Why Is the Sea So Hot? – the New Yorker

A startling rise in sea-surface temperatures suggests that we may not understand how fast the climate is changing…
A Massachusetts town spent $600K on shore protection. A winter storm washed it away days later – the Washington Post
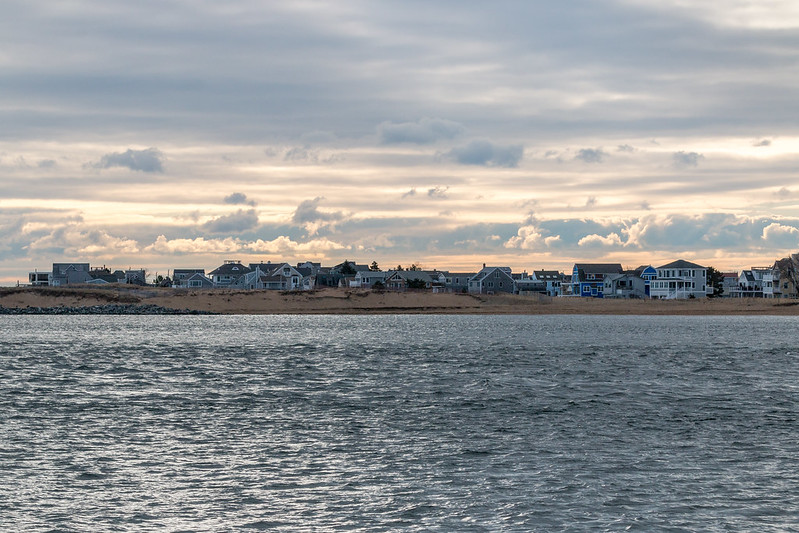

A Massachusetts beach community is scrambling after a weekend storm washed away $600,000 in sand that was trucked in to protect homes, roads and other infrastructure…
Why Oak Island is looking 18 miles off its coast for sand to nourish its eroded beach – Wilmington StarNews Online
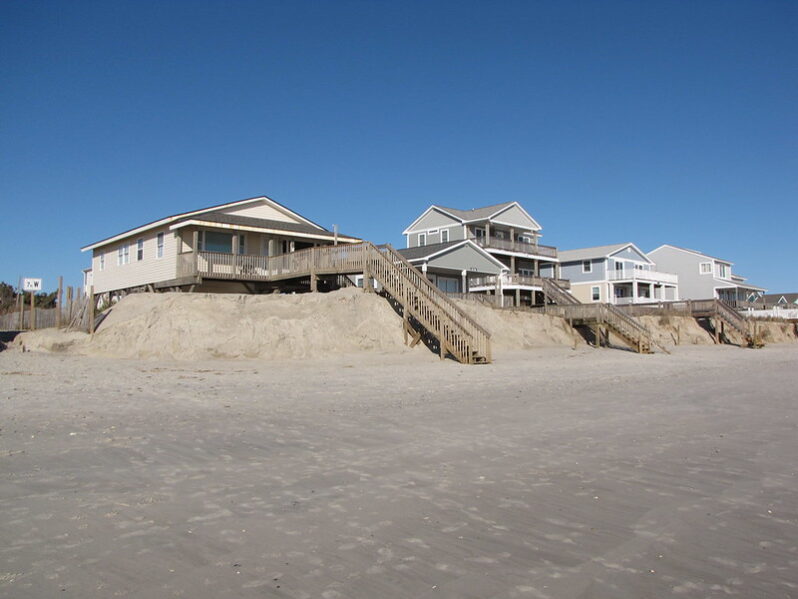

Faced with an eroding beach, Oak Island wants to pump fresh sand onto its oceanfront. But finding a viable sand source might mean going a long way offshore…
The Oceans We Knew Are Already Gone – the Atlantic

