Finding a Way Back to ‘Perfect Beach’ – the New York Times
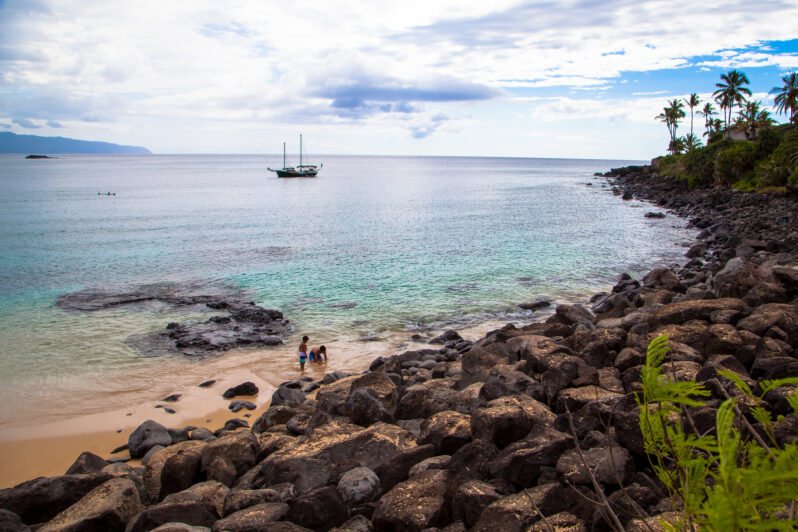

On the northern coast of Puerto Rico — about an hour’s drive west of San Juan, off a wisp of a road threaded through dense green foliage — there exists a long, empty beach that has haunted my dreams for years. On Google Maps, it appears as Punta Caracoles Beach, but I have always thought of it as Perfect Beach…
How much carbon can oysters store? Scientists are trying to find out – Grist

Scientists all along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts are trying to bring oyster populations back, and not just because they’re a popular food. Oysters are also important for healthy coastal ecosystems. And researchers are now studying how creating new oyster reefs could help fight climate change by sequestering carbon…
Natural causes: artists address climate crisis in inventive ways – The Art Newspaper

What can art do about a crisis? This is a question that a growing number of museums across the world have been faced with as they mount exhibitions addressing the climate emergency. In the past six months alone, institutions ranging from London’s Hayward Gallery (Dear Earth, now closed) to the Museum of Modern Art in New York (Emerging Ecologies: Architecture and the Rise of Environmentalism, until 20 January 2024) have opened eco-themed exhibitions. This month, a spate of new shows across London take up the baton, offering fresh perspectives on the subject’s relationship to wider society and taking the conversation out into the “real world”…
‘Take It Down and They’ll Return’: The Stunning Revival of the Penobscot River – reasons to be cheerful
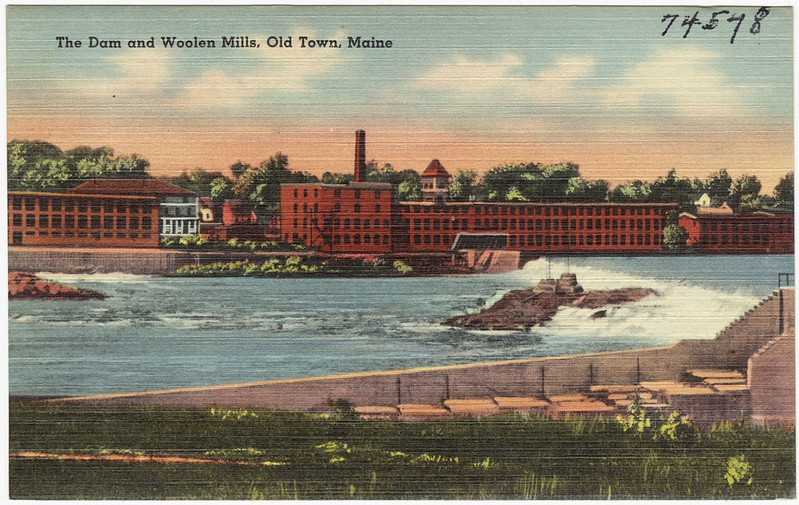

A historic project in Maine shows that when dams are removed, a river and its fish can recover with surprising speed…
Record-setting storm wallops East Coast with flooding, high winds – the Washington Post
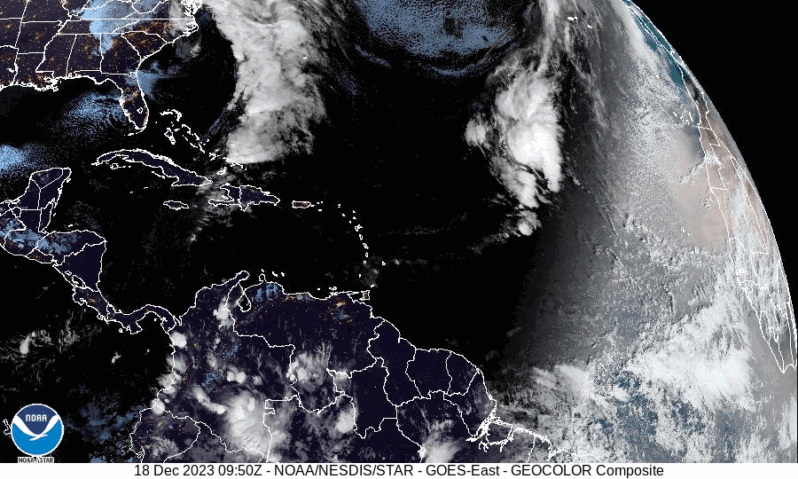
A historically intense December coastal storm is blasting the Northeast on Monday after unleashing heavy rainfall, coastal flooding and high winds from Florida to the Mid-Atlantic. More than 700,000 customers had no power midday Monday as gusts surpassed 60 mph in many locations in eastern New England…
Long Story Shorts: What Is a Core Sample? – Hakai Institute

