July 4, 2023: The Hottest Day in over 125,000 Years

“We have never seen anything like this before”
– Carlo Buontempo, director of Europe’s Copernicus Climate Change Service quoted in the Washington Post, 07-06-2023…
The world’s hottest day on record was Tuesday, scientists calculate – PBS News Hour

The entire planet sweltered to the unofficial hottest day in human recordkeeping July 3 and then blasted past that with an even hotter day on July 4, according to University of Maine scientists at the Climate Reanalyzer project…
The planet saw its hottest day on record this week – CNN

On Monday, the average global temperature reached 17.01 degrees Celsius (62.62 Fahrenheit), the highest in the US National Centers for Environmental Prediction’s data, which goes back to 1979. On Tuesday, it climbed even further, reaching 17.18 degrees Celsius and global temperature remained at this record-high on Wednesday…
What 120 Degrees Looks Like in One of Mexico’s Hottest Cities – the New York Times

People in Hermosillo are used to the heat: Enduring scorching temperatures is a local point of pride (for) the “city of sun.” But on a recent Sunday in June, temperatures reached a record high when thermometers registered 49.5 degrees Celsius, or 121 Fahrenheit…
Why a sudden surge of broken heat records is scaring scientists – the Washington Post
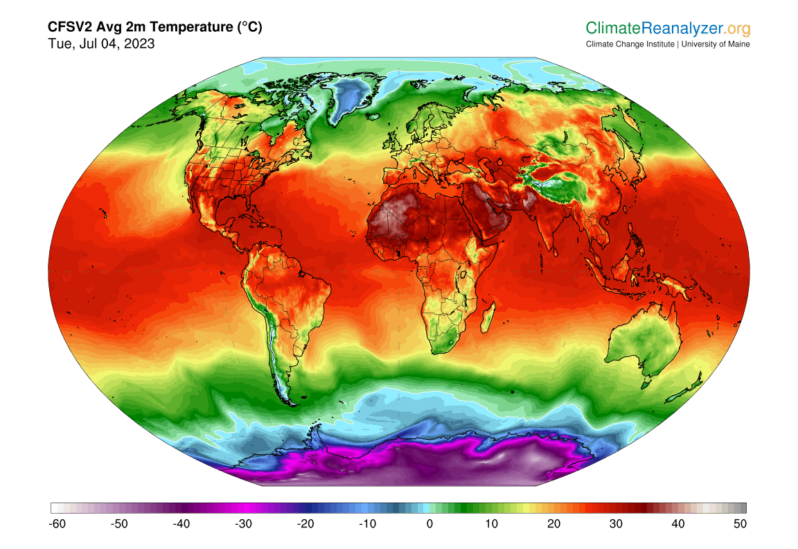
New precedents have been set in recent weeks and months, surprising some scientists with their swift evolution: historically warm oceans, with North Atlantic temperatures already nearing their typical annual peak; unparalleled low sea ice levels around Antarctica, where global warming impacts had, until now, been slower to appear; and the planet experiencing its warmest June ever charted, according to new data. And then, on Monday, came Earth’s hottest day in at least 125,000 years. Tuesday was hotter…
Hurricanes push heat deeper into the ocean than scientists realized, boosting long-term ocean warming, new research shows – the Conversation
