In the face of sea level rise, can we reimagine California’s vanishing coastline? – the Los Angeles Times
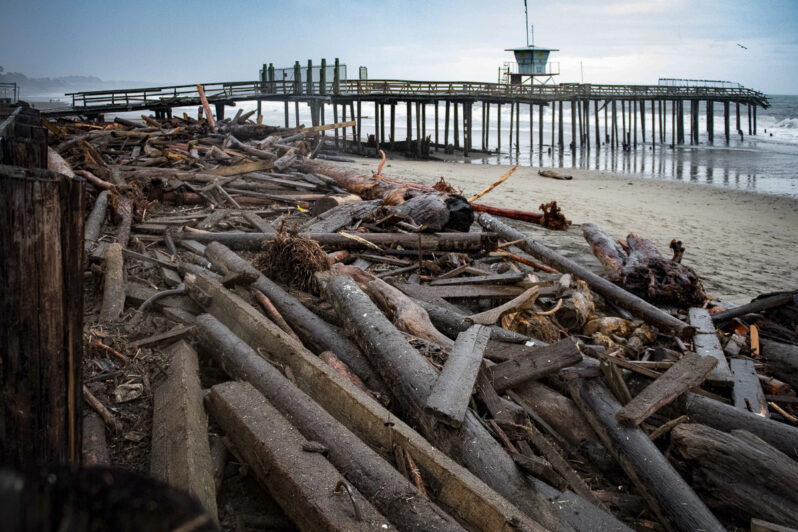

Excerpted from “California Against the Sea: Visions for Our Vanishing Coastline” (available Sept. 26, 2023) by Rosanna Xia. Reprinted in the Los Angeles Times with permission from Heyday Books, © 2023.
Hurricane Idalia’s Explosive Power Comes from Abnormally Hot Oceans – the New Yorker

Of all the astonishing facts about our blithe remaking of the world’s climate system, the most astonishing might be this: if oceans didn’t cover seventy per cent of our planet, we would have increased the average temperature to about a hundred and twenty-two degrees Fahrenheit. That’s because those oceans have absorbed something like ninety-three per cent of the extra heat trapped by the greenhouse effect and our burning of fossil fuels…
DeSantis’s Florida Approves Climate-Denial Videos in Schools – Scientific American

Florida’s Department of Education has approved classroom use of videos that spout climate disinformation and distort climate science
Climate activists are like Nazis.
Wind and solar power pollute the Earth and make life miserable.
Recent global and local heat records reflect natural temperature cycles.
These are some of the themes of children’s videos produced by an influential conservative advocacy group…
Is this ‘age of the delta’ coming to an end? – Knowable Magazine
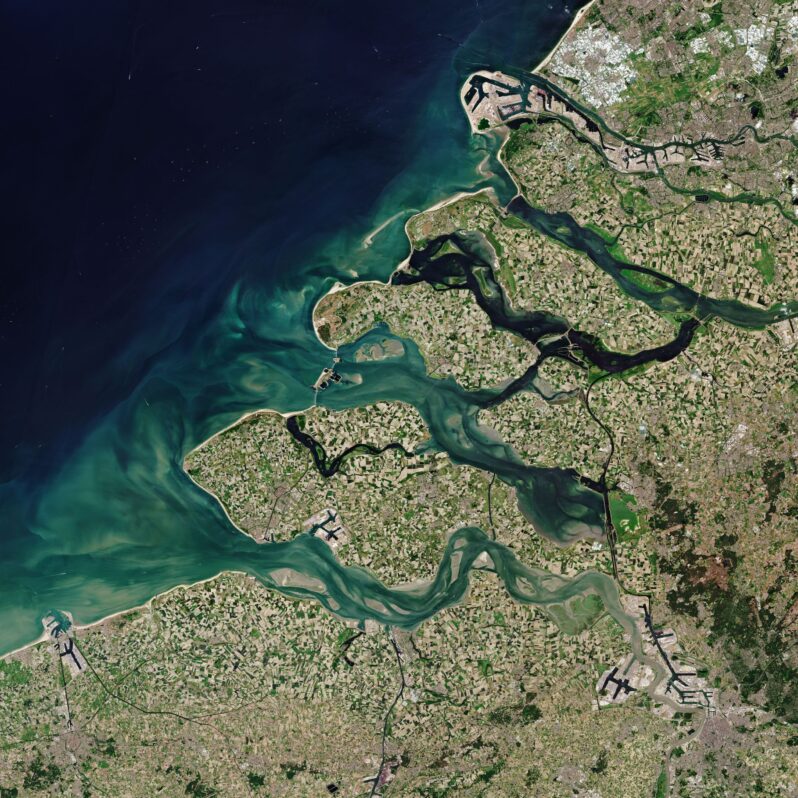