Have you ever wanted to go back in time— just to see what it was like? Well, scientists have figured out how …sort of… Watch this video to find out how tree, ice, and sediment cores can tell us all sorts of things about the past…
Can the tourism industry survive the climate crisis? – the Guardian
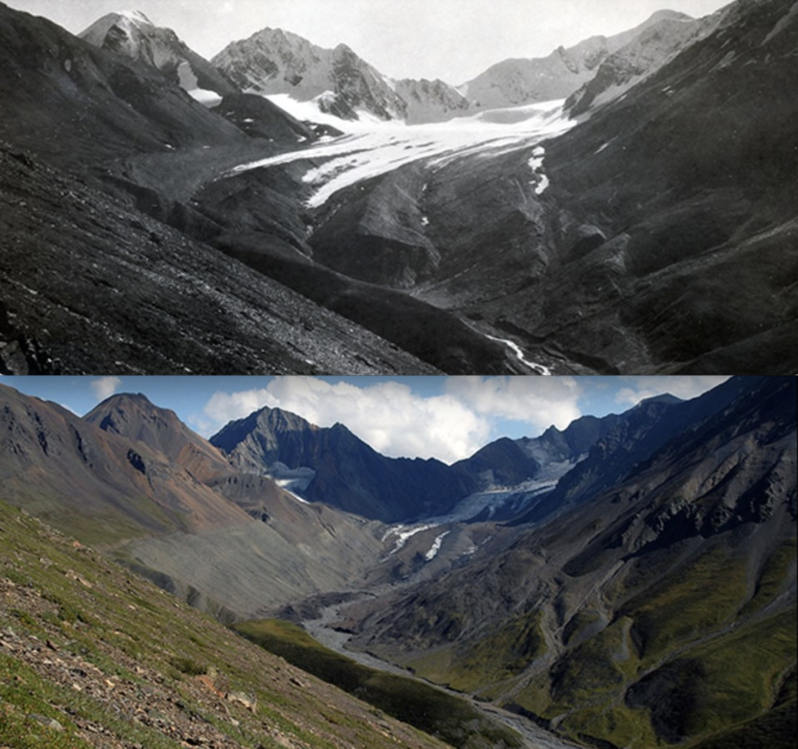

From the Solomon Islands to Denali national park, how five communities reliant on tourism are coping as climate change upends their industry…One of the terrible ironies of the climate crisis is that some of the most beautiful – and popular – places in the world are also the most vulnerable. Which means as temperatures rise, extreme weather events increase, water sources dry up and natural habitats die, these places are facing another devastating loss: tourists…
The Unsustainable Harvest of Coastal Sands – Science
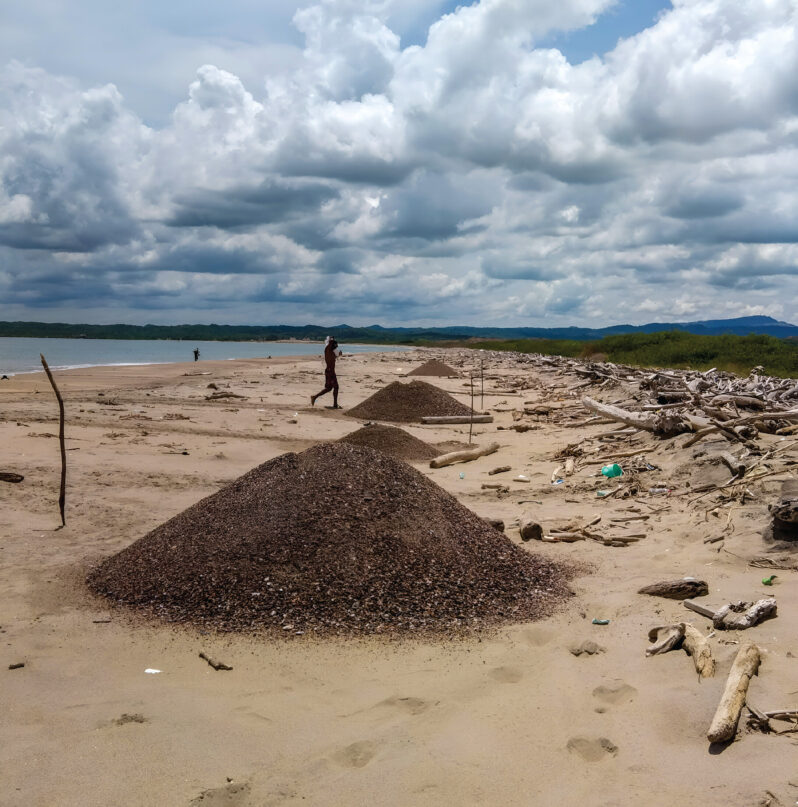

Although coasts form a crucial part of the natural wealth of the planet, their conservation is increasingly jeopardized owing to the growing human footprint. With 50% of the world’s population living within 150 km of a coastline, increasing urbanization and population pressures are threatening these fragile ecosystems…
The World’s Fastest-Sinking Megacity Has One Last Chance to Save Itself – Bloomberg

Venice is sinking. So are Rotterdam, Bangkok and New York. But no place compares to Jakarta, the fastest-sinking megacity on the planet. Over the past 25 years, the hardest-hit areas of Indonesia’s capital have subsided more than 16 feet. The city has until 2030 to figure out a solution, experts say, or it will be too late to hold back the Java Sea…
