Helene Has Killed More Than 110 People, Here Are Some of Their Stories – the New York Times
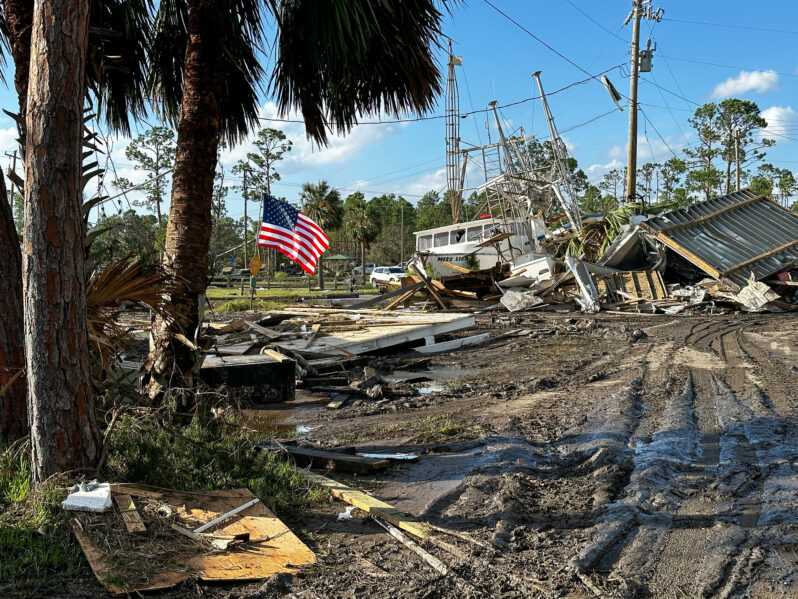

After the Category 4 hurricane made landfall on Florida’s Gulf Coast and pummeled the Southeast, some victims’ portraits were coming into focus…
John Regains Hurricane Strength as It Marches Toward Mexico – the New York Times
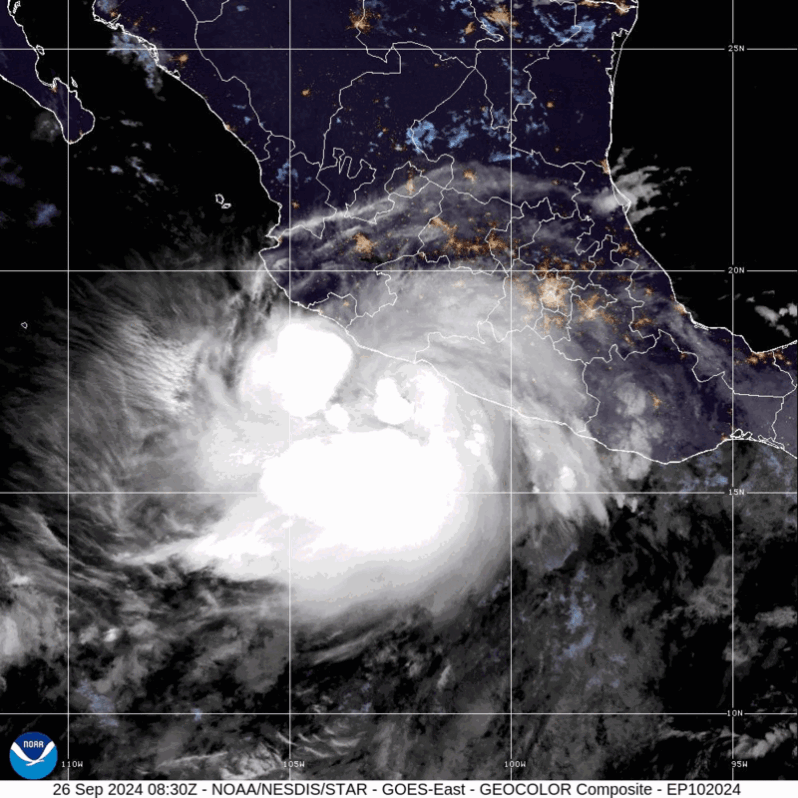
John, which battered western Mexico as a Category 3 storm earlier this week, was expected to make landfall there again on Friday…
In Charleston, floods are a ‘constant existential fear’ – the Washington Post

Charleston, S.C., is weary from a parade of floods that go back a decade. The city is taking action to confront the risk, but Debby offered more proof of how tall a task it faces….
