Earth Just Had the Hottest 12-Month Span in Recorded History – Scientific American
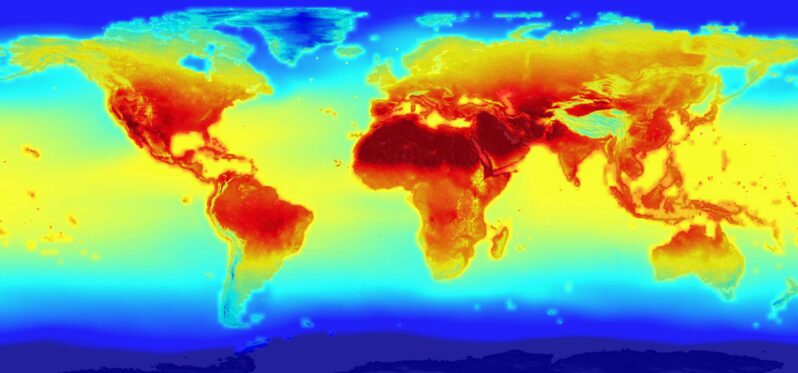
As this past October came to a close, it marked the hottest 12-month period ever recorded, a new analysis finds. This stark milestone is the latest in a string of superlatives to emerge this year that show how much carbon pollution has warmed the planet—and how that trend is accelerating. It also comes just weeks before international negotiators are set to meet and hash out issues around achieving the Paris climate accord’s fundamental goal: limiting global warming to no more than 1.5 degrees Celsius (2.7 degrees Fahrenheit) above preindustrial temperatures…
DeSantis’s Florida Approves Climate-Denial Videos in Schools – Scientific American

Florida’s Department of Education has approved classroom use of videos that spout climate disinformation and distort climate science
Climate activists are like Nazis.
Wind and solar power pollute the Earth and make life miserable.
Recent global and local heat records reflect natural temperature cycles.
These are some of the themes of children’s videos produced by an influential conservative advocacy group…
El Niño May Break a Record and Reshape Weather around the Globe – Scientific American
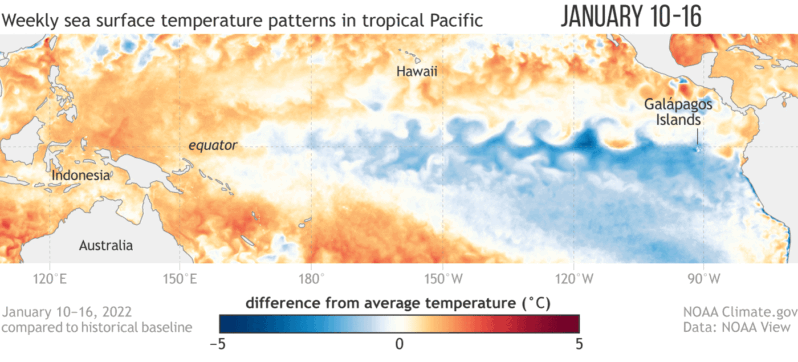
