Excerpt:
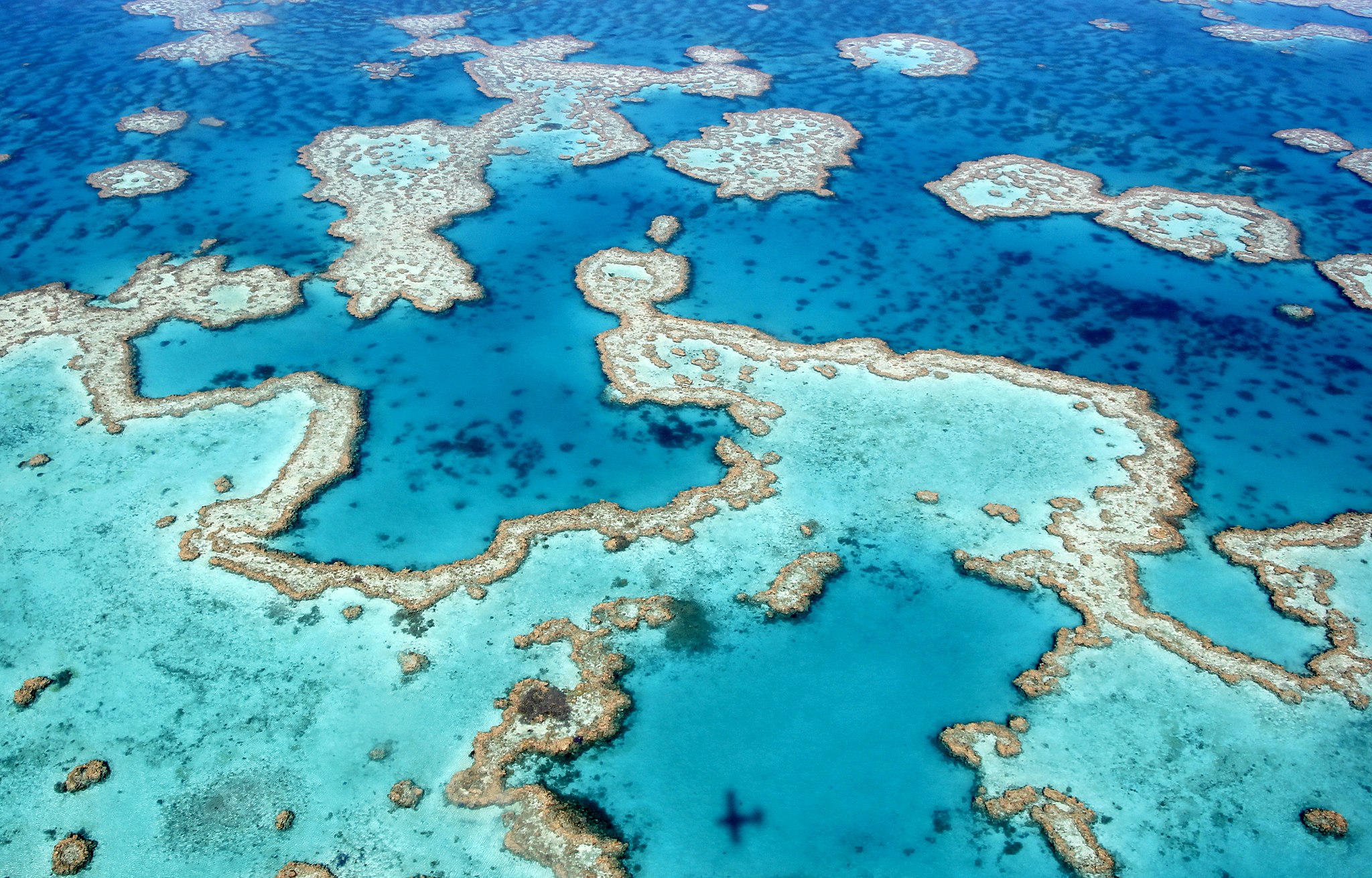
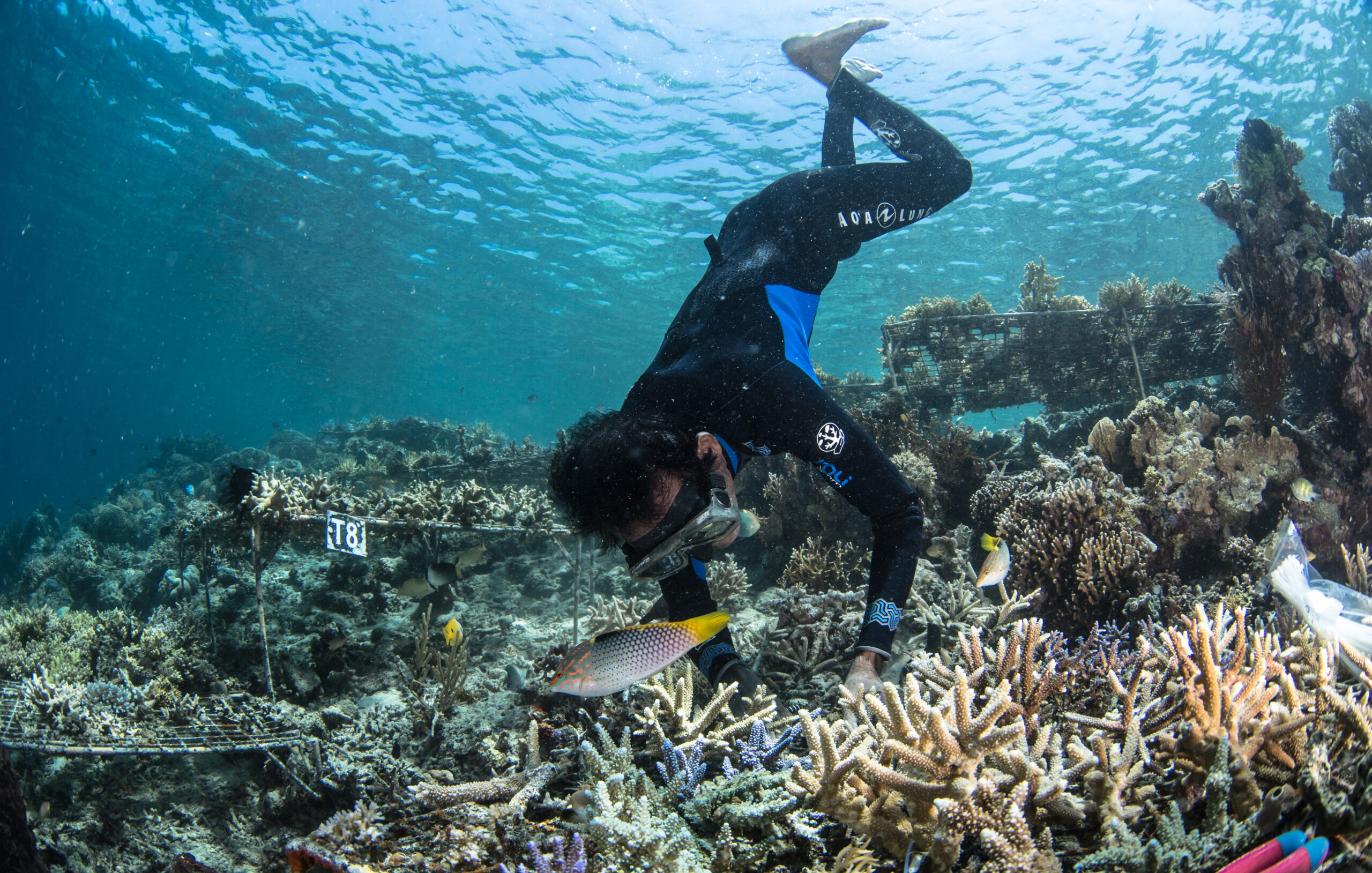
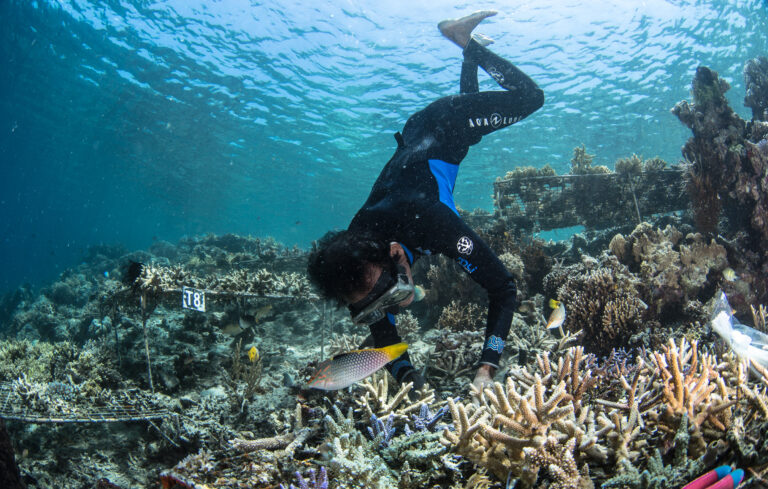
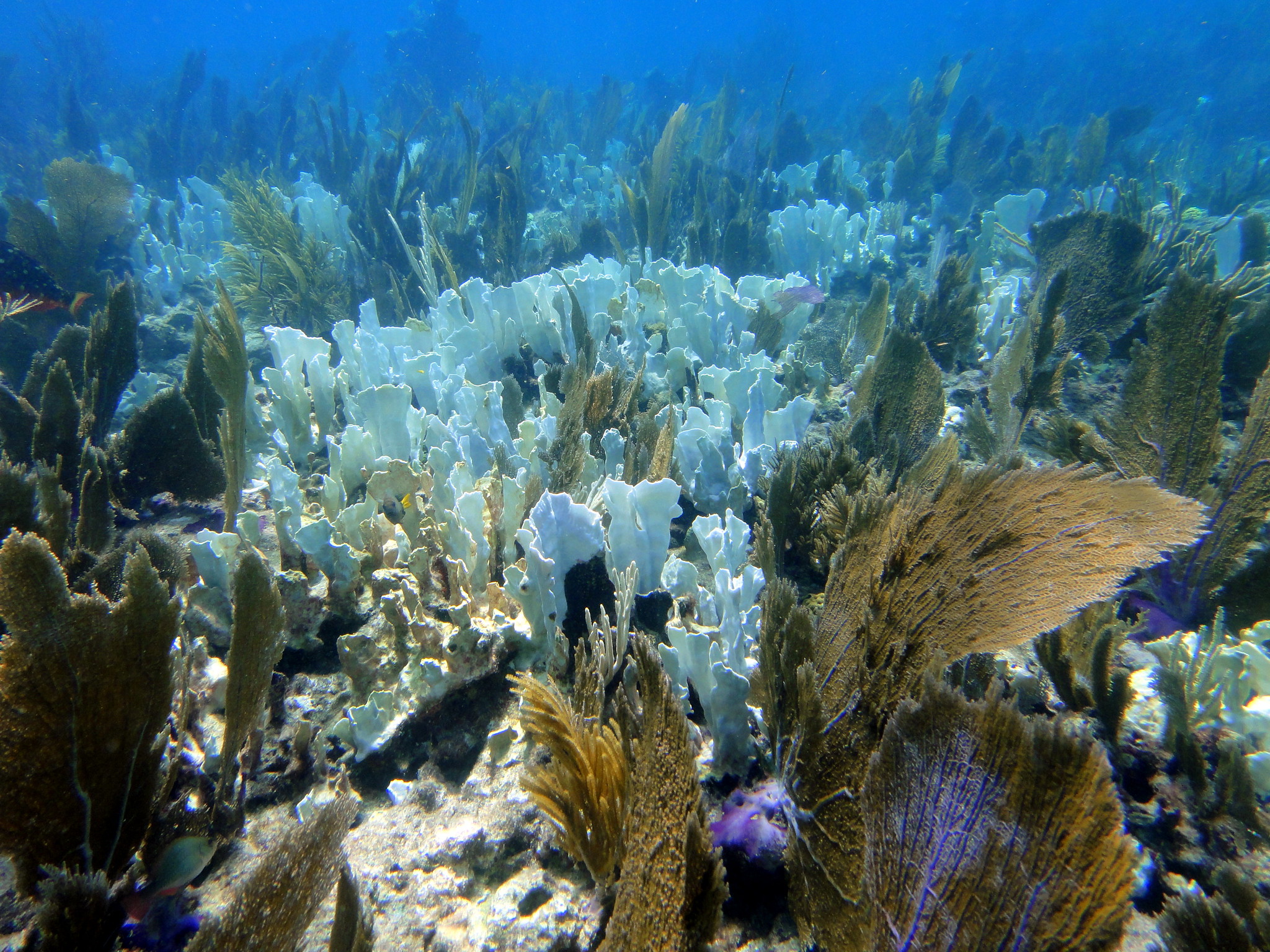
As the early-morning sun rises over the Great Barrier Reef, its light pierces the turquoise waters of a shallow lagoon, bringing more than a dozen turtles to life. These waters that surround Lady Elliot Island, off the eastern coast of Australia, provide some of the most spectacular snorkeling in the world — but they are also on the front line of the climate crisis, as one of the first places to suffer a mass coral bleaching event that has now spread across the world.
