Reef stars’ restored Indonesia’s blast-damaged corals in just 4 years – Grist Magazine
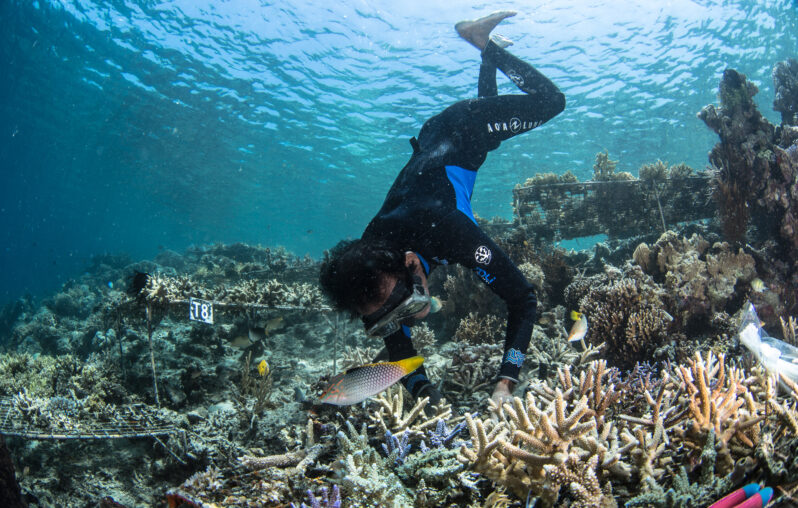

A community-based approach to restoration combined with an ingenious device can bring back reefs traumatized by dynamite fishing…
Why Is the Sea So Hot? – the New Yorker

A startling rise in sea-surface temperatures suggests that we may not understand how fast the climate is changing…
Hurricanes are intensifying more rapidly – and the most vulnerable communities are hit hardest – the Guardian
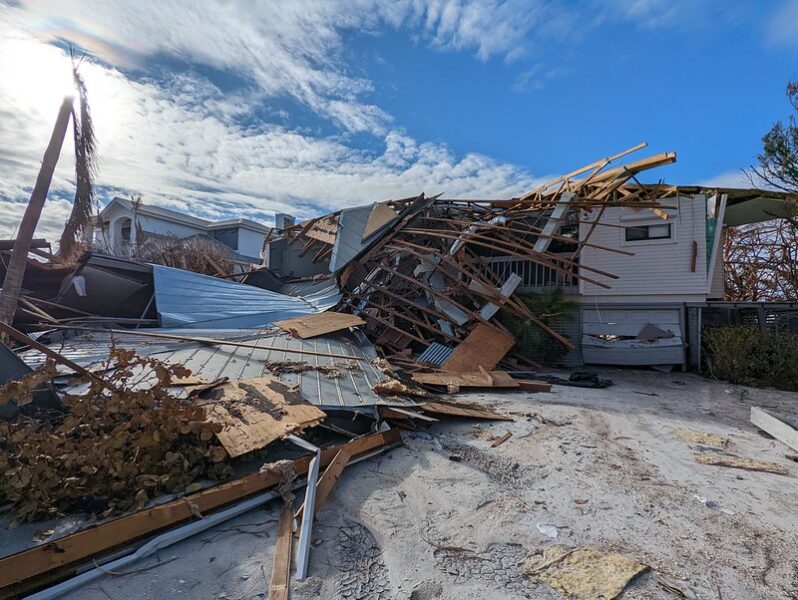

Hurricanes are more frequently escalating quickly, and the places they destroy may be those disadvantaged by racist housing policy…
The Oceans We Knew Are Already Gone – the Atlantic

As far as humanity is concerned, the transformation of our seas is “effectively permanent.”
Scientists warn that a crucial ocean current could collapse, altering global weather – the Los Angeles Times
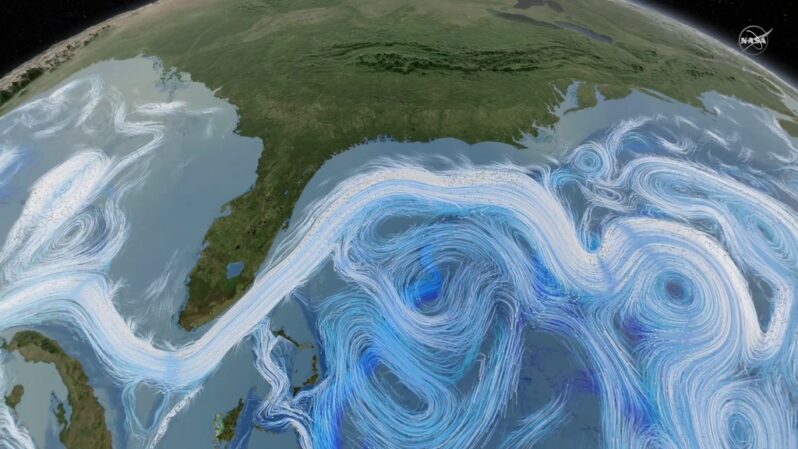
Scientists warn that a crucial ocean current could collapse, altering global weather…The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, or AMOC, is a system of ocean currents that circulate water in the Atlantic Ocean like a conveyor belt, helping to redistribute heat and regulate global and regional climates. New research, however, warns that the AMOC is weakening under a warming climate, and could potentially suffer a dangerous and abrupt collapse with worldwide consequences…
Atmospheric river storms are getting stronger, and deadlier. The race to understand them is on – the Guardian
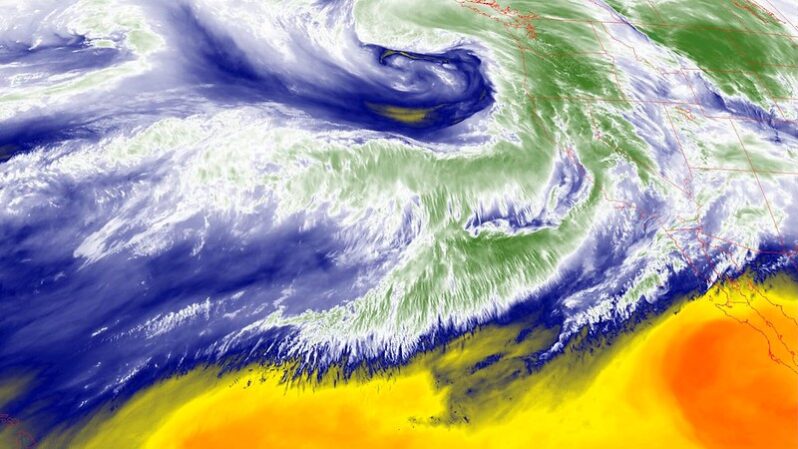