Seven years ago an exceptionally strong El Niño took hold in the Pacific Ocean, triggering a cascade of damaging changes to the world’s weather. Indonesia was plunged into a deep drought that fueled exceptional wildfires, while heavy rains inundated villages and farmers’ fields in parts of the Horn of Africa. The event also helped make 2016 the planet’s hottest year on record. Now El Niño is back…
Fossil-Fuel Interests Try to Weaken Global Plastics Treaty – Scientific American

An international effort to rein in plastic pollution is running into resistance from China, Saudi Arabia and other nations that see a future in plastics amid declining demand for oil, gas and coal. That debate is playing out over the terms of a prospective global treaty that could set limits on plastic production and consumption. Environmentalists last year scored a landmark victory when 175 countries agreed to write a treaty designed to address the problems with plastic…
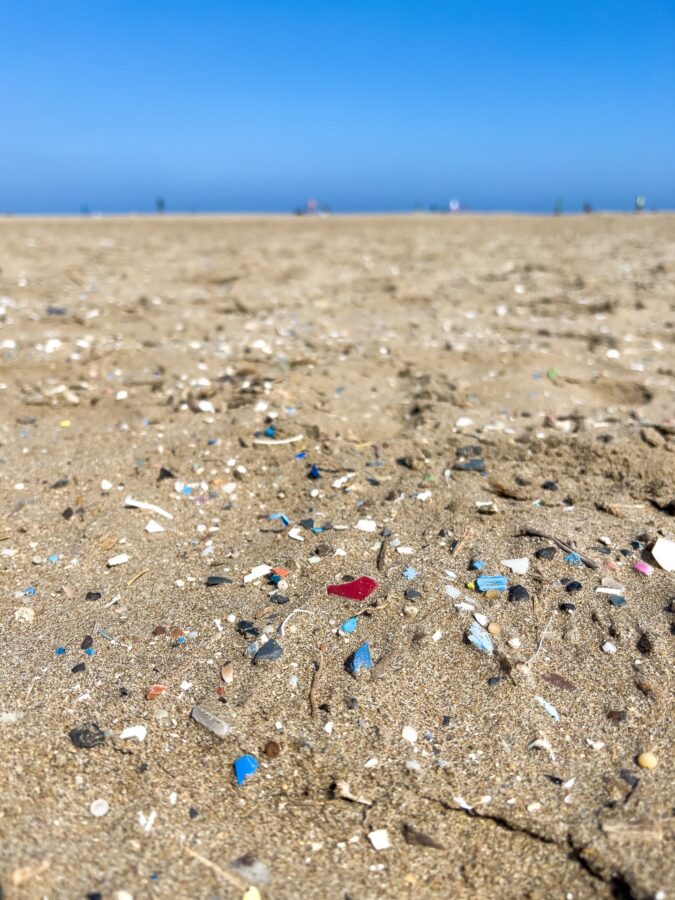
Surprising Creatures Lurk in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch – Scientific American

Scientists have long known that critters such as worms, crustaceans and mollusks could make their home on plastic debris. Animals have even crossed the Pacific Ocean on these makeshift rafts after a devastating tsunami struck Japan in 2011. But new research published on April 17 in the journal Nature Ecology & Evolution adds two details that could be concerning for existing ecosystems. First, it finds that plastic is providing a home for coastal species to thrive in the open ocean thousands of miles from shore. Second, some of these species are reproducing despite the alien environment…