The Great Barrier Reef just experienced its worst summer on record, and the US-based National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) announced last month that the world is undergoing a rare global mass coral bleaching event — the fourth since the late 1990s — impacting at least 53 countries.
The corals are casualties of surging global temperatures which have smashed historical records in the past year — caused mainly by fossil fuels driving up carbon emissions and accelerated by the El Niño weather pattern, which heats ocean temperatures in this part of the world.
CNN witnessed bleaching on the Great Barrier Reef in mid-February, on five different reefs spanning the northern and southern parts of the 2,300-kilometer (1,400-mile) ecosystem.
“What is happening now in our oceans is like wildfires underwater,” said Kate Quigley, principal research scientist at Australia’s Minderoo Foundation. “We’re going to have so much warming that we’re going to get to a tipping point, and we won’t be able to come back from that.”
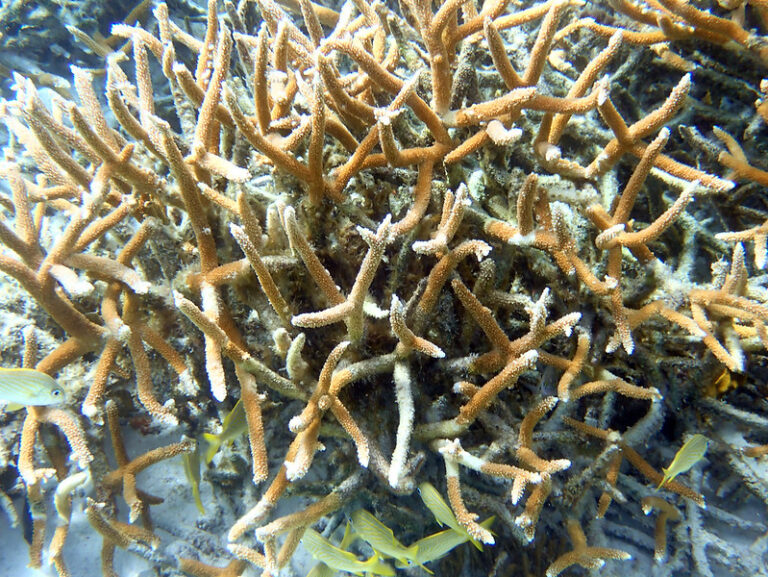
Bleaching occurs when marine heatwaves put corals under stress, causing them to expel algae from their tissue, draining their color. Corals can recover from bleaching if the temperatures return to normal, but they will perish if the water stays warmer than usual.
“It’s a die-off,” said Professor Ove Hoegh-Guldberg, a climate scientist at the University of Queensland in Australia and chief scientist at The Great Barrier Reef Foundation. “The temperatures got so warm, they’re off the charts … they never occurred before at this sort of level.”