The land near the mouth of the Mississippi River is barely land at all. Muddy water forks into a labyrinth of pathways through a seemingly endless expanse of electric-green marsh grass, below skies thick with birds. Shrimp and crabs wriggle in the water below, and oak and cypress sprout from wet soils on higher grounds. Stretching for more than a hundred miles along the coast of Louisiana, this is one of the world’s largest, and most famous, river deltas…
Before the flood: how much longer will the Thames Barrier protect London? – the Guardian
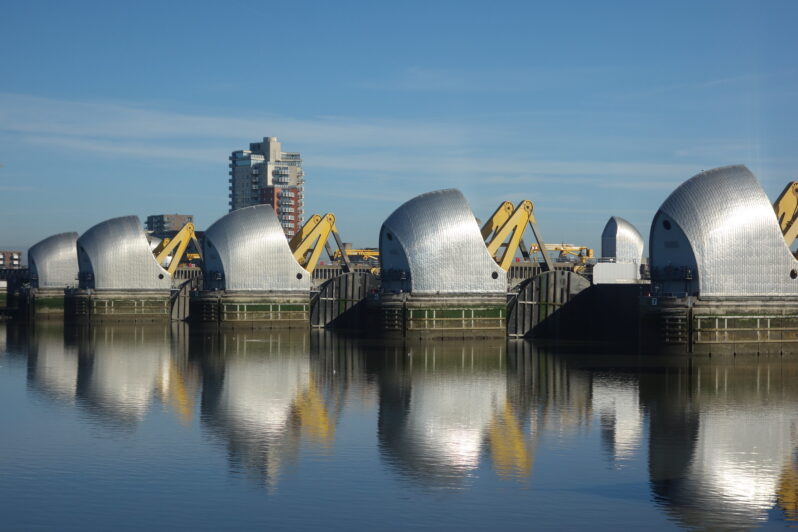

The last time the Thames broke its banks and flooded central London was on 7 January 1928, when a storm sent record water levels up the tidal river, from Greenwich and Woolwich in the east as far as Hammersmith in the west. Built on flood plains, the capital was defended only by embankments. The flood waters burst over them into Whitehall and Westminster, and rushed through crowded slums. Fourteen died and thousands were left homeless…
At last, Venice’s authorities admit the risk from sea-level rise – The Art Newspaper
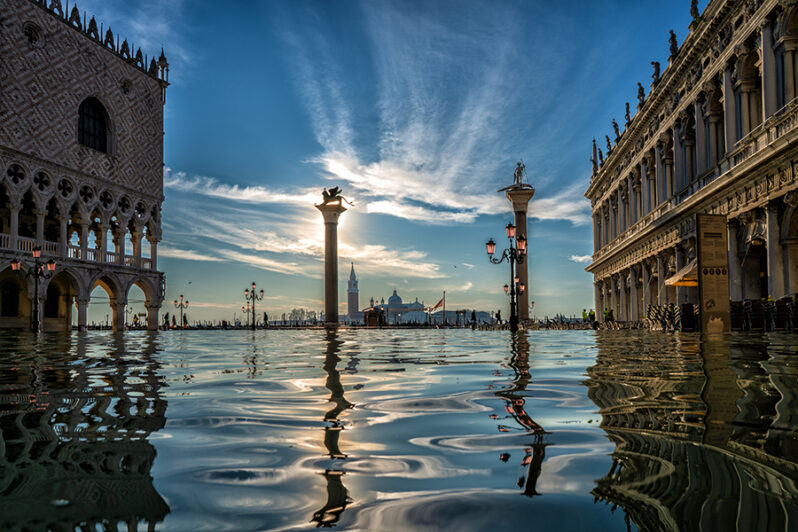

