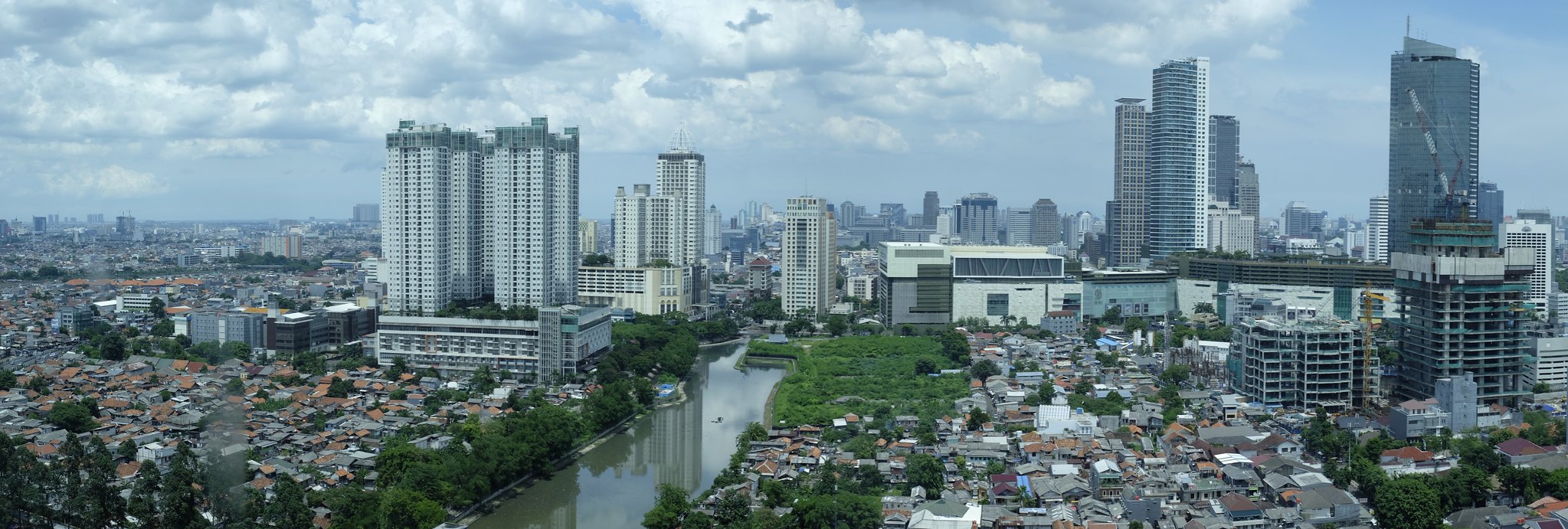
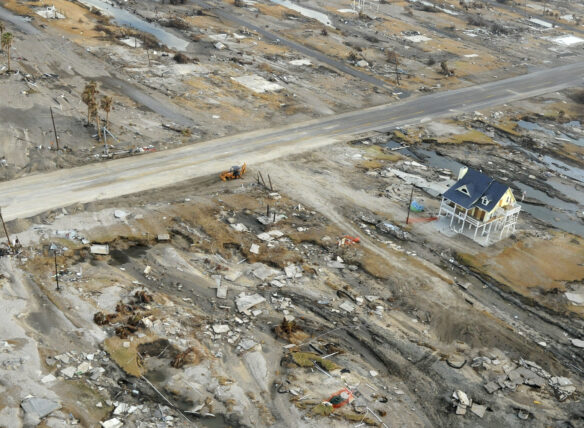
Venice is sinking. So are Rotterdam, Bangkok and New York. But no place compares to Jakarta, the fastest-sinking megacity on the planet. Over the past 25 years, the hardest-hit areas of Indonesia’s capital have subsided more than 16 feet. The city has until 2030 to figure out a solution, experts say, or it will be too late to hold back the Java Sea.
Cue Anthoni Salim, the billionaire owner of PT Air Bersih Jakarta, the firm tapped by the government to expand piped water access to the city’s 11 million residents immediately, if not sooner. As of now, one in three Jakartans doesn’t have access to piped water, relying instead on the thousands of illegal wells that dot the city — and deplete the aquifers and weaken the ground, creating prime conditions for further sinking.
If Salim’s ABJ can help deliver on the plan to bring water to every Jakarta household, experts say the city has a chance — and the company will rake in billions of dollars. If it fails, it’s likely that chaos will reign in the world’s second-biggest metropolis. Unabated sinking, combined with intensifying storms and rising sea levels, will be more than Jakarta’s seawalls can withstand, said JanJaap Brinkman, a flood expert at Dutch water research institute Deltares: “There will be so much sea water rushing in, it will never stop. There will be no escape.”
For Salim, who didn’t respond to requests for comment for this story, it’s been a long time coming. He’s amassed more than $10 billion through a handful of industries, including one of the world’s biggest instant-noodle makers, but controlling the capital’s water supply has been a personal priority since a revolution almost dismantled his family’s conglomerate 25 years ago. When the government sought bids to revamp the city’s water infrastructure, Salim’s was one of two companies to raise its hand.
ABJ’s new contract includes rights to operate the city’s five biggest water treatment plants, and to sell more than half of its treated water supply through 2048. It’ll also build a new plant and pipelines, doubling the number of connections by the end of this decade. There’s no real downside for ABJ: the company stands to net around $4.8 billion in revenue from the deal, according to Lafrik Bano Rangkuty, president director at ABJ. Even in the worst-case scenario, ABJ won’t lose money, says Simon Melhem, a director at parent company Moya Holdings Asia Ltd, which is owned by Salim. “You just don’t make decent returns.”
Jakarta, however, would be doomed…