The destruction of marine ecosystems would deliver an effective death sentence for around a quarter of all species that depend on reefs for survival — and threaten an estimated billion people who rely on reef fish for their food and livelihoods. Reefs also provide vital protection for coastlines, reducing the impact of floods, cyclones and sea level rise.
After taking off from Brisbane just after dawn, our tiny propeller plane skims miles of Queensland coastline before heading north out over the crystal-clear waters of the Coral Sea –— revealing the beauty of this vast reef system beneath its surface.
Our destination is Lady Elliot Island, a remote coral cay perched on top of the southern end of the Great Barrier Reef.
Pilot Peter Gash is the island’s leaseholder, and his family has been operating tours to the island for nearly 20 years.
“We made it our life’s work,” Gash said. “My wife and I married, I went and learned to fly airplanes so I could bring people here.”
Gash negotiates his small aircraft through bumpy crosswinds to land safely on the short, grass-covered runway.
Decades ago, the island was a barren landscape devoid of vegetation following years of mining for nutrient-rich seabird waste — known as guano — in the late 1800s.
The Gash family set about bringing this island back to life, planting around 10,000 native species of trees to create a man-made forest and nature reserve, and using solar power, batteries and a water desalination system to support a small eco-tourism resort.
The island is now home to up to 200,000 sea birds, which have helped to regenerate the coral reef fringing the island.
Additional Reading . . .
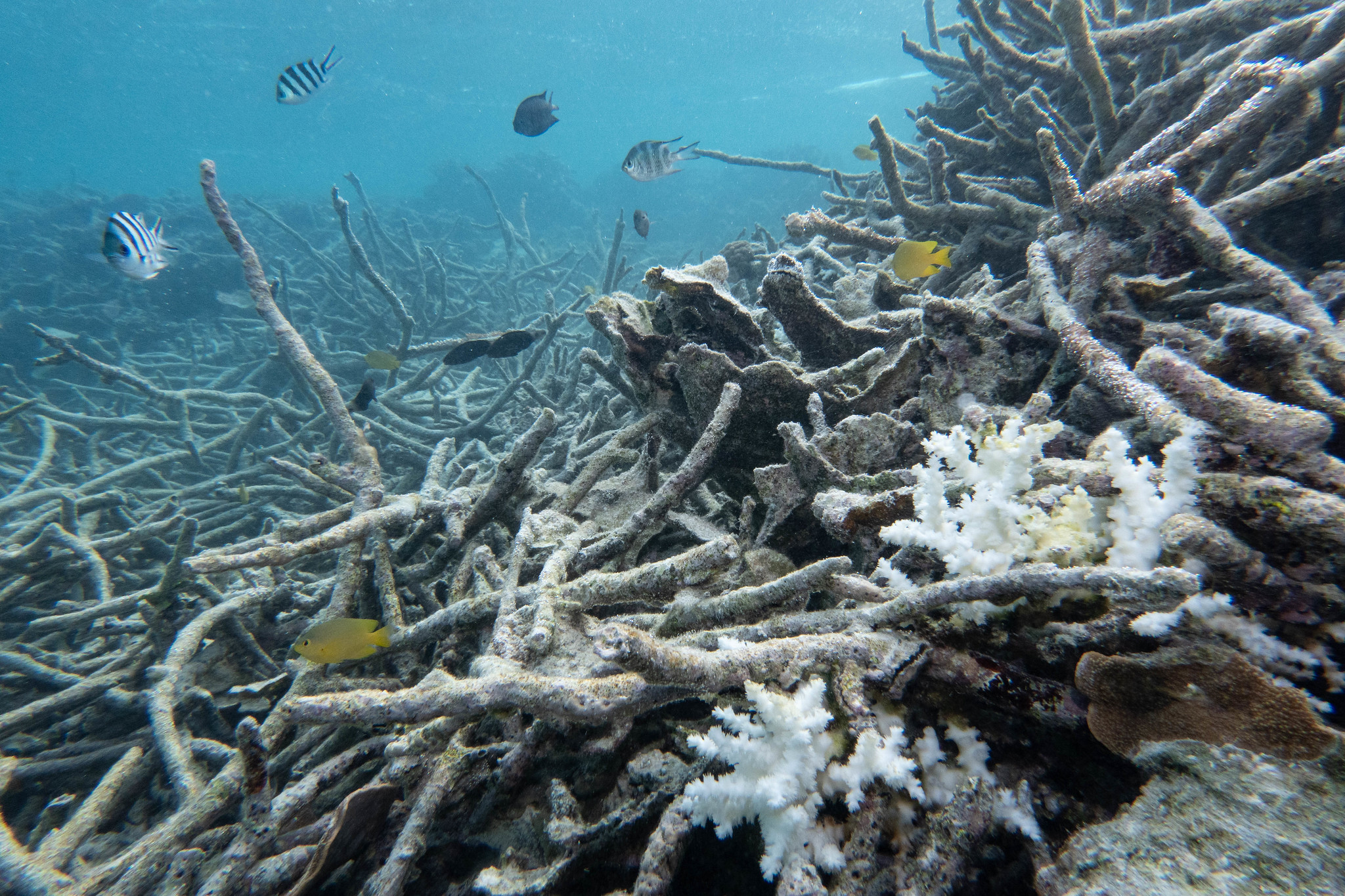

Great Barrier Reef’s worst bleaching leaves giant coral graveyard: ‘It looks as if it has been carpet bombed’ – the Guardian
