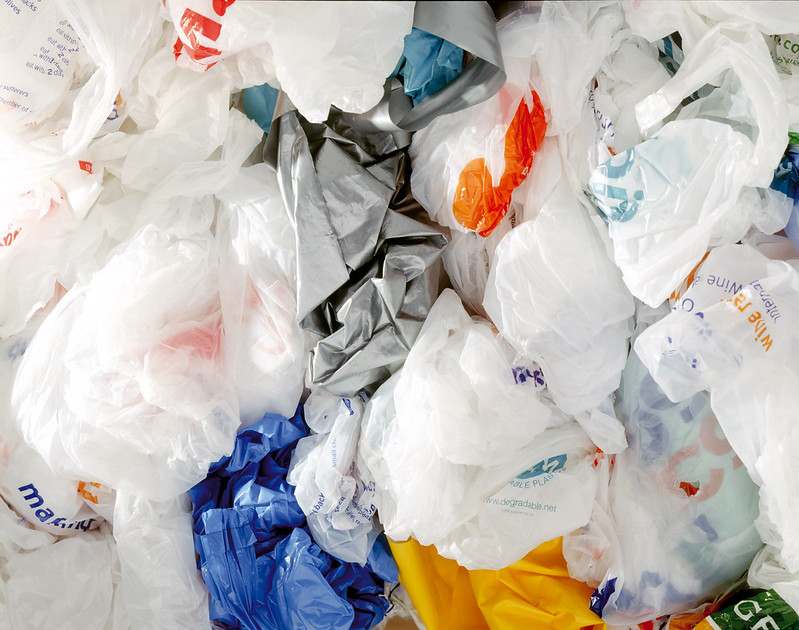

According to a report by the consumer advocacy group CALPIRG, 157,385 tons of plastic bag waste was discarded in California the year the law was passed. By 2022, however, the tonnage of discarded plastic bags had skyrocketed to 231,072 — a 47% jump…The problem, it turns out, was a section of the law that allowed grocery stores and large retailers to provide thicker, heavier-weight plastic bags to customers for the price of a dime….
In the face of sea level rise, can we reimagine California’s vanishing coastline? – the Los Angeles Times

Excerpted from “California Against the Sea: Visions for Our Vanishing Coastline” (available Sept. 26, 2023) by Rosanna Xia. Reprinted in the Los Angeles Times with permission from Heyday Books, © 2023.
How does sea level rise challenge modern notions of property lines? – Los Angeles Times

The (California) Coastal Act is a remarkable commitment to the public trust doctrine, which traces back to Justinian I, who declared in 533 C.E. that “the following things are natural law common to all: the air, running water, the sea, and consequently the seashore.” This notion — that certain lands should be held in trust by the government for the benefit of all people — evolved into English common law, which the United States then adopted and California later wrote into its state constitution…
Volcano? Climate change? Bad luck? – the Los Angeles Times
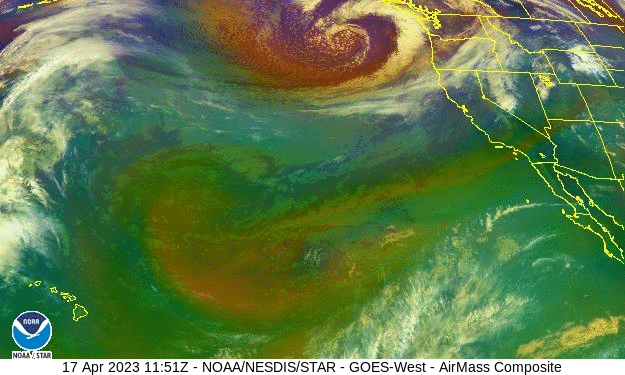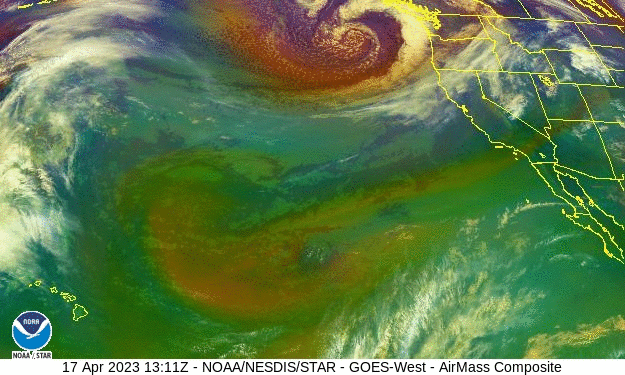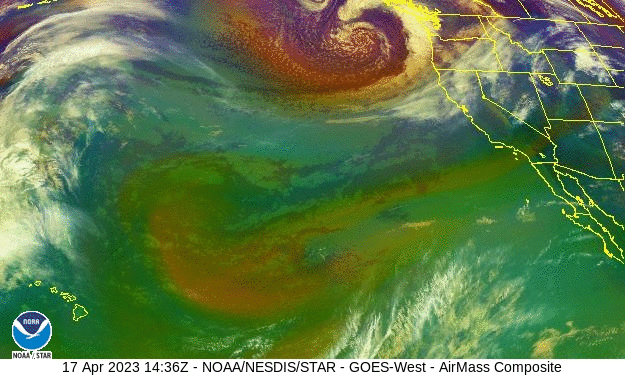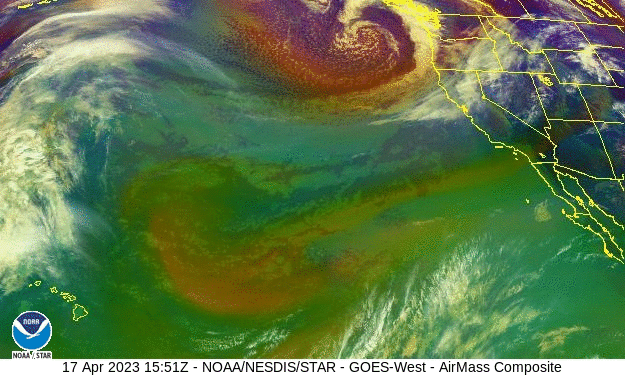
As winter approached, few anticipated what was about to hit California. Mired in a serious drought, the state was suddenly battered by an onslaught of 31 atmospheric river storms in a matter of months. While the number alone isn’t exceptional, the location, intensity and duration of these storms had a transforming effect on California’s climate. Record snowfall. Deadly flooding…But one thing remains a mystery: Why did so many of these bands of water vapor, many back-to-back, slam into California?
