Why Oak Island is looking 18 miles off its coast for sand to nourish its eroded beach – Wilmington StarNews Online
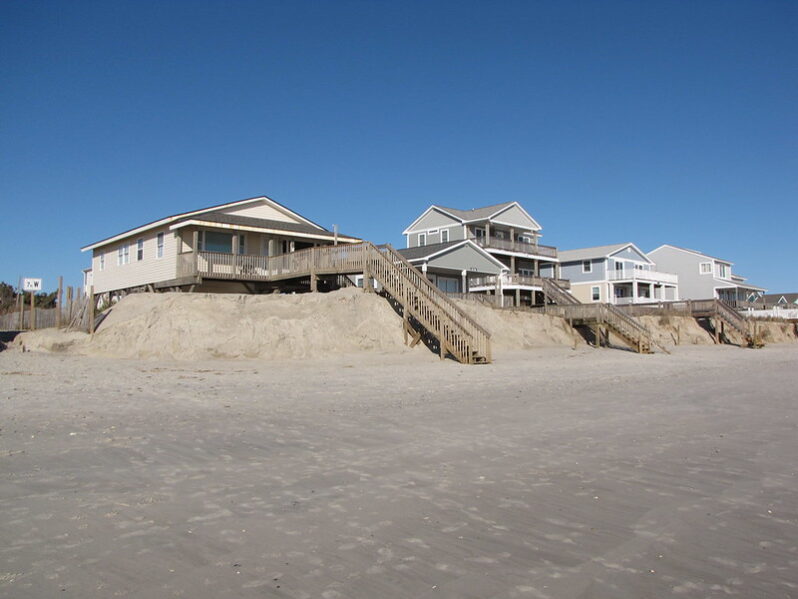

Faced with an eroding beach, Oak Island wants to pump fresh sand onto its oceanfront. But finding a viable sand source might mean going a long way offshore…
Hurricane Idalia shows nature may provide the best shoreline protection – NPR
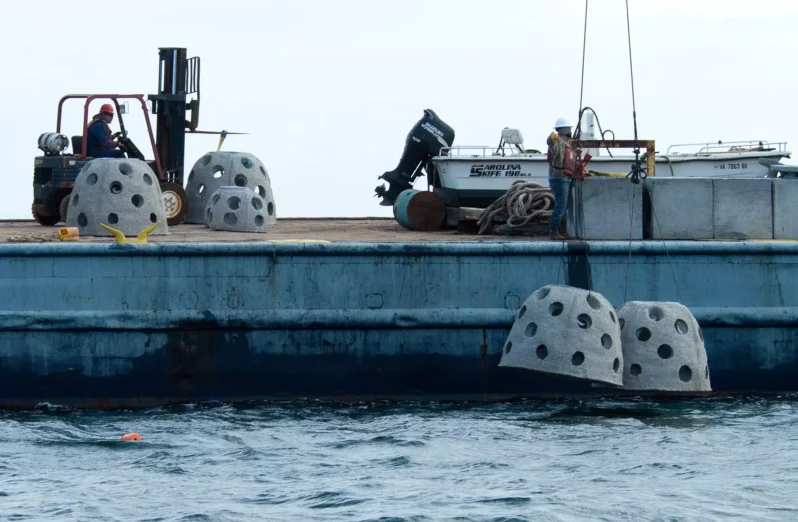