Why California Is Being Deluged by Atmospheric Rivers – Scientific American
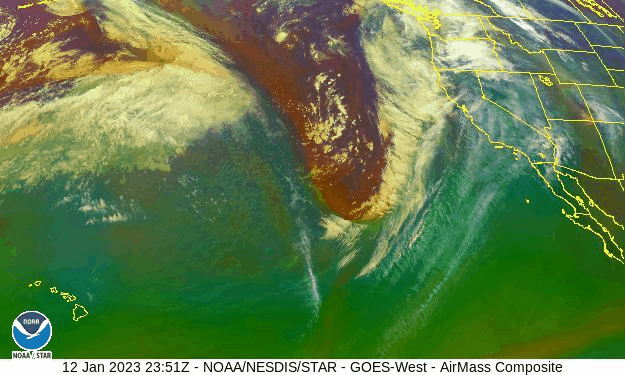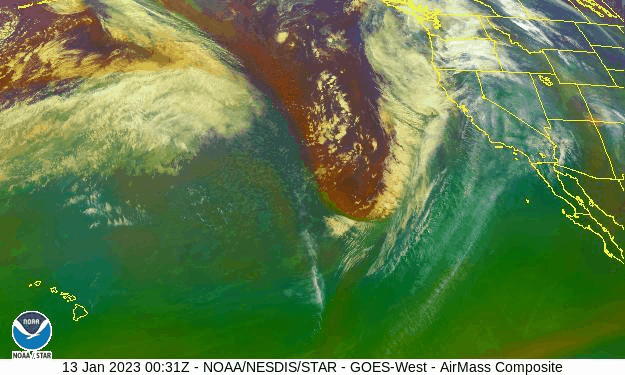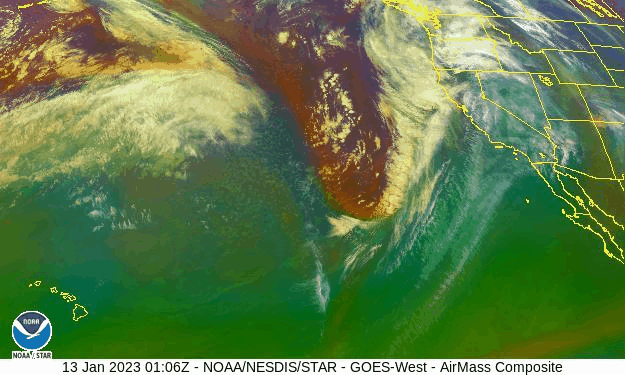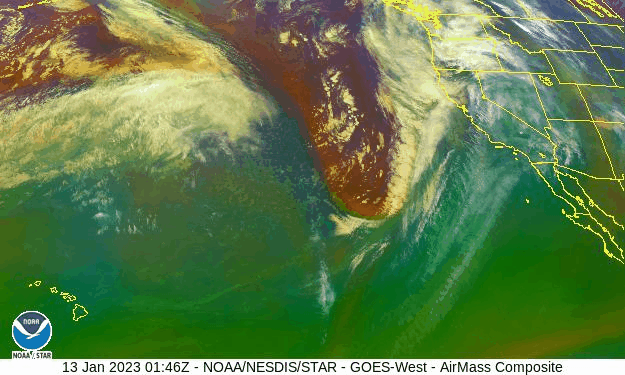
California has been hit by repeated storms fueled by torrents of moisture called atmospheric rivers that will only intensify in a warming climate
California is taking a beating from what the National Weather Service has called a “seemingly never ending parade” of strong storm systems, which started late last December and are still coming. Called atmospheric rivers, they are long, narrow currents of exceptionally wet air that shoot across the ocean, capable of dumping massive volumes of rain or snow on landfall. Although these storms deliver much of the West’s precipitation, they also cause most of the region’s flooding, with associated economic damages as high as $1 billion a year…
Why Recycling Isn’t the Answer to the Plastic Pollution Problem – Scientific American
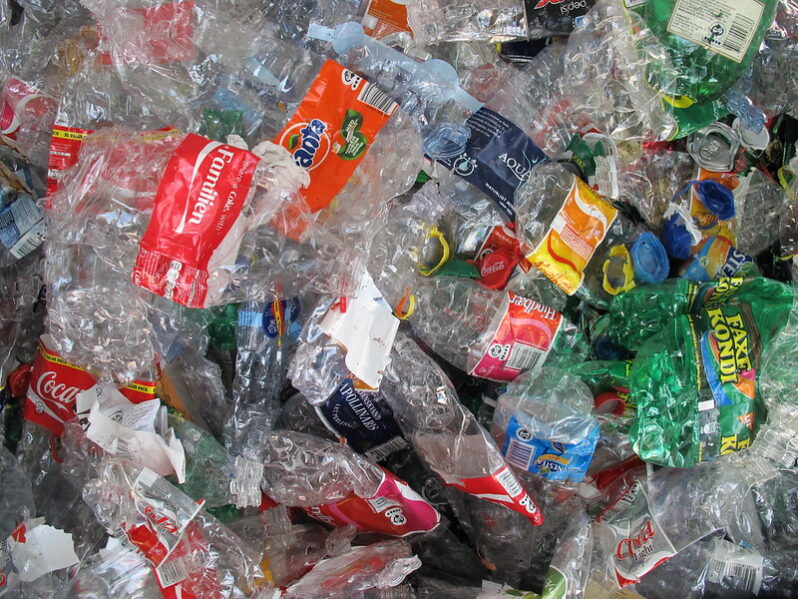

For many years, the transition to a circular plastic economy has been understood to require a combination of efforts… ‘reduce, reuse, recycle’. The principles are based on the top three levels of the waste hierarchy, whereby reducing is better than reusing, which is, in turn, more favourable than recycling. In practice, however…