Hurricane Idalia shows nature may provide the best shoreline protection – NPR
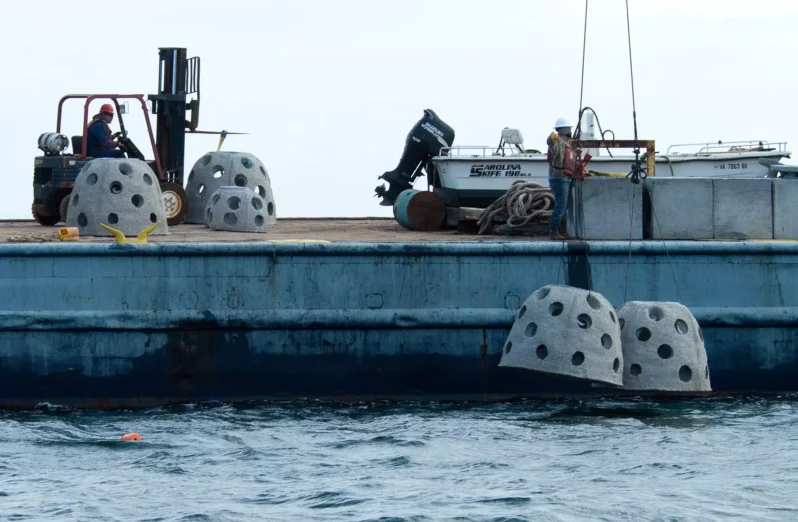

When Hurricane Idalia slammed into Florida’s Gulf Coast in August (2023), one of the hardest hit areas was Cedar Key. A nearly 7-foot storm surge battered the small fishing community…(NOAA) says Idalia caused an estimated $3.6 billion in damage…But on Cedar Key, when the water receded, scientists found some good news amid all the damage. Nature-based “living shoreline” projects built to protect roads, buildings and other structures were relatively undamaged…
Here’s How the Next Two Atmospheric Rivers Will Affect California – the New York Times
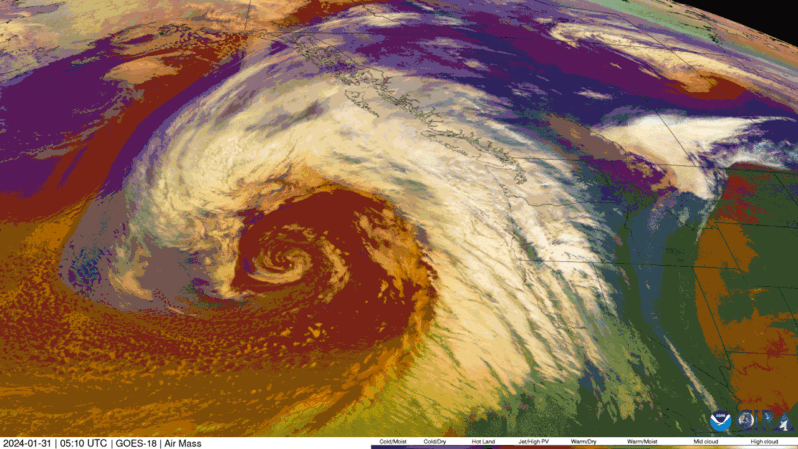
A “Pineapple Express” hitting California through Thursday will set the stage for another week of unsettled weather across the state…
Record-setting storm wallops East Coast with flooding, high winds – the Washington Post
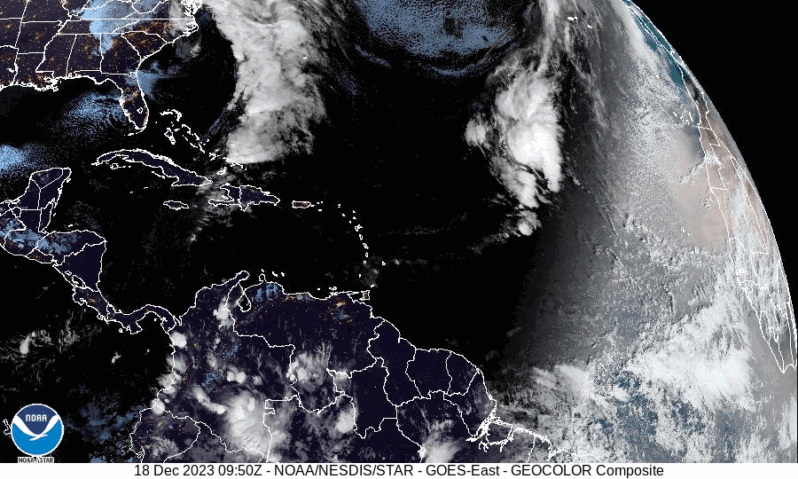
A historically intense December coastal storm is blasting the Northeast on Monday after unleashing heavy rainfall, coastal flooding and high winds from Florida to the Mid-Atlantic. More than 700,000 customers had no power midday Monday as gusts surpassed 60 mph in many locations in eastern New England…
How sea level rise made Idalia’s storm surge worse – the Washington Post
In mid-November 2021, a great storm begins brewing in the central Pacific Ocean north of Hawai‘i. Especially warm water, heated by the sun, steams off the sea surface and funnels into the sky.
A tendril of this floating moisture sweeps eastward across the ocean. It rides the winds for a day until it reaches the coasts of British Columbia and Washington State. There, the storm hits air turbulence, which pushes it into position—straight over British Columbia’s Fraser River valley….
