Two Studies on Greenland Reveal Ominous Signs for Sea Level Rise – the New York Times
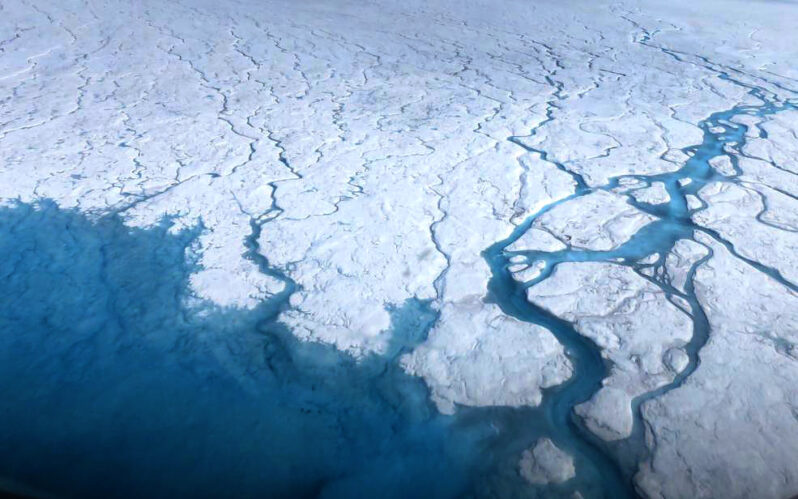

Greenland’s mountain glaciers and floating ice shelves are melting faster than they were just a few decades ago and becoming destabilized, according to two separate studies published this week. The island’s peripheral glaciers, located mostly in coastal mountains and not directly connected to the larger Greenland ice sheet, retreated twice as fast between 2000 and 2021 as they did before the turn of the century, according to a study published on Thursday. “It got a lot harder to be a glacier in Greenland in the 21st century than it had been even in the 1990s,” said Yarrow Axford, a professor of geological sciences at Northwestern University and a co-author of the paper, published in the journal Nature Climate Change…
What the Melting of Antarctic Ice Shelves Means for the Planet – Inside Climate News
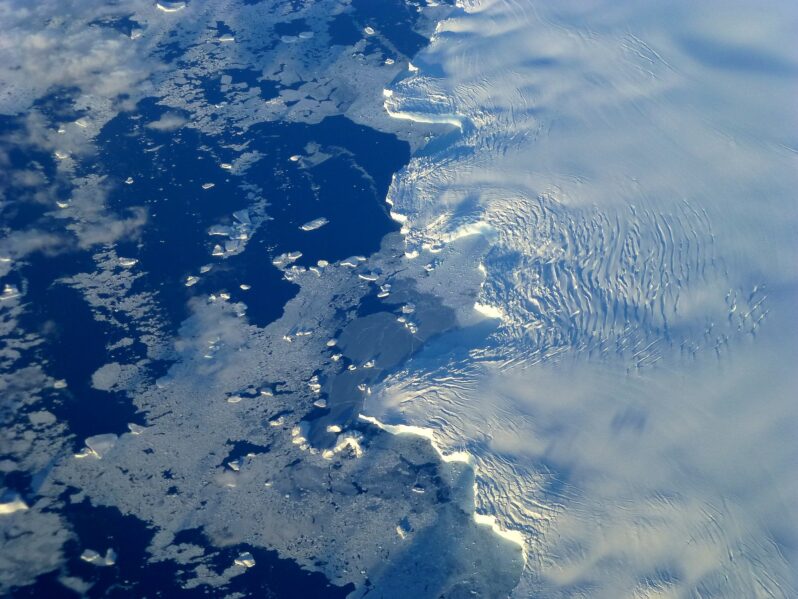