As far as humanity is concerned, the transformation of our seas is “effectively permanent.”
Decades after the US buried nuclear waste abroad, climate change could unearth it – Grist Magazine
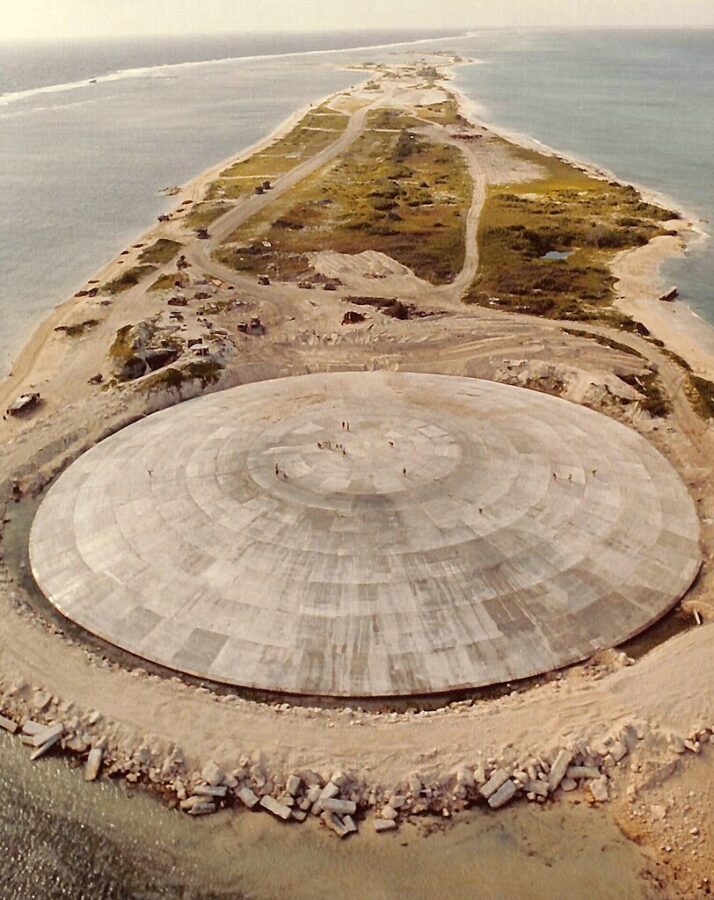

A new report says melting ice sheets and rising seas could disturb waste from U.S. nuclear projects in Greenland and the Marshall Islands…The report summarizes disagreements between Marshall Islands officials and the U.S. Department of Energy regarding the risks posed by U.S. nuclear waste. The GAO recommends that the agency adopt a communications strategy for conveying information about the potential for pollution to the Marshallese people.
The East Coast Is Sinking | Interactive – the New York Times
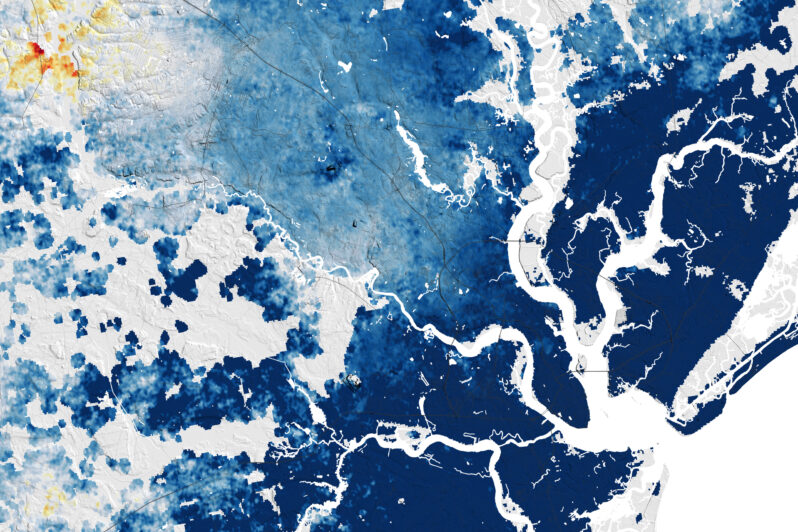
New satellite-based research reveals how land along the coast is slumping into the ocean, compounding the danger from global sea level rise.
A major culprit: overpumping of groundwater.
A ‘collapse’ is looming for Louisiana’s coastal wetlands, scientists say – the Washington Post
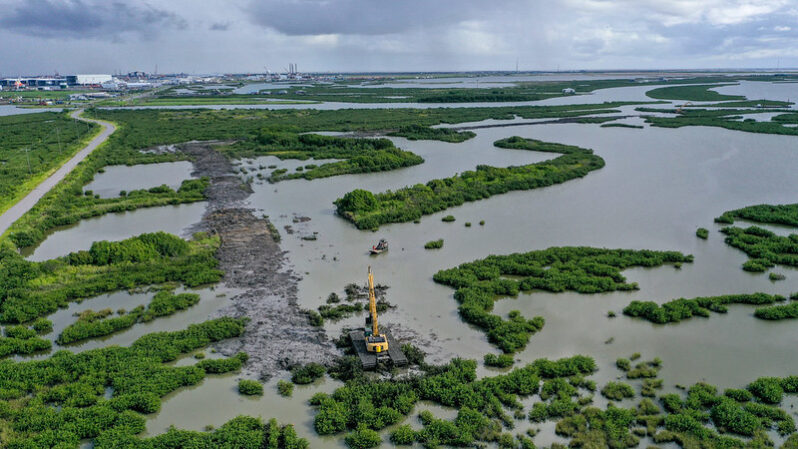

