Morro Bay, located 12 miles from controversial coastal Diablo Canyon nuclear plant, California. Photo source: ©© Mike Baird
Excerpts;
To say that Tuesday’s east coast magnitude 5.8 earthquake surprised everyone would be an understatement.
The earthquake rocked the East Coast and prompted two nuclear reactors near the Virginia epicenter to automatically switch to emergency power sources…
Read Full Article, Guardian UK
Quake Raises Safety Concerns, Reuters
Why We Build Nuclear Plants In Earthquake Zones ? By Cleo Paskal, In Huffington Post
Asian Nuclear Renaissance Taking Place On Seismically Charged Region, AP Article
Asia, the world’s most seismically charged region, is undergoing a nuclear renaissance as it struggles to harness enough power for its huge populations and booming economies. The skeleton of what will soon be one of the world’s biggest nuclear plants is slowly taking shape along China’s southeastern coast, right on the doorstep of Hong Kong’s bustling metropolis. Like Japan’s Dai-ichi plant they lie within a few hundred miles of the type of fault known to unleash the largest tsunami-spawning earthquakes.
Magnitude-5.8 Earthquake Strikes National Capital Area: USGS
By USGS
A magnitude 5.8 earthquake struck the National Capital Area on Tuesday, August 23, at 1:51p.m. (EDT), causing moderate shaking and potentially significant damage, and was felt throughout Northern Virginia and neighboring areas. No casualties are expected.
The earthquake occurred near Louisa and Mineral, Va., approximately 100 miles southwest of Washington, DC. It was a shallow earthquake, and shaking was recorded all along the Appalachians, from Georgia to New England.
There have been several aftershocks.
The information provided by the USGS is part of a government-wide response effort, in coordination with the Department of the Interior, the Department of Homeland Security, and the White House.
The earthquake occurred in the Central Virginia Seismic Zone, which has produced earthquakes in the past. The most notable was an earthquake that occurred in 1875 that scientists believe was about a magnitude 4.5.
This earthquake is almost as strong as the strongest recorded earthquake in Virginia, a magnitude 5.9, which occurred in May 1897 in Giles County, Va. The strongest recorded earthquake to strike the East Coast was the 1886 Charleston, S.C., earthquake, which was about a magnitude 7.3.
Over 10,000 reports of felt shaking have already been received from more than 3400 zip codes all over the eastern United States.
The earthquake was felt so widely because it was a shallow earthquake, and geologic conditions in the eastern U.S. allow the effects of earthquakes to propagate and spread much more efficiently than in the western United States.
Western rock is relatively young, which means it absorbs a lot of the shaking caused by earthquakes. Thus, western earthquakes result in intense shaking close to the epicenter, but fade more quickly the farther the earthquakes travel.
In the eastern United States, on the other hand, the rock is far older, and so earthquakes can have a much larger and more widespread impact. Earthquake energy can therefore spread farther and have a greater impact.
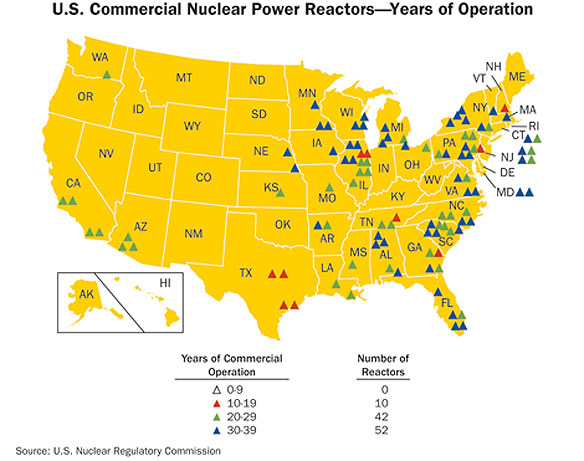
Map of USA Power Reactor Sites. Image source: US Nuclear Regulatory Commission