Antarctica’s ice shelves are the gatekeepers between the continent’s glaciers and the open ocean. As the planet warms, these shelves shrink, exposing more and more ice, which leads to more melting. This frozen continent rests under a massive ice sheet averaging more than a mile thick. But a recent study in Science Advances found that Antarctica had 68 ice shelves that shrunk significantly between 1997 and 2021, adding up to about 8.3 trillion tons lost during that time…
West Antarctic ice sheet faces ‘unavoidable’ melting, a warning for sea level rise – the Washington Post
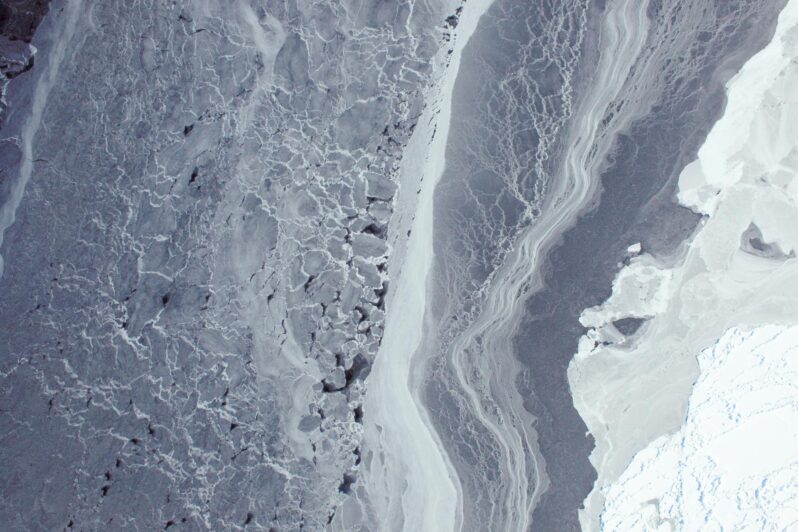

Accelerating ice losses are all but “unavoidable” this century in vulnerable West Antarctic ice shelves as waters warm around them, according to new research. And the analysis could mean scientists were too conservative in predicting about one to three feet of sea level rise by 2100…
Greenland’s ice shelves hold back sea level rise. There are just 5 left – the Washington Post
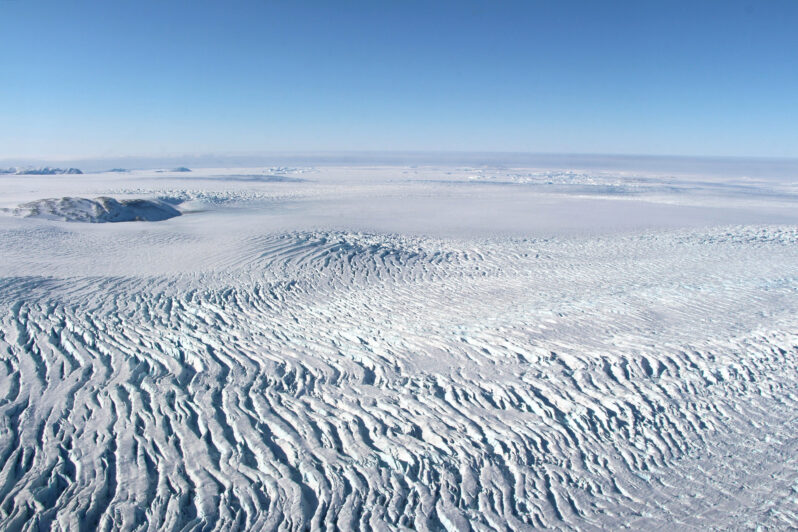