When Hurricane Idalia slammed into Florida’s Gulf Coast in August (2023), one of the hardest hit areas was Cedar Key. A nearly 7-foot storm surge battered the small fishing community…(NOAA) says Idalia caused an estimated $3.6 billion in damage…But on Cedar Key, when the water receded, scientists found some good news amid all the damage. Nature-based “living shoreline” projects built to protect roads, buildings and other structures were relatively undamaged…
The Marshall Islands Aren’t Giving In to Sea Level Rise – Hakai Magazine
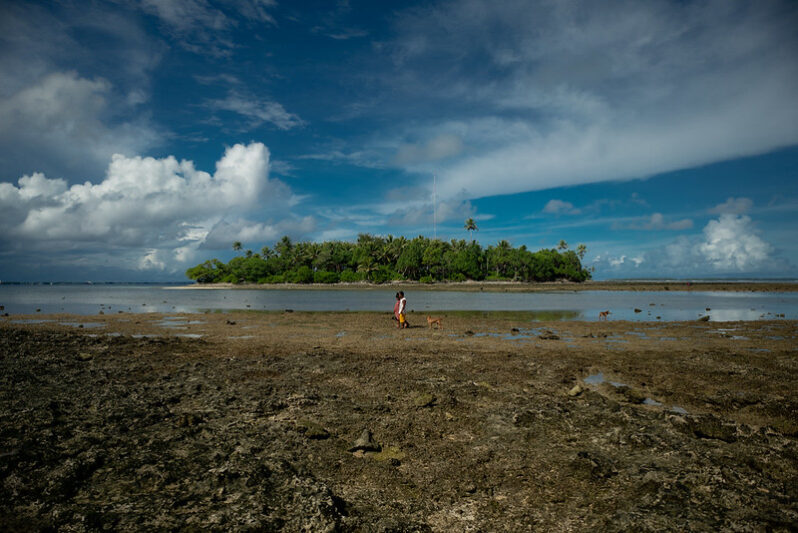

The precariously placed island nation has put together a comprehensive—if expensive—plan to survive sea level rise…
Prepare for a ‘Gray Swan’ Climate – the Atlantic

The next climate extremes are both predictable and unprecedented, and they’re coming on fast…
Can the tourism industry survive the climate crisis? – the Guardian
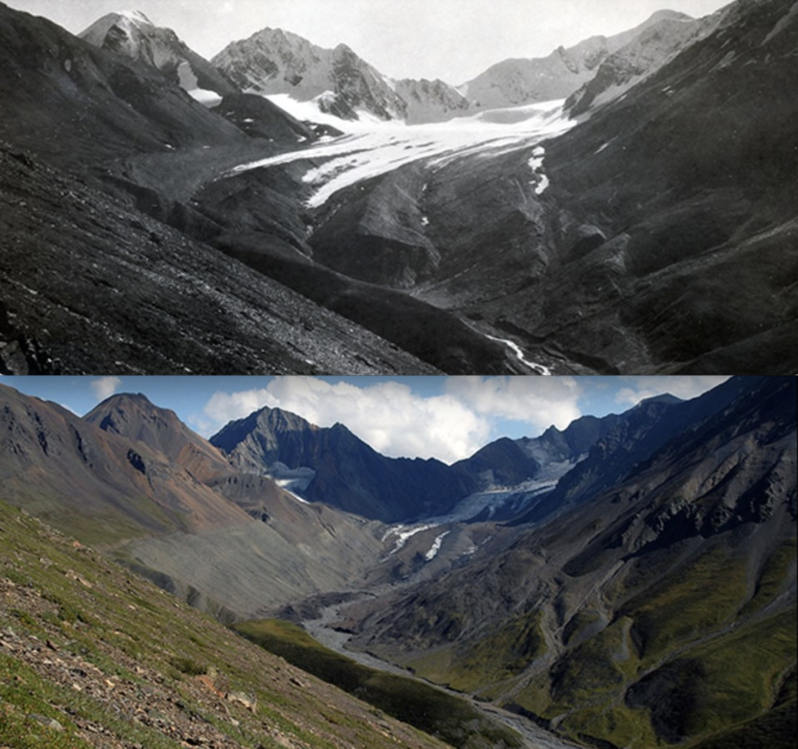

From the Solomon Islands to Denali national park, how five communities reliant on tourism are coping as climate change upends their industry…One of the terrible ironies of the climate crisis is that some of the most beautiful – and popular – places in the world are also the most vulnerable. Which means as temperatures rise, extreme weather events increase, water sources dry up and natural habitats die, these places are facing another devastating loss: tourists…
The World’s Fastest-Sinking Megacity Has One Last Chance to Save Itself – Bloomberg