Last month the Australian Institute of Marine Science and the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park Authority released a report warning that the reef was experiencing “the highest levels of thermal stress on record”. The authority’s chief scientist, Dr Roger Beeden, spoke of extensive and uniform bleaching across the southern reefs, which had dodged the worst of much of the previous four mass bleaching events to blight the Great Barrier Reef since 2016…

Corals are bleaching in every corner of the ocean, threatening its web of life – the Washington Post
First around Fiji, then the Florida Keys, then Australia’s Great Barrier Reef, and now in the Indian Ocean. In the past year, anomalous ocean temperatures have left a trail of devastation for the world’s corals, bleaching entire reefs and threatening widespread coral mortality — and now, scientists with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and International Coral Reef Initiative say the world is experiencing its fourth global bleaching event, the second in the last decade…

The Widest-Ever Global Coral Crisis Will Hit Within Weeks, Scientists Say – the New York Times
The world’s coral reefs are in the throes of a global bleaching event caused by extraordinary ocean temperatures…It is the fourth such global event on record and is expected to affect more reefs than any other. Bleaching occurs when corals become so stressed that they lose the symbiotic algae they need to survive. Bleached corals can recover, but if the water surrounding them is too hot for too long, they die…
BBC News – (04-15-2024):
Corals turning white and dying after record heat, say scientists | BBC News
ABC News – Australia (04-15-2024):
‘Moved to tears’: The hottest year on record unleashes a mass coral bleaching tragedy
PBS NewsHour (04-18-2024):
Record-breaking ocean heat triggers massive coral reef bleaching
Island News (04-17-2024):
Record heat stress hits Great Barrier Reef: Experts warn of serious bleaching
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
Beaches | Coasts of the Month . . .
Photos of the Month . . .
