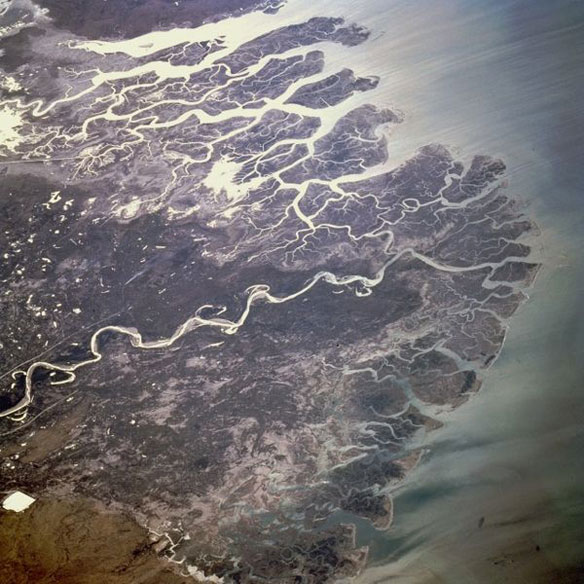
The Indus River Delta forms where the Indus River flows into the Arabian Sea in Pakistan.
The delta covers an area of about 41,440 km² (16,000 square miles), and is approximately 210 km across where it meets the sea, and is a large mangrove ecoregion on the Arabian Sea coast. However, since the 1940s, the delta has received less water as a result of large scale irrigation works capturing large amounts of the Indus water before it reaches the delta. Pollution from the industrial city and port of Karachi is a threat to habitats in the delta, as is depletion of the Indus as water is extracted. Most of the Indus delta mangroves have been cleared for firewood and to create grazing land.The result has been catastrophic for both the environment and the local population. Captions: Wikipedia. Photo source: NASA
By IRIN,
On a theoretical level, climate change and sea intrusion are not things Din Muhammad Chandio, a fisherman and farmer, understands much about.
But practically-speaking Chandio has seen them push him deeper into poverty in the town of Keti Bunder in Thatta District on the coast of Pakistan’s Sindh Province.
“I earned a living mainly through fishing, and some farming. Now both are impossible because our lands have become barren due to seawater flowing in. The lack of fresh water flowing down the [Indus] river also means fishing is affected.”
These trends are being studied by the World Wide Fund for Nature Pakistan (WWF-P) which is in the middle of a five-year project to build climate change resistance on Pakistan’s coastline, where communities are vulnerable to cyclones, rising sea levels and storm surges.
According to their baseline study, published last year, encroaching seas are leaving farmland increasingly saline and water-logged, and leading to a decline in fresh water fish stocks.
In one of the villages studied, Kharo Chan, the report’s authors found 45 percent of income declines were a result of the environmental degradation of fisheries, and 65 percent due to the environmental degradation of agricultural land.
The River Indus, which is Pakistan’s longest and runs the length of the country, has seen its flow reduced in recent years by the creation of hydroelectric dams upstream, retreating Himalayan glaciers and poor water management.
In Keti Bunder 77 percent of household heads surveyed in the study depend exclusively on fishing for their livelihood, making them vulnerable to changes in catch sizes.
Chandio said his monthly income had dropped by a third to around US$120 in the past three years, and feeding his family of eight has become increasingly difficult. Seeing the way things were going, his two adult sons recently left to try and find work in Karachi.
“Because of sea erosion, people in areas such as Badin District, Thatta District and so on, have lost homes because the sea has literally taken them away,” Ayub Khaskheli, information secretary of Karachi-based NGO Pakistan Fisher-folks Forum, told IRIN.
” Tahir Qureshi, senior adviser (coastal) for the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) in Karachi, blamed the construction of dams and barrages on the Indus for the sea’s intrusion into the Indus Delta. ”
IRIN
He said that due to the loss of their homes, people were desperate and had in some cases been forced to move further inland or leave coastal areas altogether.
“Crops such as potatoes and vegetables grown by women and used to feed families cannot be cultivated any longer. They simply do not grow in the now barren soil.”
Khaskheli said the fact that seawater had entered drinking water supplies obtained through wells and hand pumps had “also caused many problems for people in these communities”.
Despondency
Environmental journalist Afia Salam told IRIN climate variability had created a “striking despondency among people”.
“The town of Keti Bunder has been relocated three times, having to move inwards because of the encroachment of the sea. The able-bodied young men have left looking for livelihoods elsewhere as agriculture is no more, and marine catch has been severely reduced.”
This sense of despondency exists too in other areas of Thatta, such as Kharo Chan, a `taluka’ (administrative unit) where Shamshad Bibi, the mother of four young children, lives in her village.
“The 10 acres or so of land we had is mainly destroyed. Nothing grows on it because of the salt water. Now we just keep a small herd of goats and my husband tries to fish when he can. There is no future here for my children,” she told IRIN.
Tahir Qureshi, senior adviser (coastal) for the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) in Karachi, blamed the construction of dams and barrages on the Indus for the sea’s intrusion into the Indus Delta.
“So far no scientific work has been done by the academia or national research institutions on sea level rise in order to investigate its contribution to this ecological disaster along the coast of Sindh. Mangroves are the soil binder and are the first defence line against all natural disasters,” he said.
The IUCN has, with other groups, promoted mangrove cultivation to hold back erosion. Mangrove cover along the 350km Sindh coastline is 200,000 hectares, sharply down, according to environmentalists.
“Loss of land will destroy us”
WWF-P says it is working to build both disaster preparedness in coastal communities and help farming and fishing to adapt.
“Communities react through coping measures, e.g. moving inland, or through reactive adaption when they respond to a new situation as it arises. We are trying to promote planned adaption to the change,” said WWF-P’s Bajwa. Modes of adaptation being considered for promotion include changing planting periods and the types of crops farmers grow.
Certainly, people living in coastal areas are desperate to see change come their way.
“The continued loss of land will destroy us. The barley my father and grandfather planted simply does not grow here any longer,” said Hussain Ahmed from his village in Thatta.
“Even fodder for livestock is hard to grow, and the shrimp we used to take to markets in huge baskets have shrunk drastically in number.”
He said that, as a direct result, “there is less food to place on the family table, less money to educate my children and nothing at all for health care. The sea, which once helped us by providing fish, has turned against us and is taking over our lands.”
Original Article, “Pakistan’s coast – where the sea is an enemy not a friend,”IRIN
Miracle at Keti Bunder, Pakistan, by Khan, Rina Saeed (2009-07-10)
The villagers were fast asleep when the sea-water suddenly rose up and a high tide silently flooded their homes. These people are amongst the poorest of the poor in Pakistan, living in wooden shacks on the mud flats of the fan-shaped Indus Delta. They are completely dependent upon fishing for their survival, and this is where the Indus River meets the Arabian Sea. “It was sudden and completely unexpected. No doubt it was because of the global climate change and the lack of fresh water in the delta,” explained Zahid Jalbani, who is the Site Manager for the Indus for All Programme, and is currently mobilizing the local community to take charge of their natural resources…