Venice is sinking. So are Rotterdam, Bangkok and New York. But no place compares to Jakarta, the fastest-sinking megacity on the planet. Over the past 25 years, the hardest-hit areas of Indonesia’s capital have subsided more than 16 feet. The city has until 2030 to figure out a solution, experts say, or it will be too late to hold back the Java Sea…
Earth on verge of five catastrophic climate tipping points, scientists warn – the Guardian
Humanity faces ‘devastating domino effects’ including mass displacement and financial ruin as planet warms…“Tipping points in the Earth system pose threats of a magnitude never faced by humanity,” said Tim Lenton, from the University of Exeter’s Global Systems Institute. “They can trigger devastating domino effects, including the loss of whole ecosystems and capacity to grow staple crops, with societal impacts including mass displacement, political instability and financial collapse…”
Inside the Marshall Islands’ life-or-death plan to survive climate change – Grist Magazine
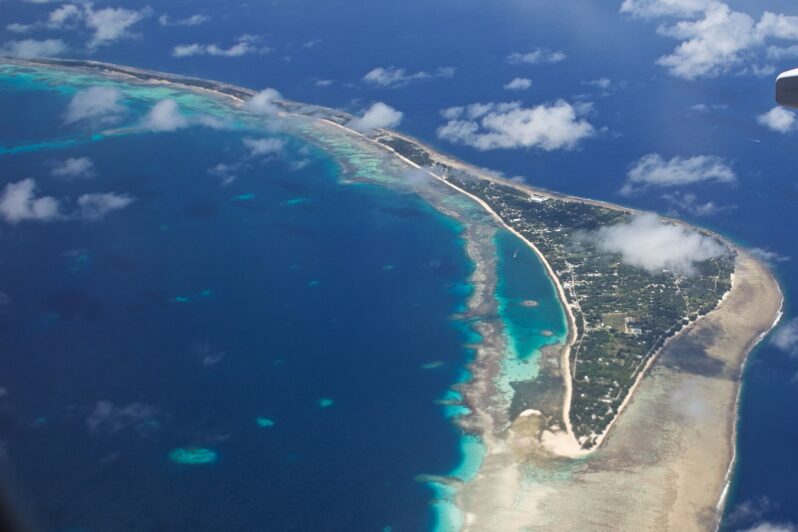

The Pacific island nation is seeking $35 billion to protect against sea-level rise and prevent a mass exodus…“We call it our national adaptation plan, but it is really our survival plan,” said John Silk, the foreign minister of the Republic of the Marshall Islands…
A disappearing island: ‘The water is destroying us, one house at a time’ – NPR
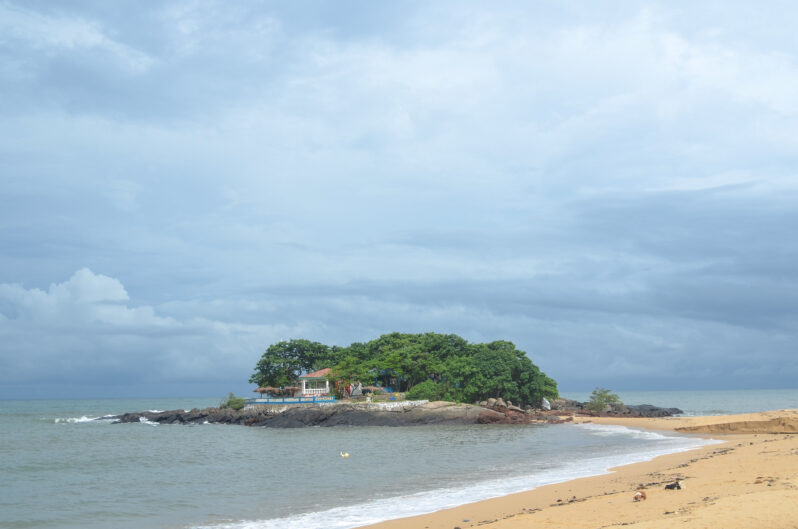

With nearly a third of its population living in coastal areas, and its heavy reliance on subsistence agriculture and fishing, Sierra Leone has been identified as one of the world’s most vulnerable countries to the impacts of climate change, despite having contributed just a tiny fraction of global CO2 emissions. With a GDP per capita of barely $2,000, it is also one of the least prepared to deal with those impacts….