Excerpt:
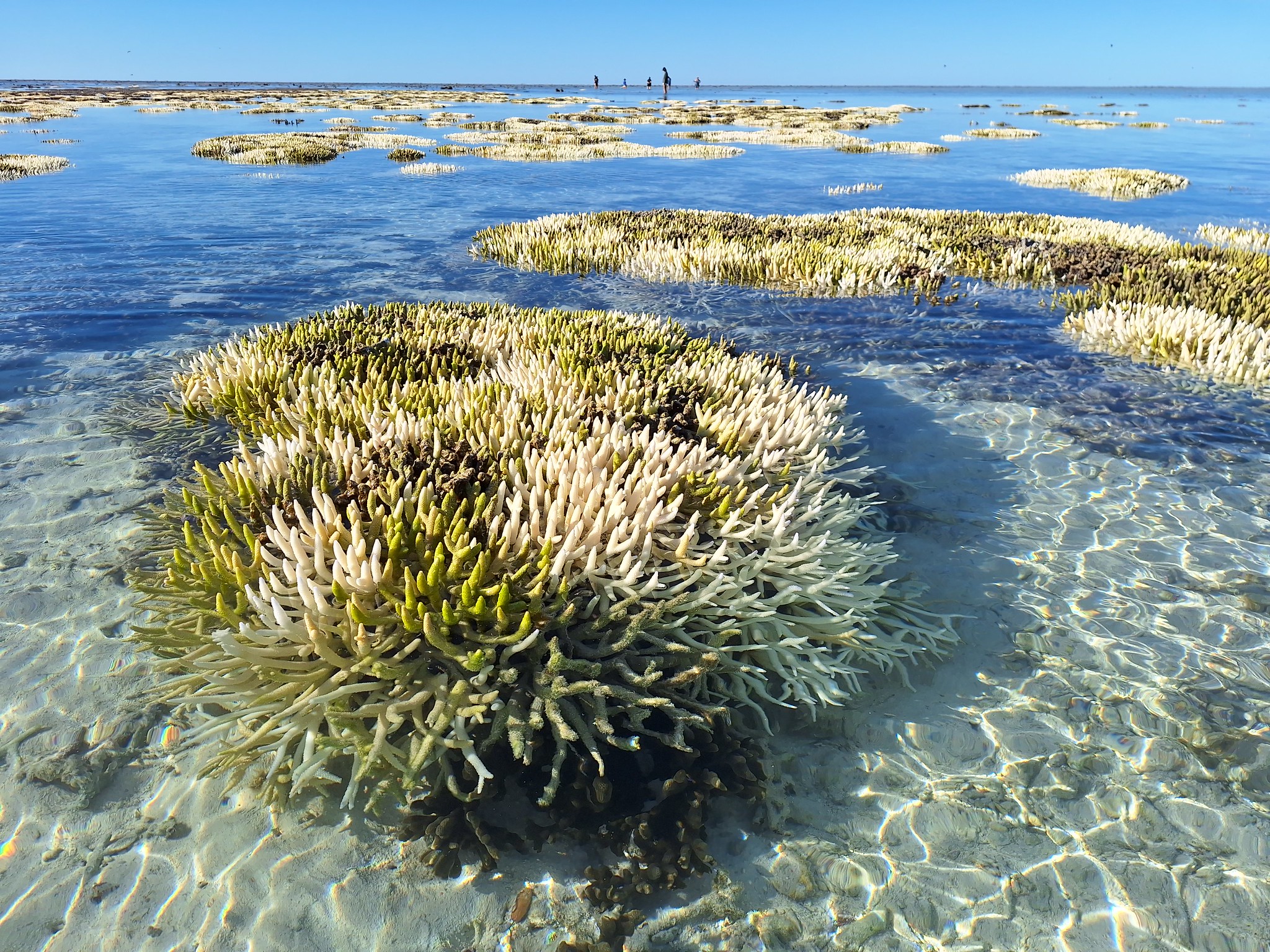
Kimbe Bay is an area of staggering marine biodiversity within the Pacific Ocean’s Eastern Coral Triangle. The bay contains 76% (605) of the world’s coral reef and 800 species of fish. This marine region, however, is under threat from overfishing, habitat degradation and climate change. Naomi and her team at The Sea Women of Melanesia work directly with local communities, primarily women, to design and implement Locally Managed Marine Areas (LMMAs) to allow reefs to recover…
Sounds from a Healthy Coral Reef
- Steve Simpson
Coral Bleaching Explained:
The Story of Frank the Coral
the Coral Garden - Tullio Rossi, PhD
(04-07-2016)
Excerpt:
Frank the coral has been living peacefully on the beautiful Great Barrier Reef for 400 years. However, Frank noticed that in the last century it started to get gradually hotter… until in 2016 the water temperature went completely out of control putting Frank’s life at risk. Will this old giant resist the stress of a changing climate?