Seven years ago an exceptionally strong El Niño took hold in the Pacific Ocean, triggering a cascade of damaging changes to the world’s weather. Indonesia was plunged into a deep drought that fueled exceptional wildfires, while heavy rains inundated villages and farmers’ fields in parts of the Horn of Africa. The event also helped make 2016 the planet’s hottest year on record. Now El Niño is back…
The Atlantification of the Arctic Ocean Is Underway – Hakai Magazine
In the Fram Strait off Greenland’s west coast, Véronique Merten encountered the foot soldiers of an invasion.
Merten was studying the region’s biodiversity using environmental DNA, a method that allows scientists to figure out which species are living nearby by sampling the tiny pieces of genetic material they shed, like scales, skin, and poop. And here, in a stretch of the Arctic Ocean 400 kilometers north of where they’d ever been seen before: capelin.
And they were everywhere…
El Niño May Break a Record and Reshape Weather around the Globe – Scientific American
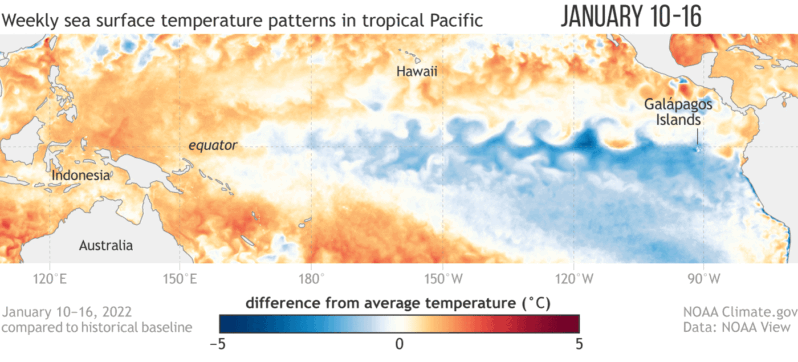
Seven years ago an exceptionally strong El Niño took hold in the Pacific Ocean, triggering a cascade of damaging changes to the world’s weather. Indonesia was plunged into a deep drought that fueled exceptional wildfires, while heavy rains inundated villages and farmers’ fields in parts of the Horn of Africa. The event also helped make 2016 the planet’s hottest year on record. Now El Niño is back…
As Ocean Oxygen Levels Dip, Fish Face an Uncertain Future – Yale Environment 360
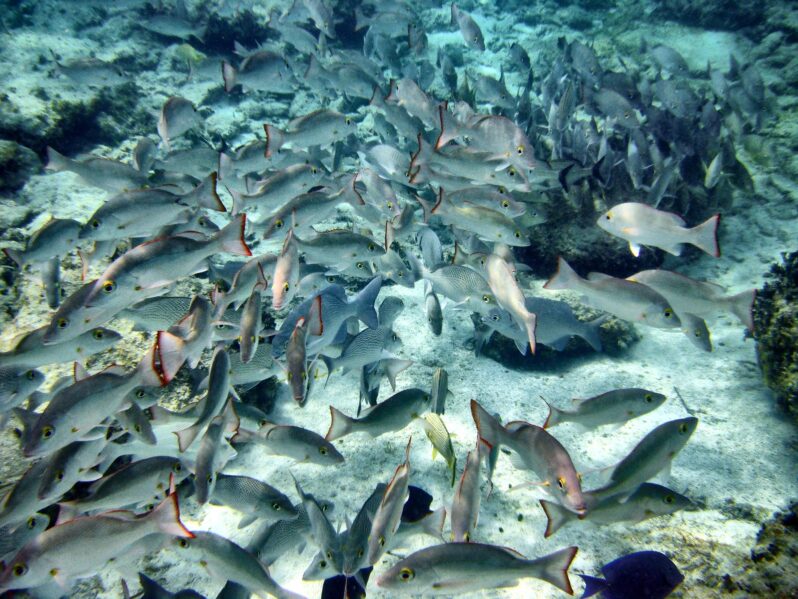

Global warming not only increases ocean temperatures, it triggers a cascade of effects that are stripping the seas of oxygen. Fish are already moving to new waters in search of oxygen, and scientists are warning of the long-term threat to fish species and marine ecosystems.
ff the coast of southeastern China, one particular fish species is booming: the oddly named Bombay duck, a long, slim fish with a distinctive, gaping jaw and a texture like jelly. When research ships trawl the seafloor off that coast, they now catch upwards of 440 pounds of the gelatinous fish per hour — a more than tenfold increase over a decade ago. “It’s monstrous,” says University of British Columbia fisheries researcher Daniel Pauly of the explosion in numbers…