And now there are only five large shelves left, stretching out from their fjords toward the Greenland Sea and the Arctic Ocean. That includes three major ones — Petermann, Ryder and Nioghalvfjerdsbrae (often referred to as 79 North for its location in degrees latitude) — whose respective glaciers could ultimately account for 3.6 feet of sea level rise if they were to melt entirely — a process that would take centuries to play out…
Research Confirms Link Between Snow Crab Decline and Marine Heatwave – NOAA Fisheries
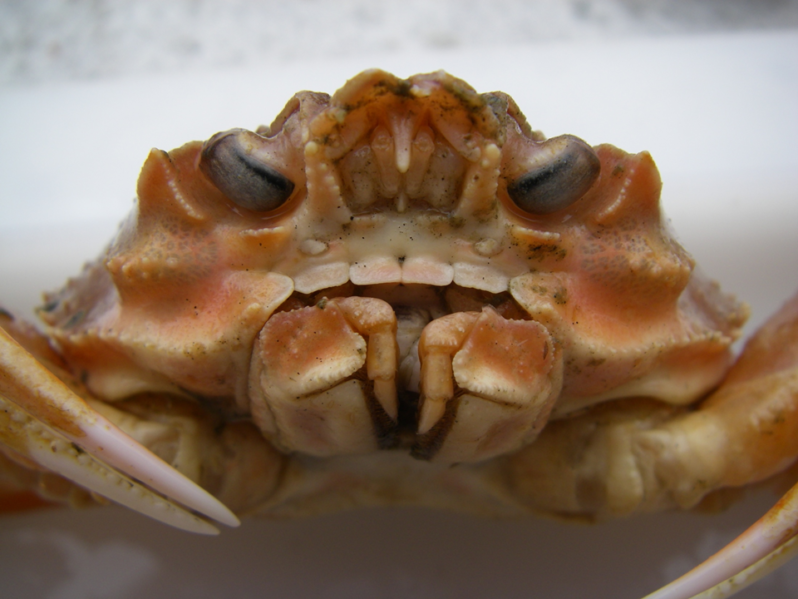

“During the marine heatwave, snow crabs faced a triple threat,” said lead author and Alaska Fisheries Science Center stock assessment scientist Cody Szuwalski. “Their metabolism increased, so they needed more food; their habitat was reduced so there was less area to forage; and crabs caught in our survey weighed less than usual. These conditions likely set them up for the dramatic decline we saw in 2021…”
World’s Oceans Changing Colour Due to Climate Breakdown – the Guardian
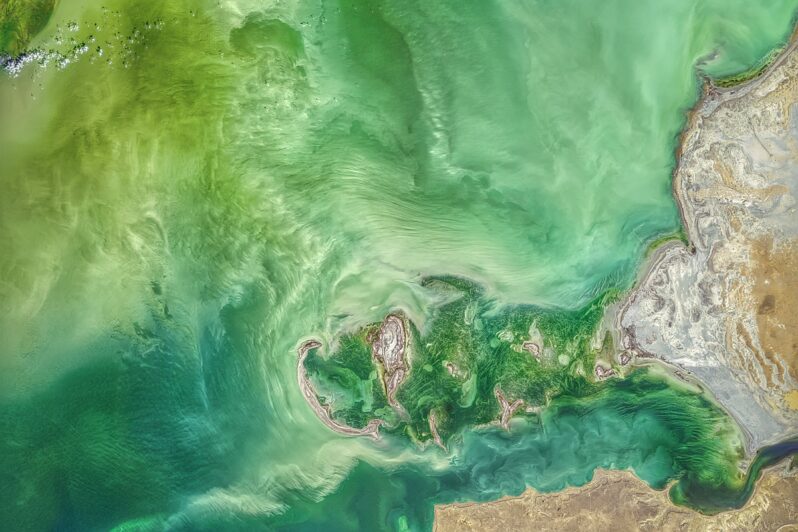