At a conference organised by the new Venice Sustainability Foundation in June, major public figures agreed for the first time that sea-level rise is the main problem facing the city now…
Coastal Flooding Will Be More Extensive Sooner than Scientists Thought – Hakai Magazine
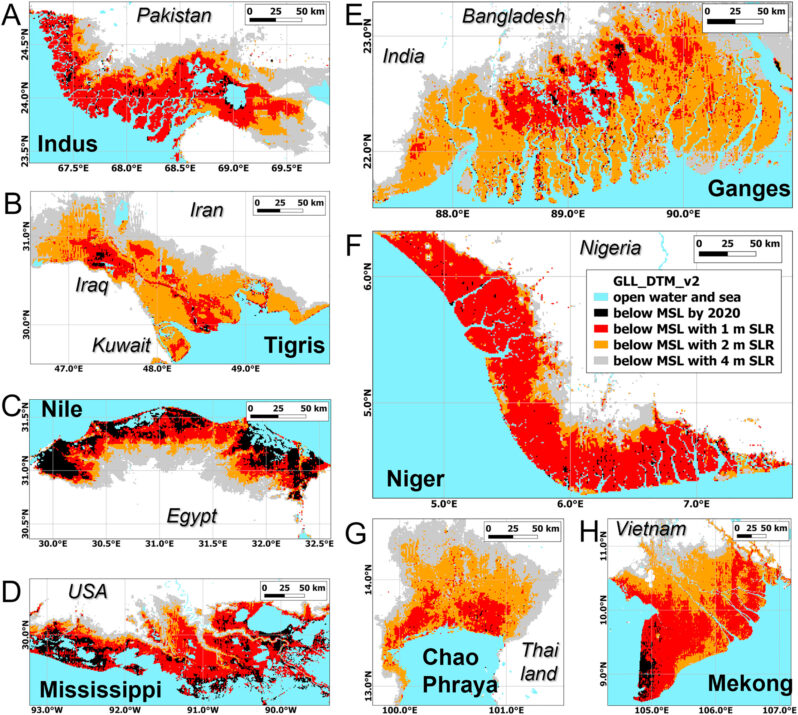
Updated, more accurate data gives a new look at the effects of sea level rise.
Around the world, communities are bracing for sea level rise: the Netherlands is stabilizing its dikes, Senegal is relocating neighborhoods, Indonesia is moving its entire capital city. These projects are hefty, expensive, and slow…
Every Coastal Home Is Now a Stick of Dynamite – the Atlantic
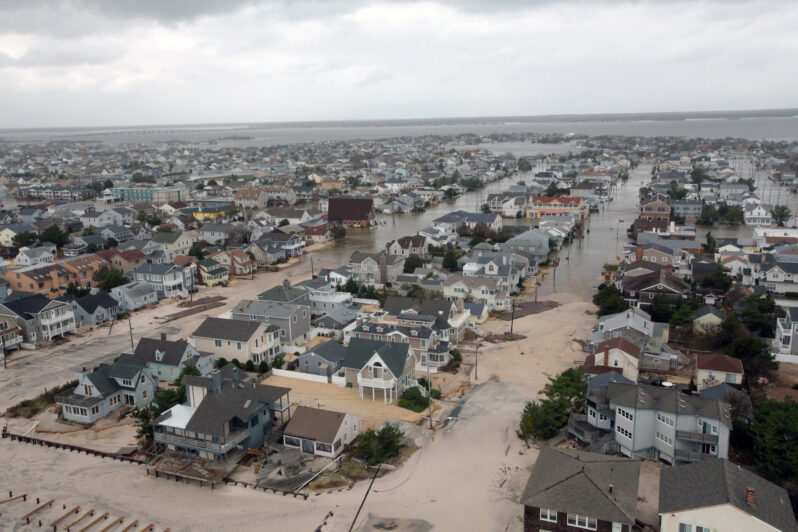

Wealthy homeowners will escape flooding. The middle class can’t.
The Langfords got out of Houston just in time. Only two months after Sara and her husband, Phillip, moved to Norfolk, Virginia, in June 2017, Hurricane Harvey struck, destroying their previous house and rendering Sara’s family homeless…
How does sea level rise challenge modern notions of property lines? – Los Angeles Times
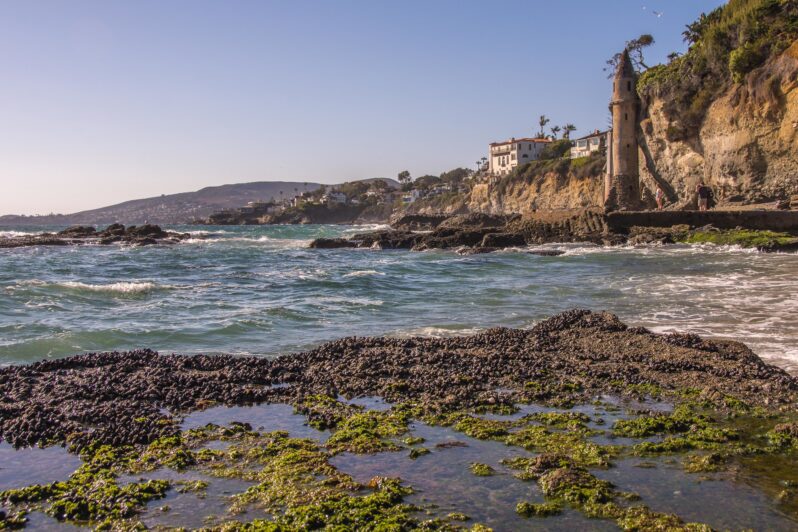

The (California) Coastal Act is a remarkable commitment to the public trust doctrine, which traces back to Justinian I, who declared in 533 C.E. that “the following things are natural law common to all: the air, running water, the sea, and consequently the seashore.” This notion — that certain lands should be held in trust by the government for the benefit of all people — evolved into English common law, which the United States then adopted and California later wrote into its state constitution…