Scientists say the overwhelming majority of the state’s wetlands — a natural buffer against hurricanes — are in a state of ‘drowning’ and could be gone by 2070…
2022 Six Part Series on “Sand Dealers” – Le Monde
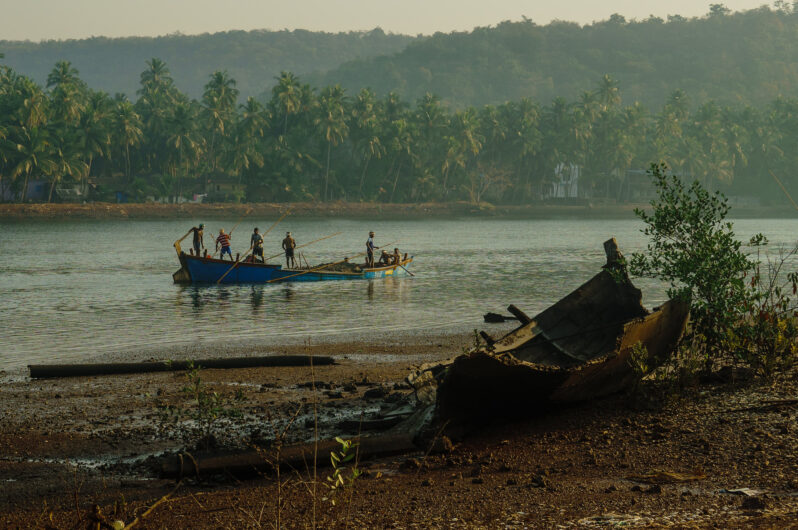

Published in 2022, links to Le Monde’s Series on Sand are provided here…
Can the ‘sand motor’ save West Africa’s eroding coast? – Grist Magazine
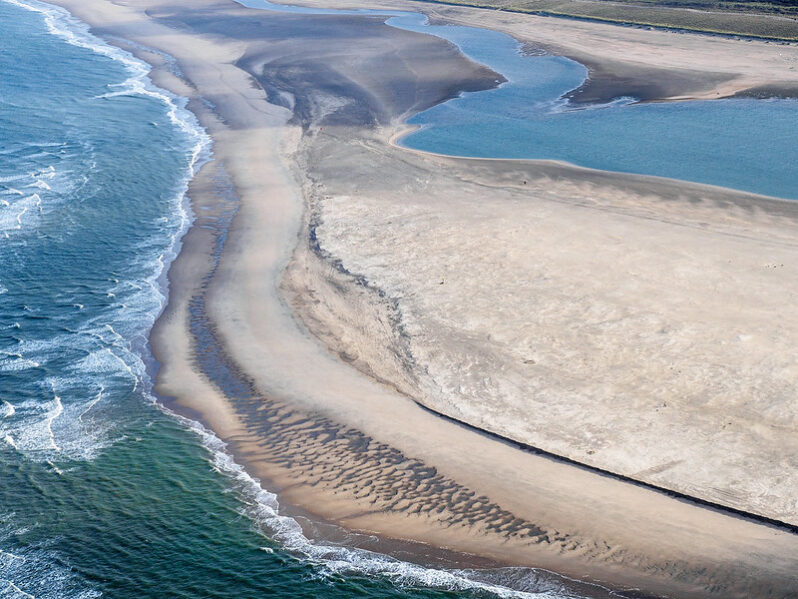

As sea levels rise, engineers are using massive Dutch-inspired sand sculptures to protect shorefront settlements…It’s called the “sand motor,” and it comes from the Netherlands, a low-lying nation with centuries of experience in coastal protection…