CURRENT NEWS + RECENT POSTS
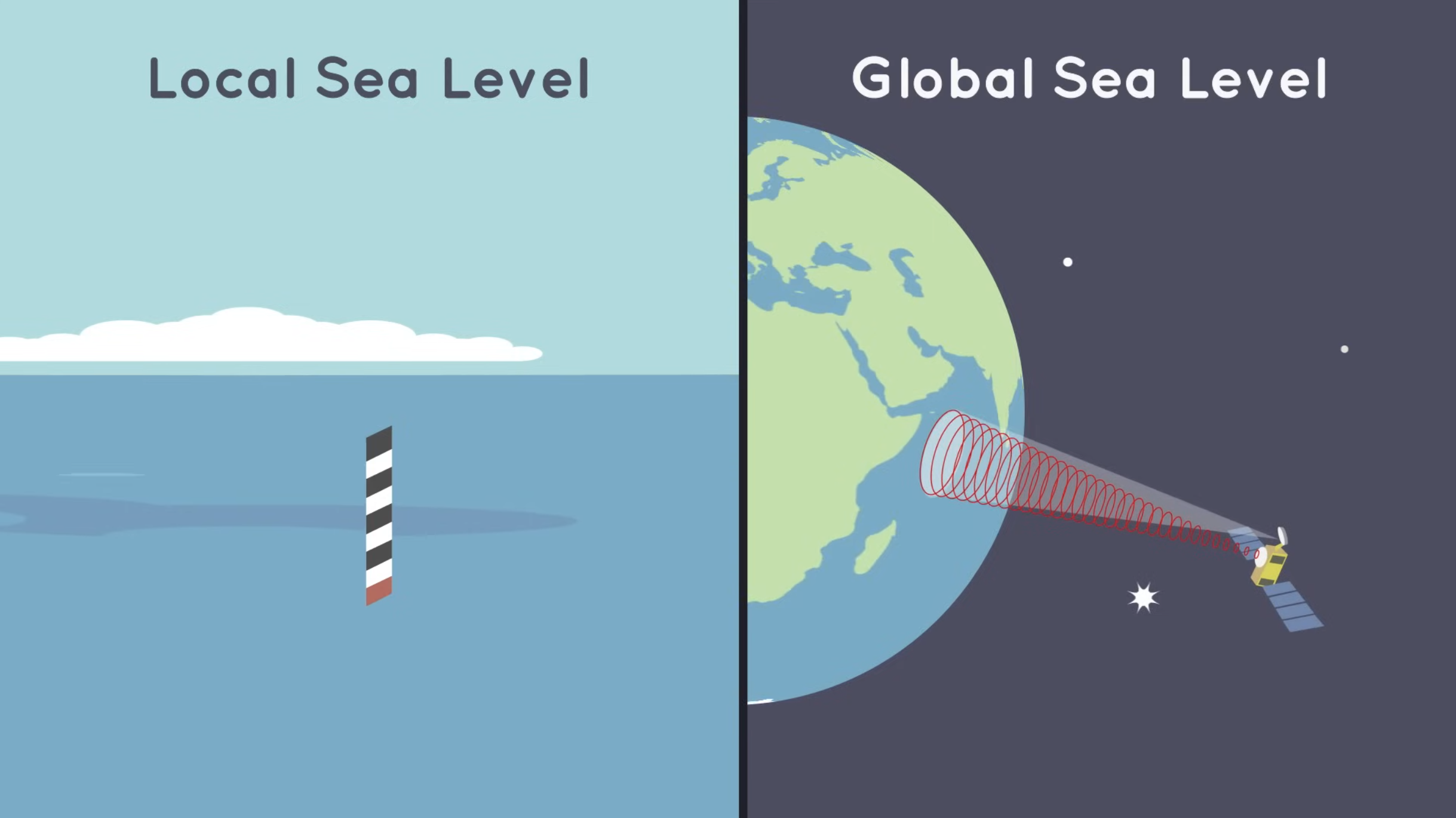

What Causes Sea Level Rise? – NASA Space Place

2022 Six Part Series on “Sand Dealers” – Le Monde