As the climate crisis supercharges storms over the Pacific, scientists are creating tools that can measure them from the inside..
Weaving the Harbor Back to Life – Hakai Magazine
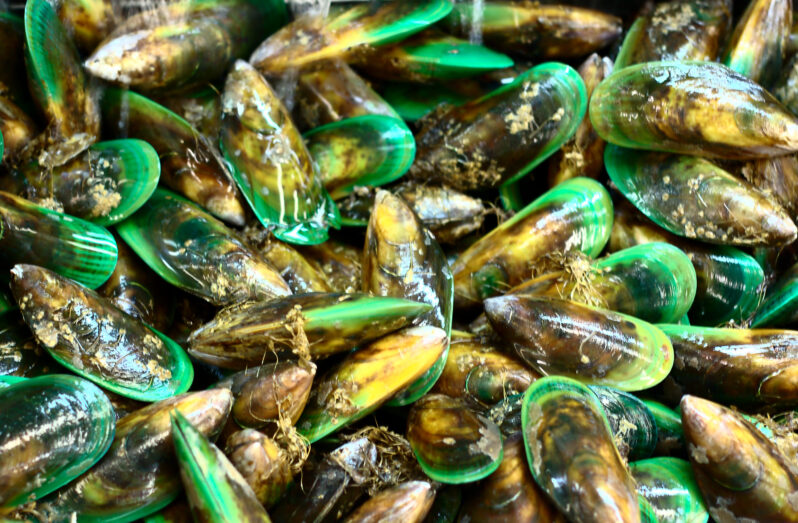

How Māori knowledge is helping to revive the mussel population in New Zealand’s Ōhiwa Harbour…
Ancient Warning of a Rising Sea | Interactive – the Washington Post

By studying the long-dead coral reefs, researchers have revealed not only how high sea levels can reach, but where the deluge will hit hardest. As temperatures surge and ice sheets melt, the fossils show, the oceans won’t rise evenly around the planet. Instead, the loss of polar ice will trigger profound changes in Earth’s gravity and shape — which, in turn, will create dramatic disparities in where ocean water flows…
Melting Ice Shelves
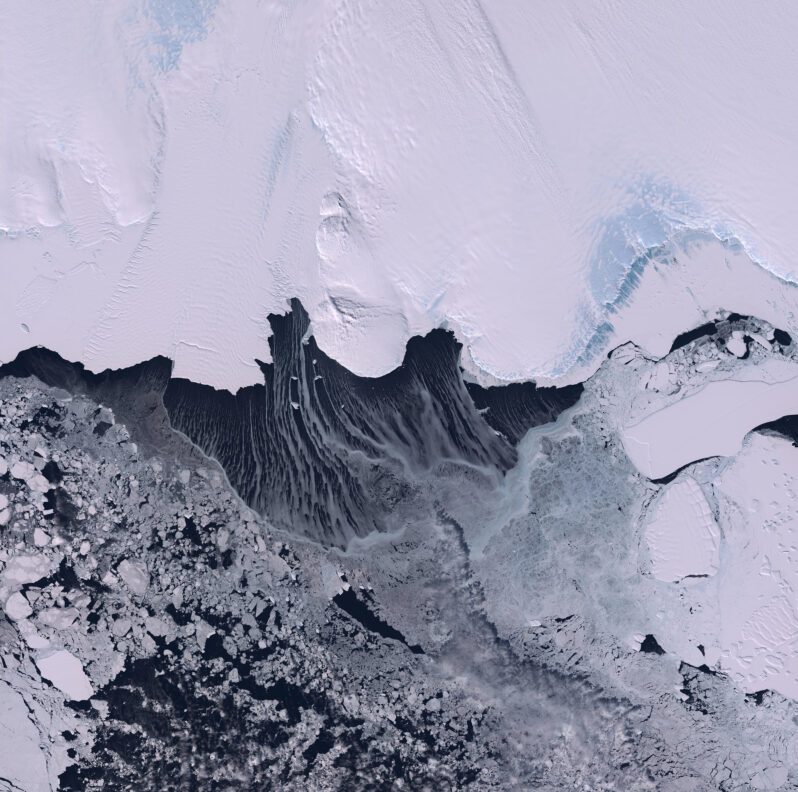

“Together, the Antarctic and Greenland Ice Sheets contain more than 99 percent of freshwater ice on Earth. If they both completely melted, they would raise sea level by an estimated 67.4 meters (223 feet). Long-term satellite data indicate that through most of the twentieth century, the ice sheets made very little contribution to sea level, and were nearly in balance in annual snowfall gain and ice or meltwater loss. However, the stability of the ice sheets has changed considerably in the twenty-first century…” – Ice Sheets Today