A River Runs above Us – Hakai Magazine
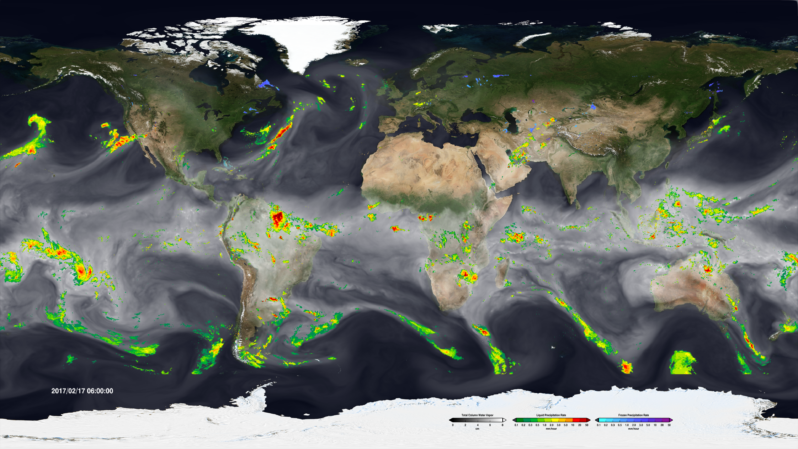
In mid-November 2021, a great storm begins brewing in the central Pacific Ocean north of Hawai‘i. Especially warm water, heated by the sun, steams off the sea surface and funnels into the sky.
A tendril of this floating moisture sweeps eastward across the ocean. It rides the winds for a day until it reaches the coasts of British Columbia and Washington State. There, the storm hits air turbulence, which pushes it into position—straight over British Columbia’s Fraser River valley….
Opinion | Interactive: The Plan to Save New York From the Next Sandy Will Ruin the Waterfront. It Doesn’t Have To – the New York Times
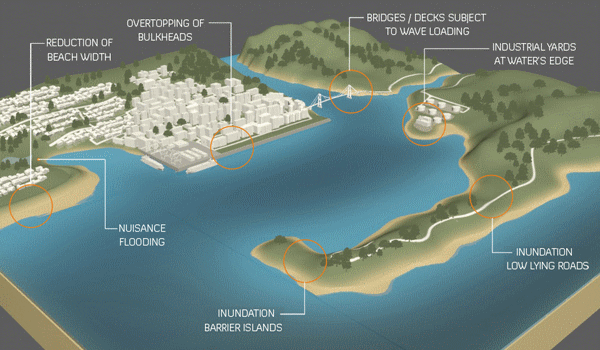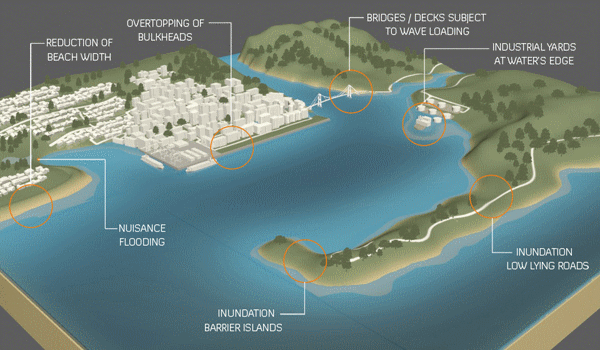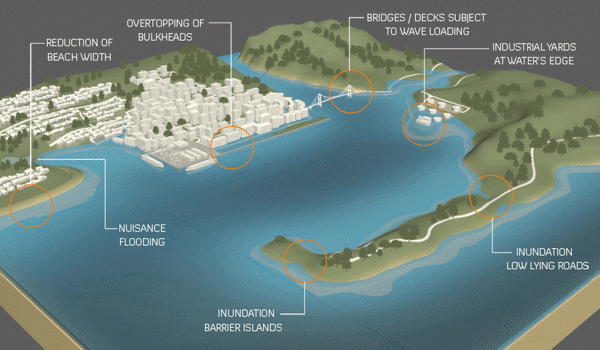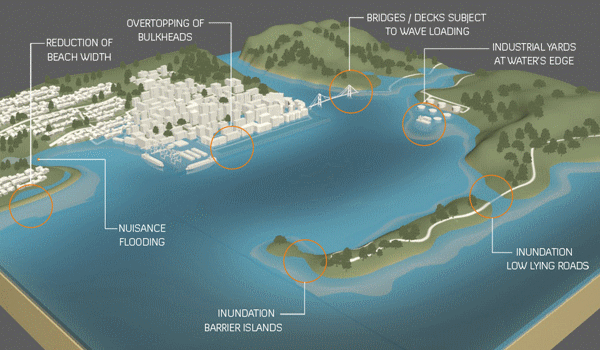
Last September, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers unveiled its proposal to protect the greater New York and New Jersey metro area from the next catastrophic flood. It is an epic plan that includes dozens of miles of floodwalls, levees and berms along the shoreline and 12 storm surge barriers — arrays of movable gates — across entrances to waterways throughout the region.
The plan is estimated to cost a staggering $52.6 billion. It’s by far the most expensive project ever proposed by the Corps.
The trouble is that despite its great ambitions, the Corps’s plan demonstrates the shortcomings of relying on massive shoreline structures for flood protection…