The sea is becoming greener due to changes in plankton populations, analysis of Nasa images finds…
A First: Category 5 Storms Have Formed in Every Ocean Basin this Year – the Washington Post
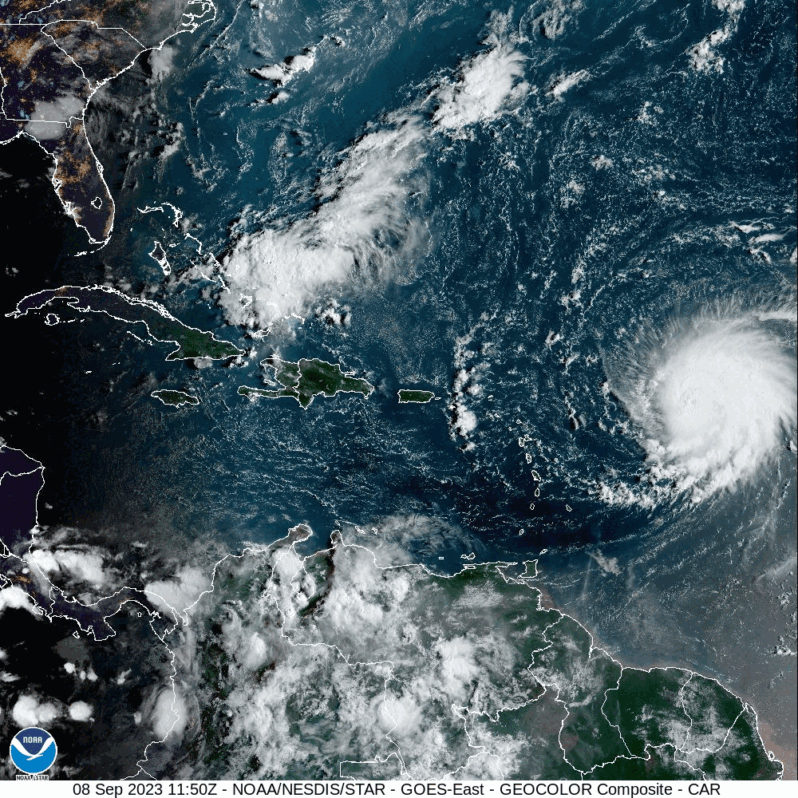
Hurricane Lee intensified with breakneck speed Thursday over record-warm Atlantic waters, its peak winds catapulting from 80 to 160 mph in just 18 hours. Lee is now a top tier Category 5 hurricane, according to the National Hurricane Center, and will probably strengthen even more…
In the face of sea level rise, can we reimagine California’s vanishing coastline? – the Los Angeles Times
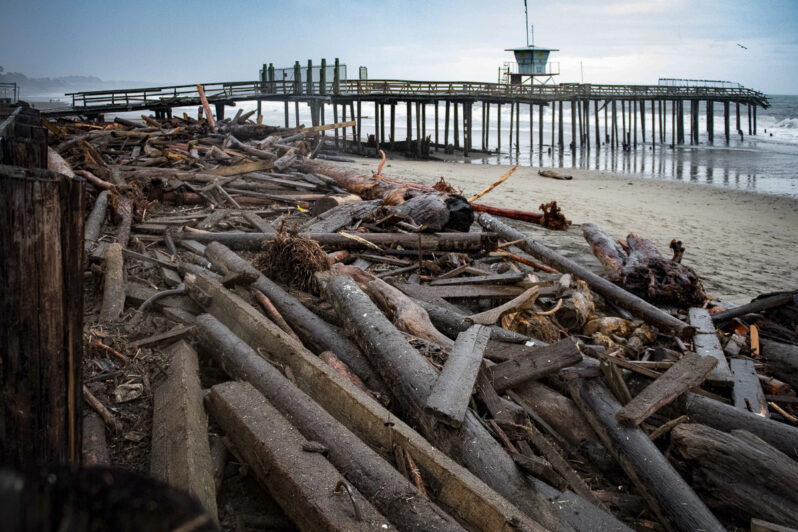

Excerpted from “California Against the Sea: Visions for Our Vanishing Coastline” (available Sept. 26, 2023) by Rosanna Xia. Reprinted in the Los Angeles Times with permission from Heyday Books, © 2023.
Hurricane Idalia’s Explosive Power Comes from Abnormally Hot Oceans – the New Yorker

Of all the astonishing facts about our blithe remaking of the world’s climate system, the most astonishing might be this: if oceans didn’t cover seventy per cent of our planet, we would have increased the average temperature to about a hundred and twenty-two degrees Fahrenheit. That’s because those oceans have absorbed something like ninety-three per cent of the extra heat trapped by the greenhouse effect and our burning of fossil fuels…
